"src/include/base.hip.hpp" did not exist on "e7b8705b913c1bb7d216255f1f233ea03c096f1e"
Merge pull request #199 from microsoft/master
merge master
Showing
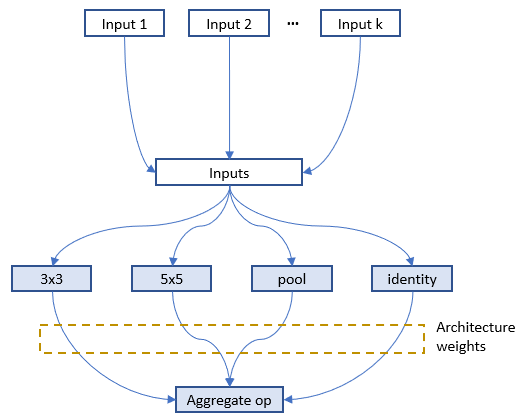
docs/img/darts_mode.png
0 → 100644
13.5 KB
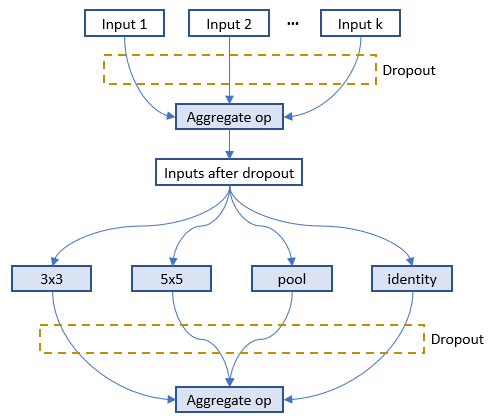
docs/img/oneshot_mode.png
0 → 100644
14.3 KB