"vscode:/vscode.git/clone" did not exist on "129e013b41133e9bf236642fa43362e68623716a"
omnisql
Showing
.gitignore
0 → 100644
Dockerfile
0 → 100644
README.md
0 → 100644
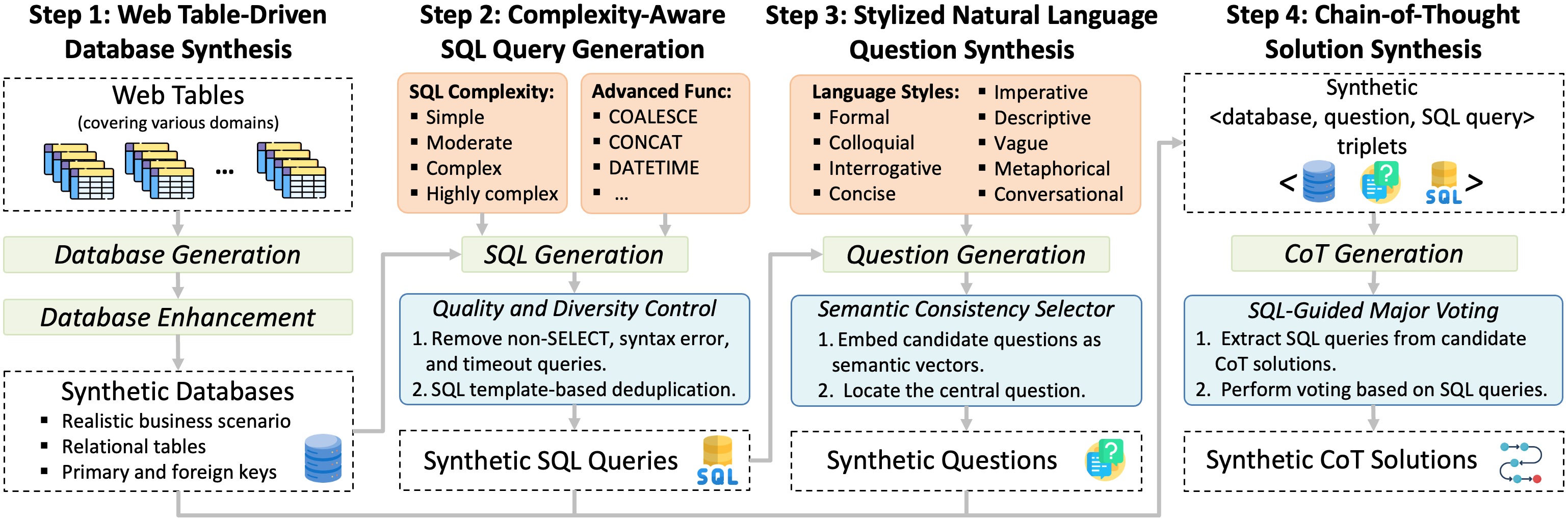
assets/framework.png
0 → 100644
447 KB
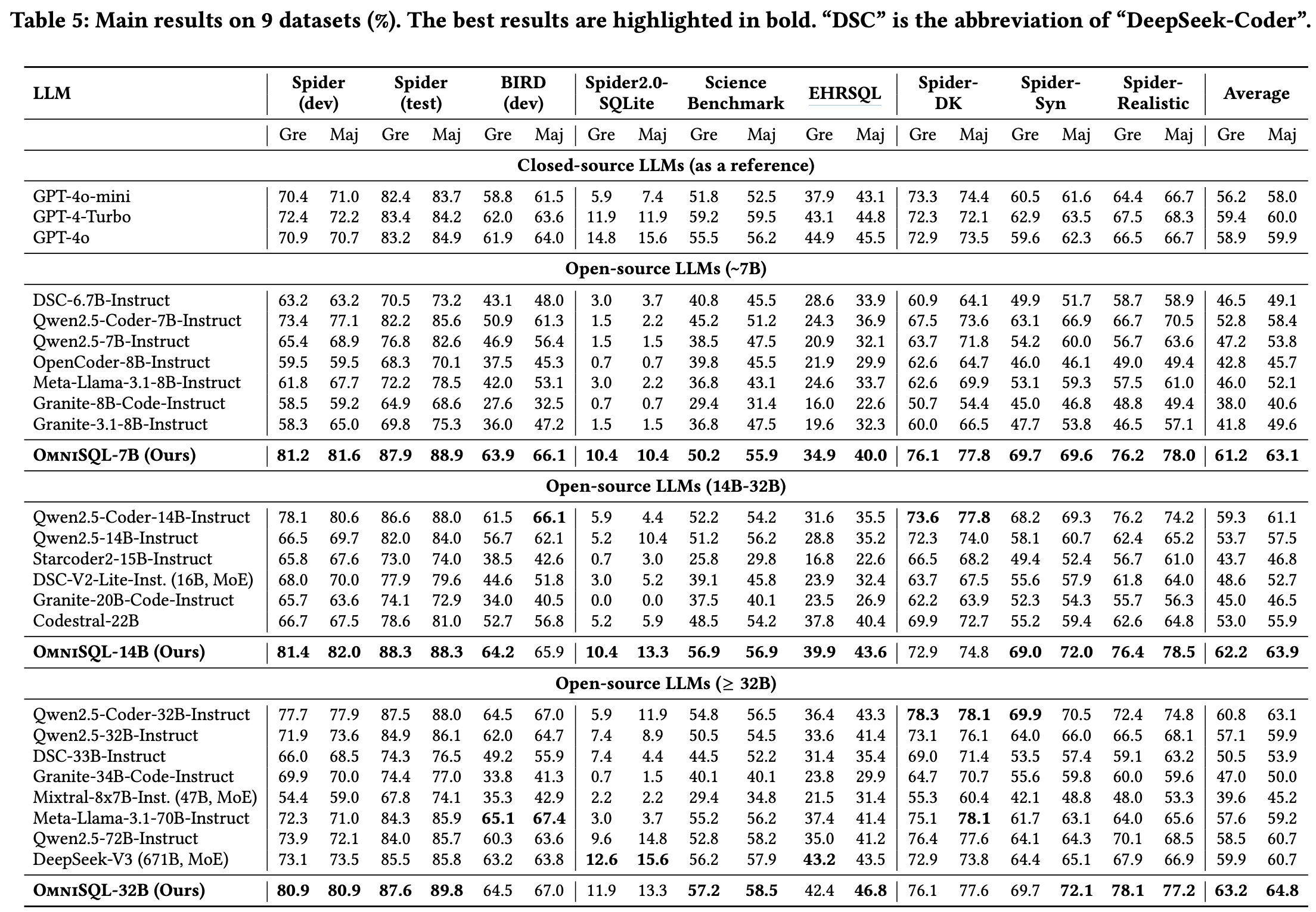
assets/main_results.png
0 → 100644
590 KB
data_synthesis/README.md
0 → 100644