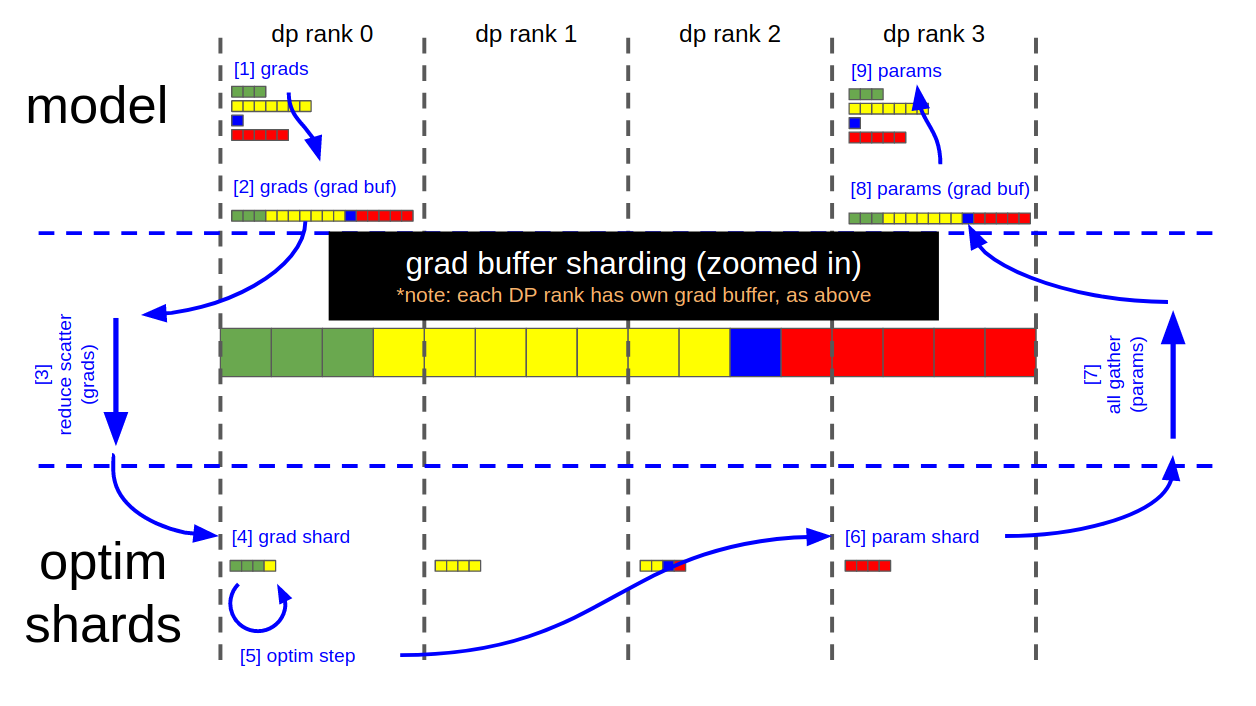
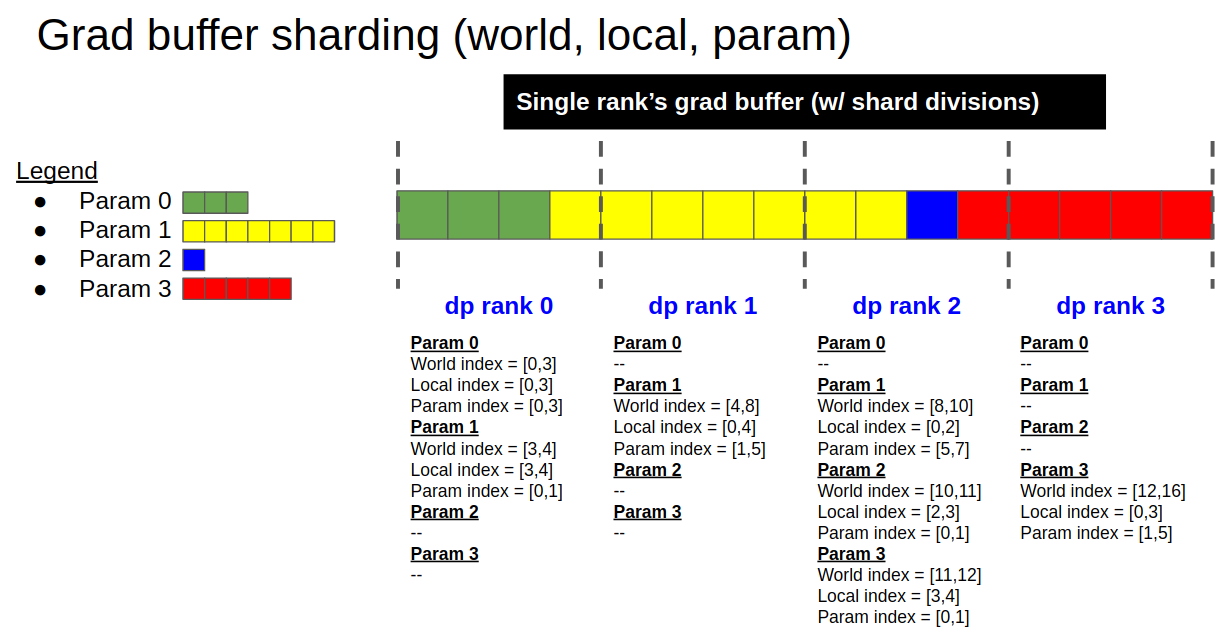
update to core_v0.9
Showing
CHANGELOG.md
0 → 100644
CODEOWNERS
0 → 100644
Dockerfile.ci
0 → 100644
Dockerfile.linting
0 → 100644
MANIFEST.in
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
diff.log
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
87.9 KB
96.8 KB
docs/llama_mistral.md
0 → 100644