v1.0
parents
Showing
LICENSE
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
MiniMax_M1_tech_report.pdf
0 → 100644
File added
README.md
0 → 100644
README_origin.md
0 → 100644
config.json
0 → 100644
configuration_minimax_m1.py
0 → 100644
doc/Lightning_Attention.png
0 → 100644
171 KB
doc/MiniMax.png
0 → 100644
372 KB
doc/PermitRootLogin.png
0 → 100644
40.1 KB
doc/amd_iommu.png
0 → 100644
127 KB
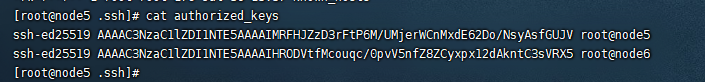
doc/id_rsa.png
0 → 100644
82.7 KB
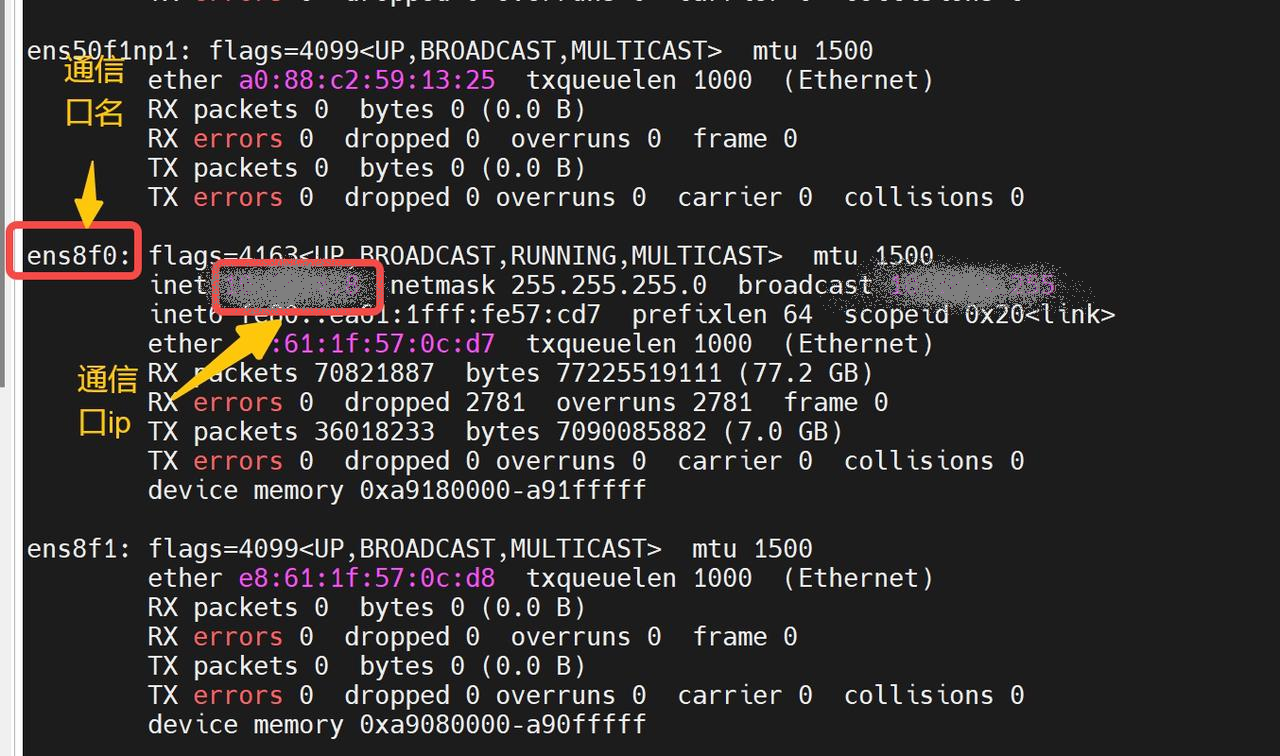
doc/ip.png
0 → 100644
1.06 MB
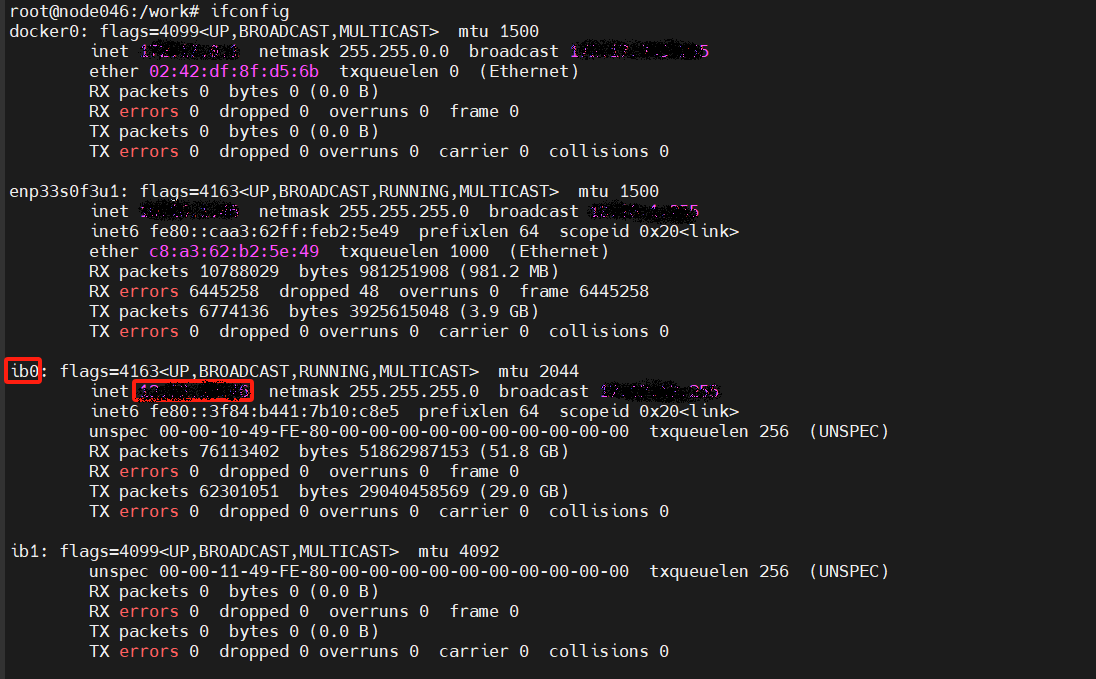
doc/ip_bw.png
0 → 100644
97.1 KB
docker/Dockerfile
0 → 100644
docker/requirements.txt
0 → 100644
docs/function_call_guide.md
0 → 100644