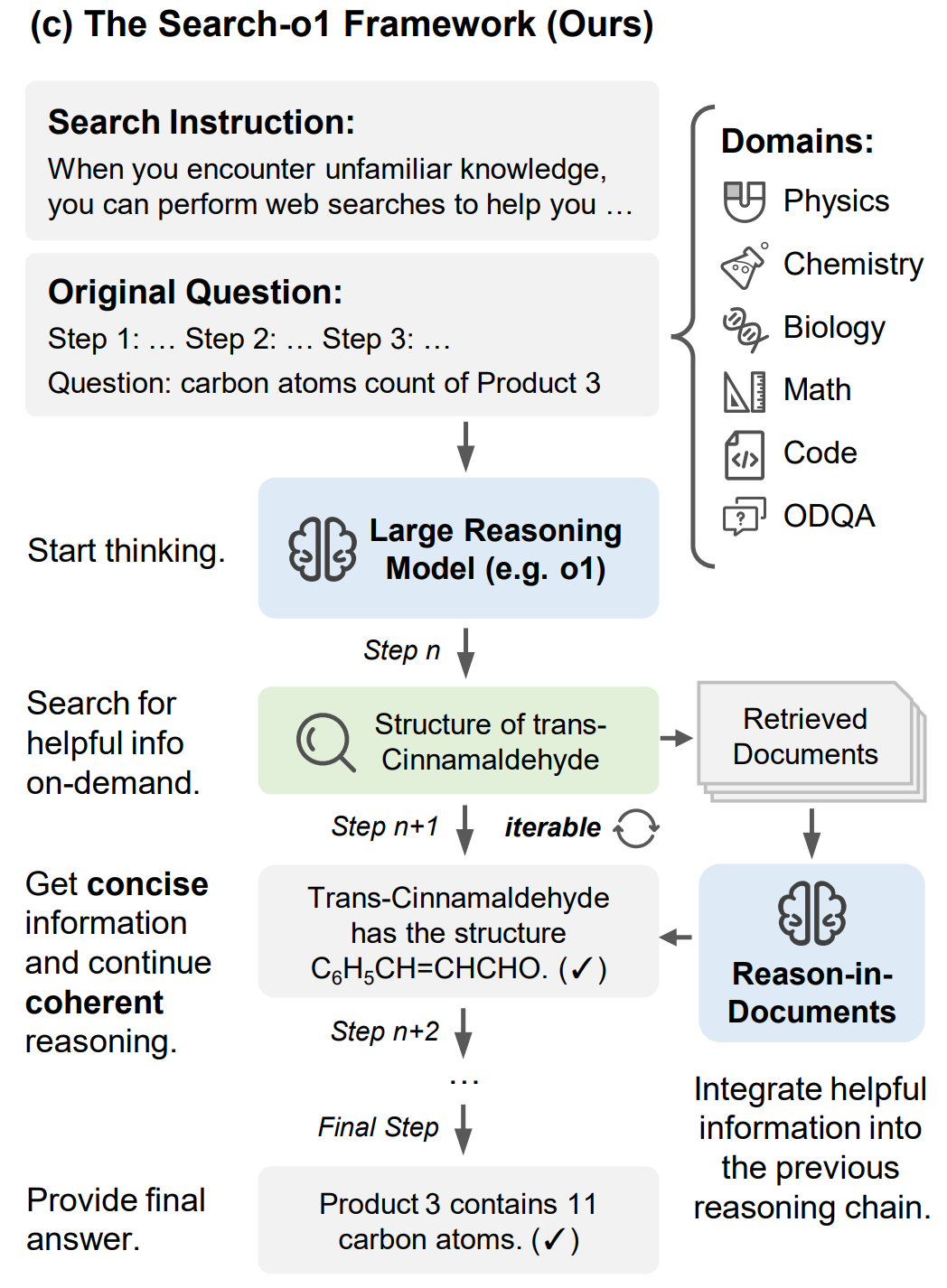
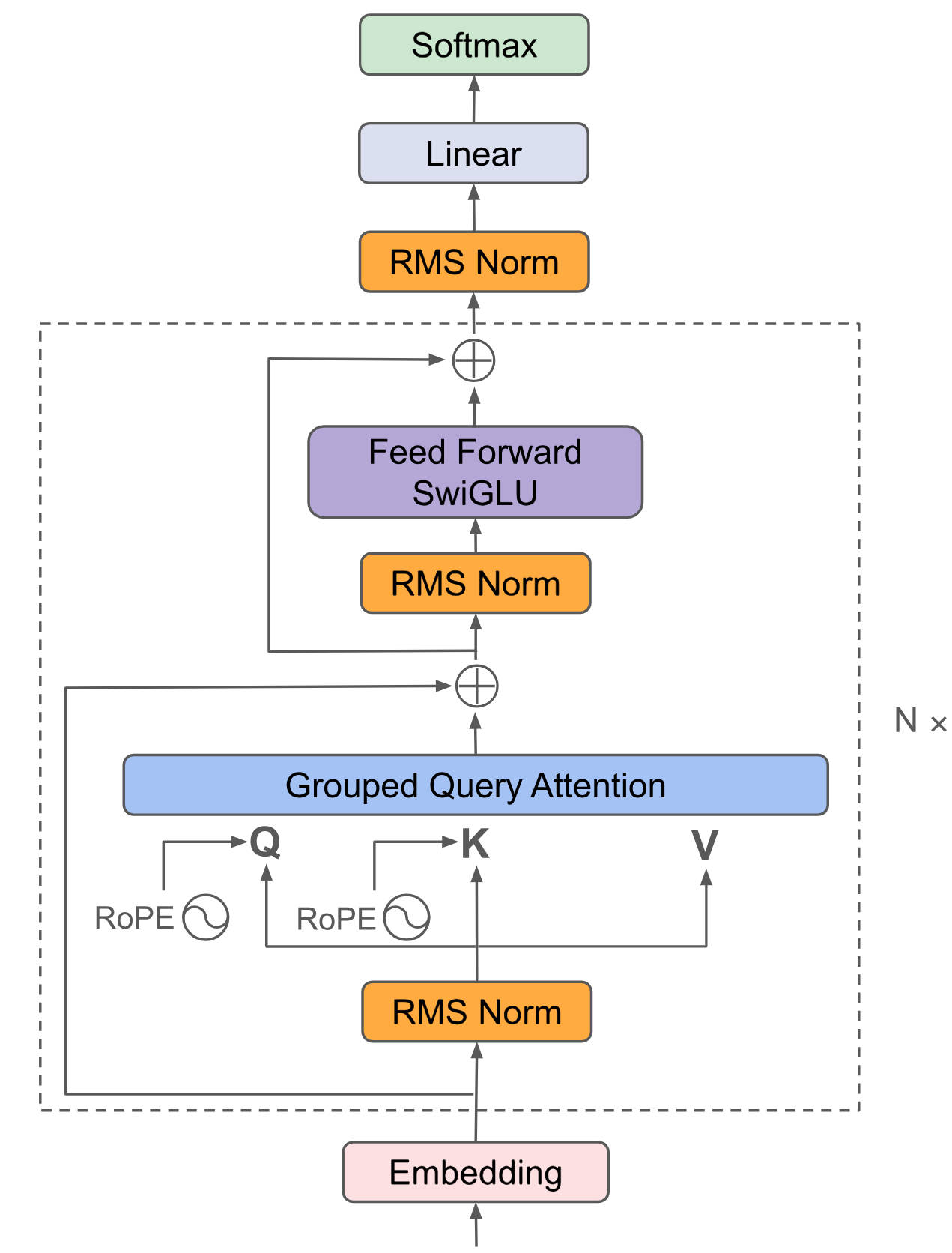
"...composable_kernel.git" did not exist on "e823d518cb46ad61ddb3c70eac8529e0a58af1f8"
v1.0
Showing
.gitattributes
0 → 100644
LICENSE
0 → 100644
README.md
0 → 100644
README_origin.md
0 → 100644
data/AIME/test.json
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
data/GPQA/README.md
0 → 100644
data/GPQA/diamond.json
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
data/GPQA/gpqa_diamond.csv
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
data/GPQA/gpqa_experts.csv
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
data/GPQA/gpqa_extended.csv
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
data/GPQA/gpqa_main.csv
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
data/GPQA/license.txt
0 → 100644
data/data_pre_precess.ipynb
0 → 100644
direct_gen.sh
0 → 100644
doc/algorithm.png
0 → 100644
267 KB
doc/llama3.png
0 → 100644
356 KB
docker/Dockerfile
0 → 100644