stylegan3
Showing
.gitignore
0 → 100644
Dockerfile
0 → 100644
LICENSE.txt
0 → 100644
README.md
0 → 100644
README_ORIGIN.md
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
README_old.md
0 → 100644
avg_spectra.py
0 → 100644
calc_metrics.py
0 → 100644
dataset_tool.py
0 → 100644
dnnlib/__init__.py
0 → 100644
dnnlib/util.py
0 → 100644
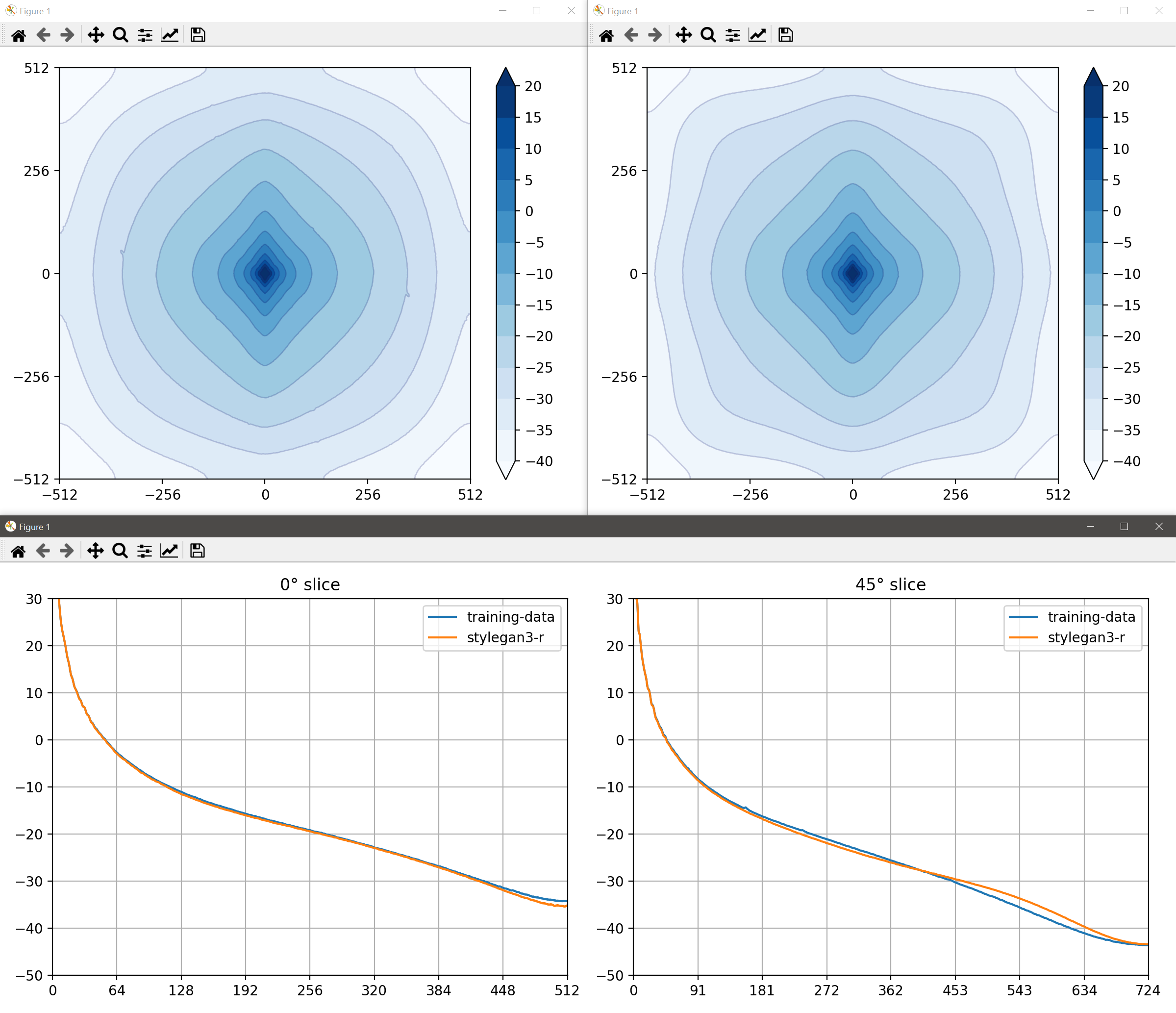
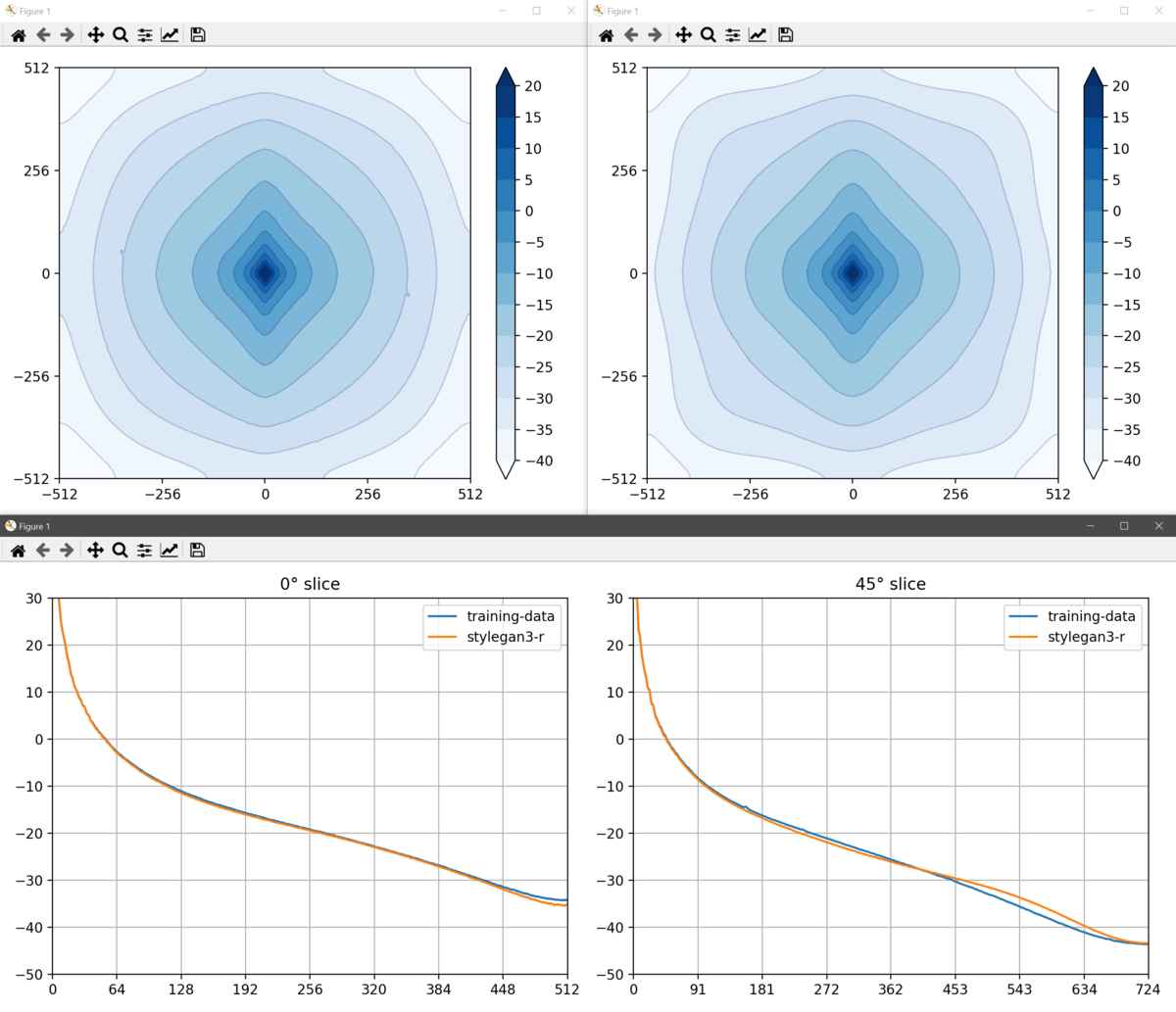
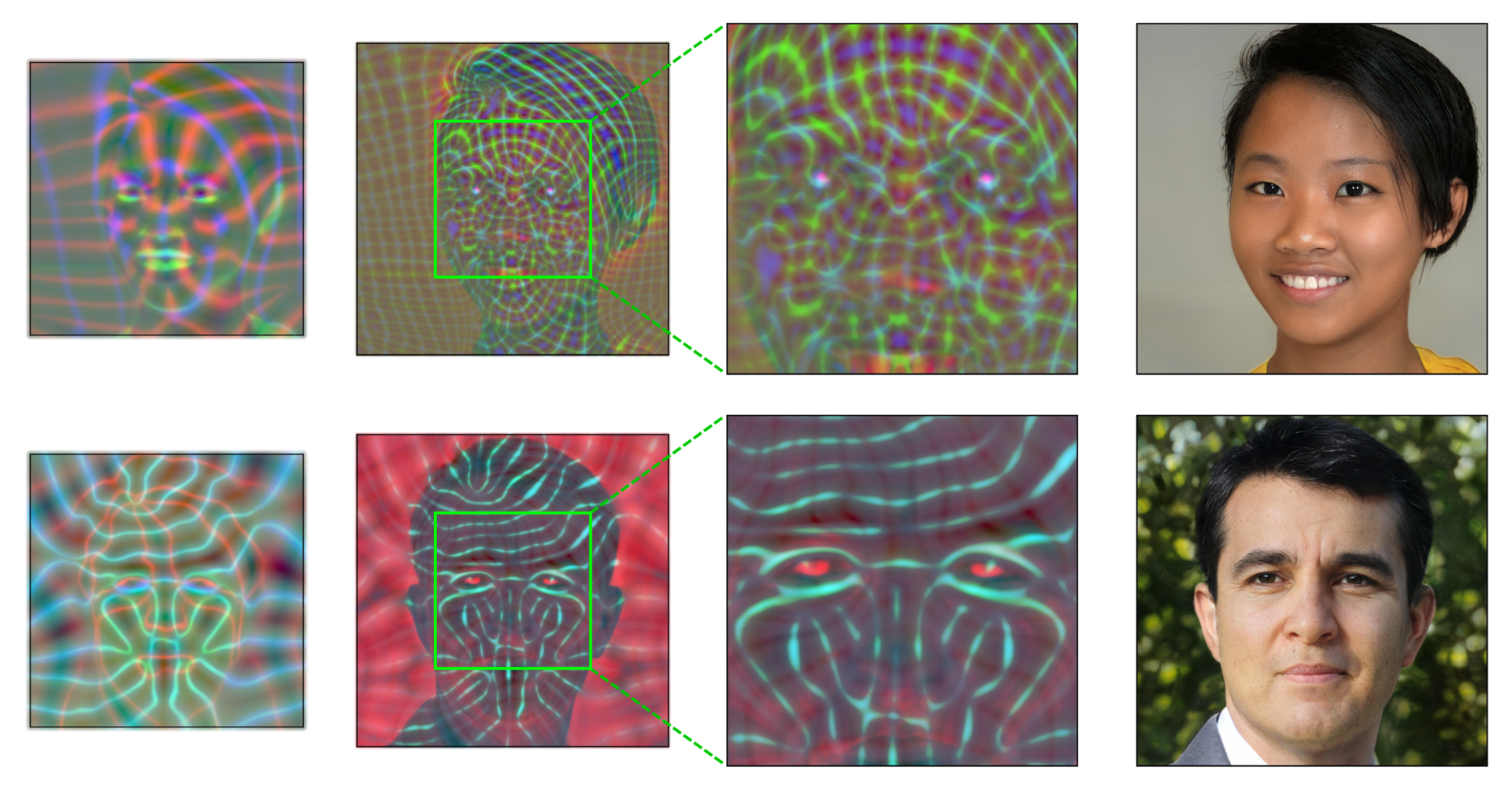
docs/avg_spectra_screen0.png
0 → 100644
375 KB
219 KB
docs/configs.md
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
docs/dataset-tool-help.txt
0 → 100644
1.74 MB
docs/train-help.txt
0 → 100644
docs/troubleshooting.md
0 → 100644
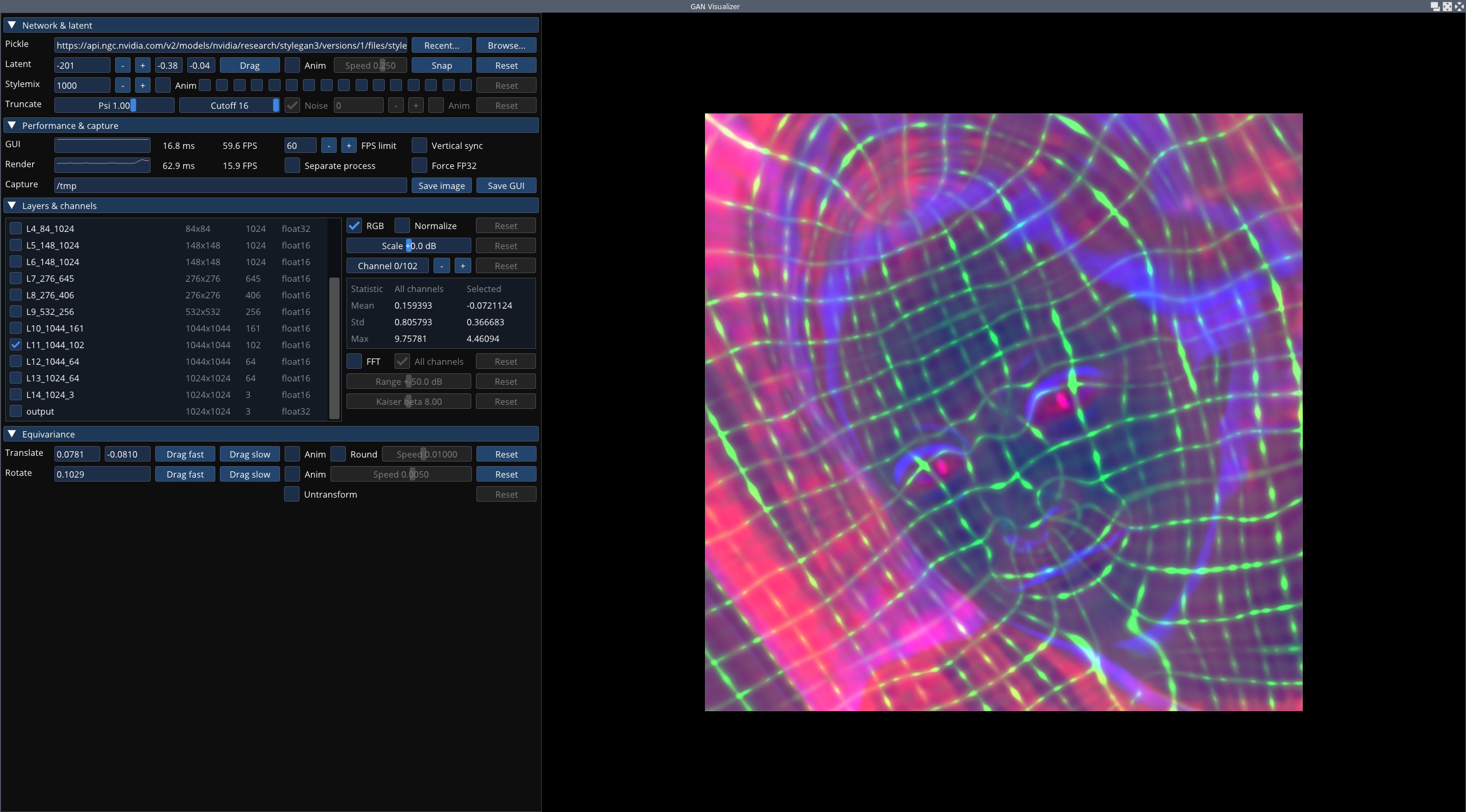
docs/visualizer_screen0.png
0 → 100644
1.2 MB
498 KB