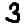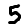Merge remote-tracking branch 'tensorflow/master'
Showing
official/mnist/dataset.py
0 → 100644
official/mnist/example3.png
0 → 100644
368 Bytes
official/mnist/example5.png
0 → 100644
367 Bytes
official/mnist/examples.npy
0 → 100644
File added
research/fivo/README.md
0 → 100644
research/fivo/bounds.py
0 → 100644