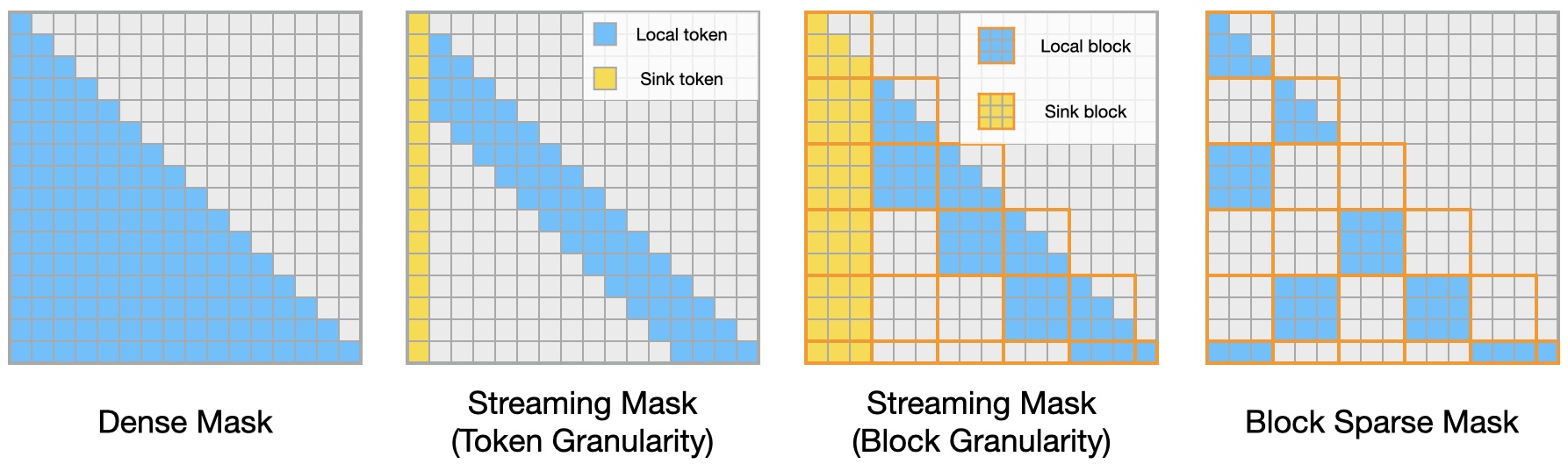
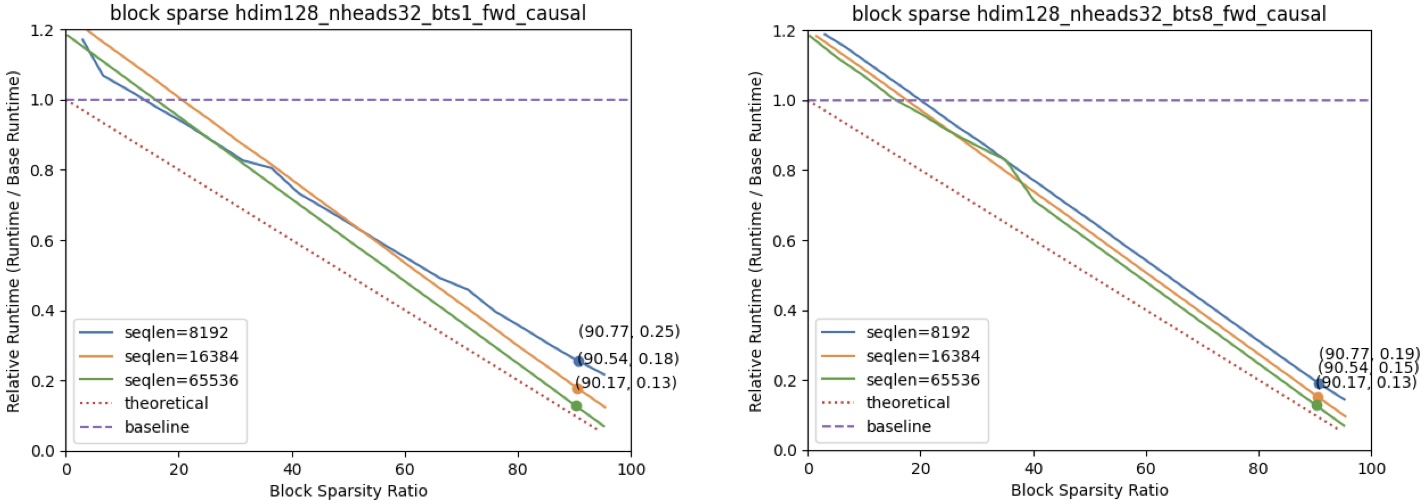
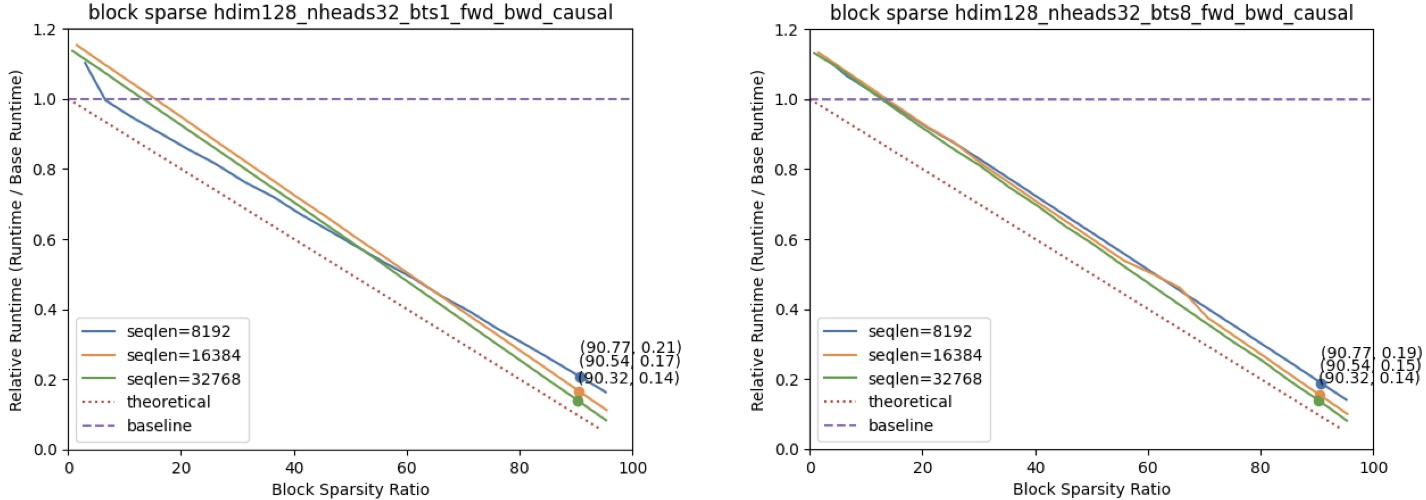
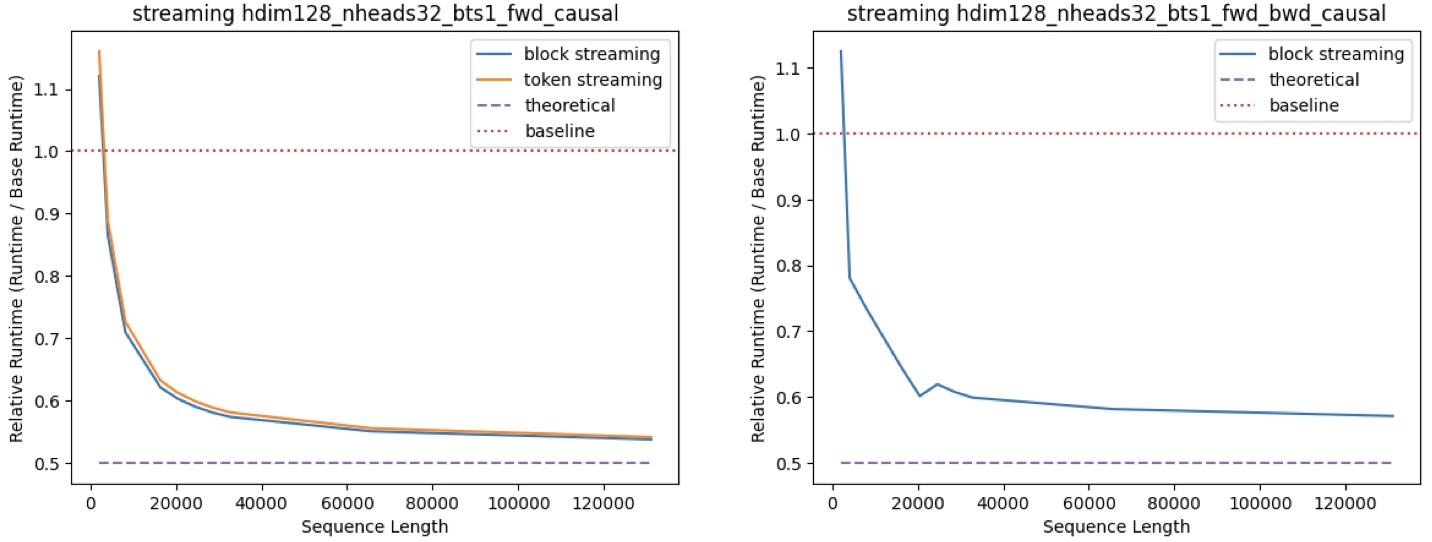
[release] v0.0.1
parents
Showing
.gitignore
0 → 100644
.gitmodules
0 → 100644
LICENSE
0 → 100644
MANIFEST.in
0 → 100644
Makefile
0 → 100644
README.md
0 → 100644
216 KB
144 KB
138 KB
124 KB
This diff is collapsed.
This diff is collapsed.