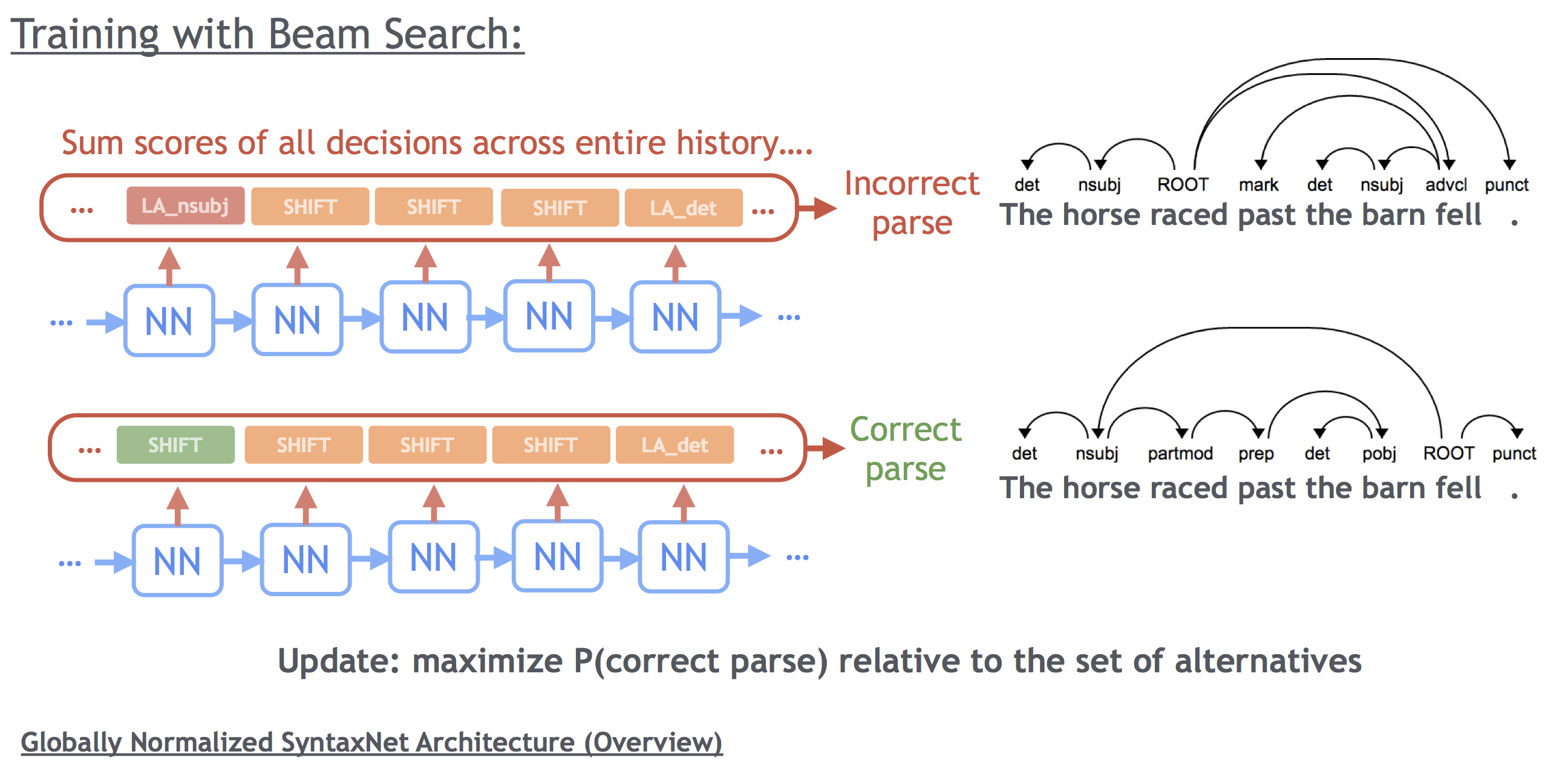
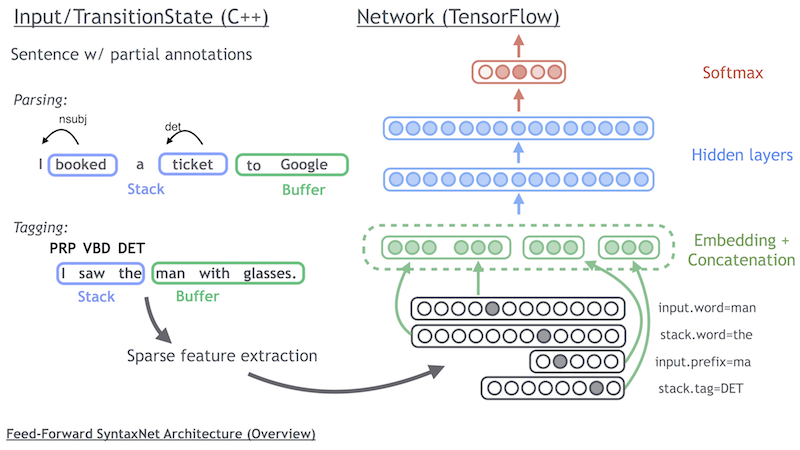
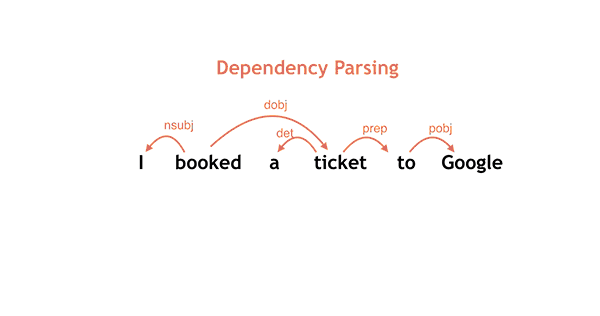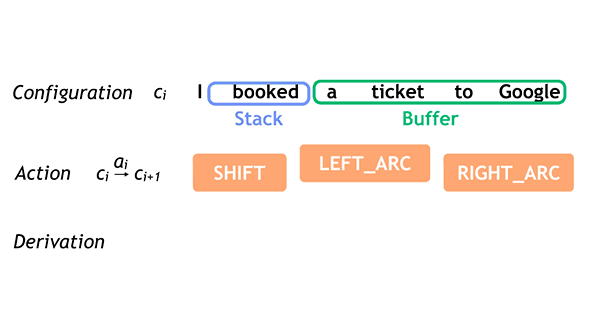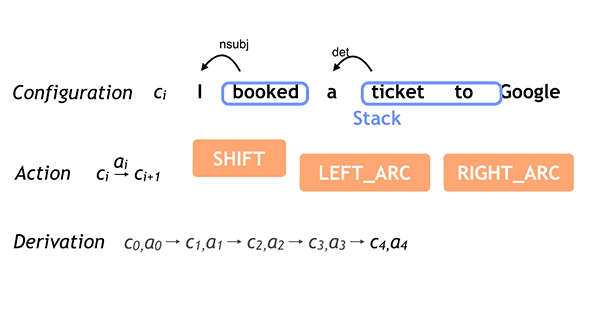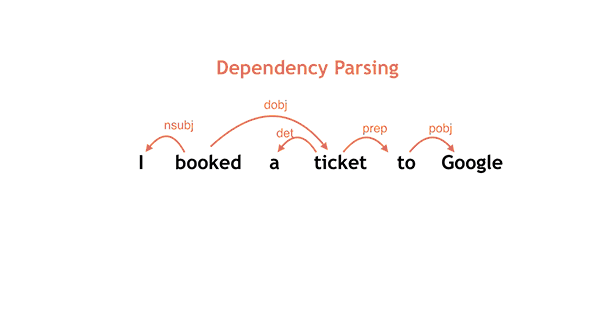
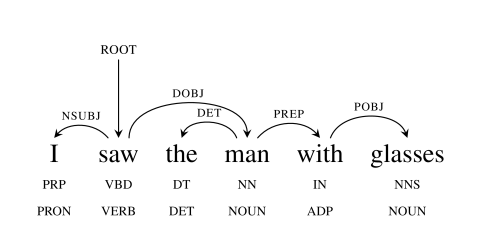
Adding SyntaxNet to tensorflow/models (#63)
Showing
.gitignore
deleted
100644 → 0
.gitmodules
0 → 100644
syntaxnet/.gitignore
0 → 100644
syntaxnet/README.md
0 → 100644
syntaxnet/WORKSPACE
0 → 100644
346 KB
194 KB
syntaxnet/looping-parser.gif
0 → 100644
750 KB
syntaxnet/sawman.png
0 → 100644
11 KB
syntaxnet/syntaxnet/BUILD
0 → 100644
syntaxnet/syntaxnet/affix.cc
0 → 100644
syntaxnet/syntaxnet/affix.h
0 → 100644
syntaxnet/syntaxnet/base.h
0 → 100644
syntaxnet/syntaxnet/demo.sh
0 → 100755