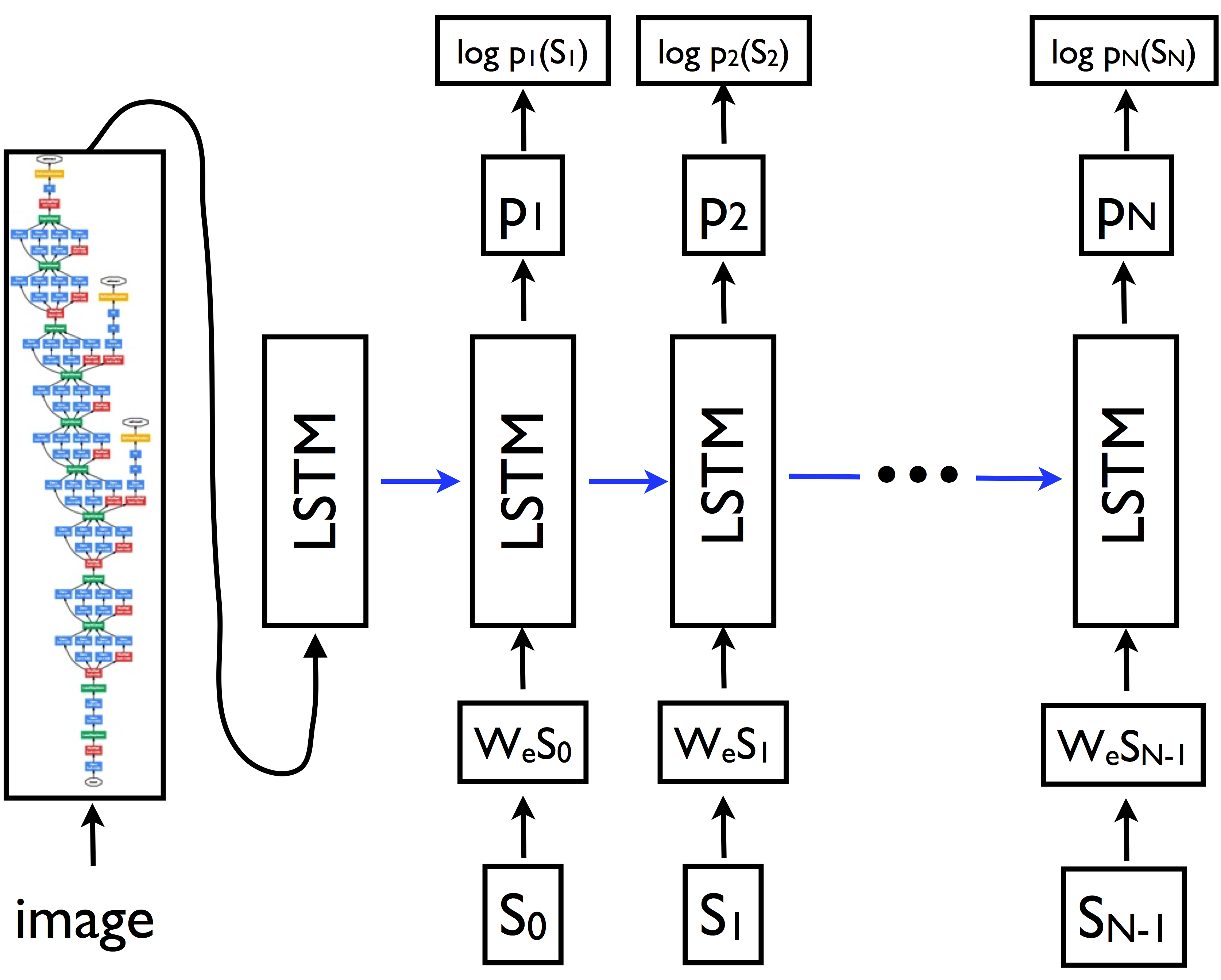
Open source the image-to-text model based on the "Show and Tell" paper.
Showing
im2txt/.gitignore
0 → 100644
im2txt/README.md
0 → 100644
im2txt/WORKSPACE
0 → 100644
190 KB
421 KB
880 KB
im2txt/im2txt/BUILD
0 → 100644
im2txt/im2txt/evaluate.py
0 → 100644
im2txt/im2txt/ops/BUILD
0 → 100644