init
Showing
LICENSE.txt
0 → 100644
README_o.md
0 → 100644
config.py
0 → 100644
configs/default.txt
0 → 100644
criterion.py
0 → 100644
dataset/Davis.txt
0 → 100644
File added
File added
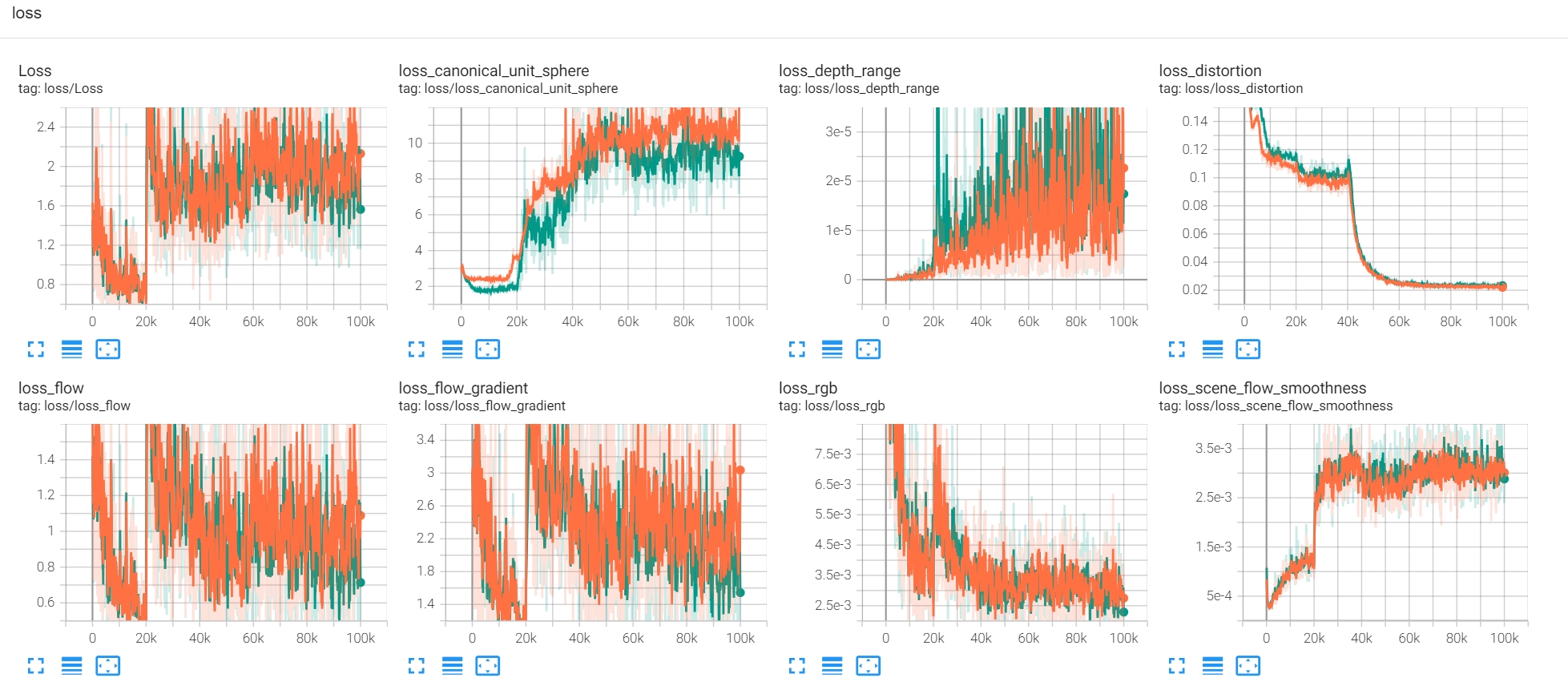
doc/loss.png
0 → 100644
602 KB
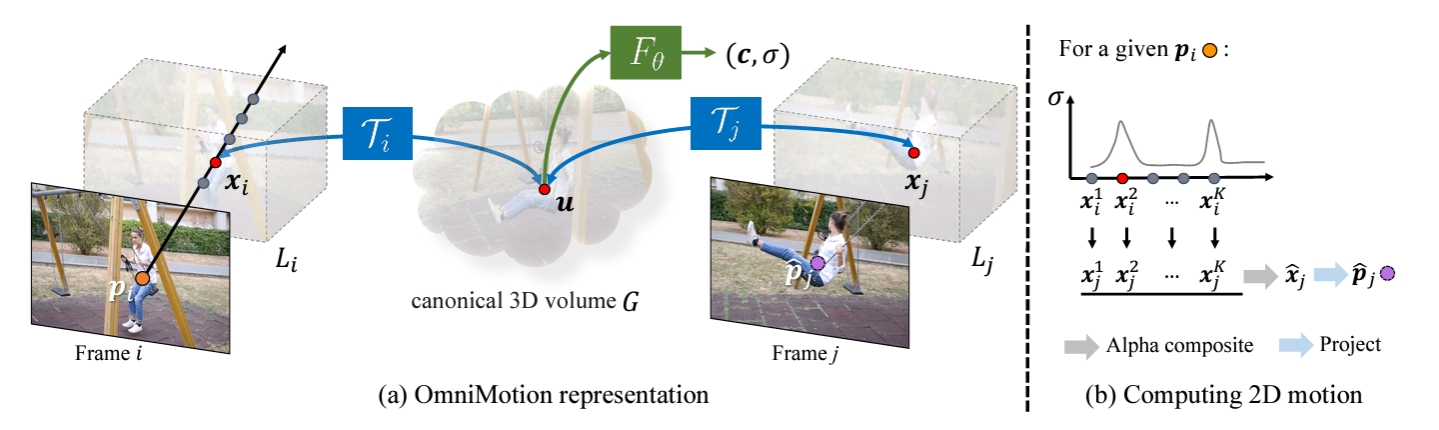
doc/基本原理.png
0 → 100644
211 KB
docker/Dockerfile
0 → 100644
get_davis.py
0 → 100644
loaders/__init__.py
0 → 100644
File added
File added
File added
File added
File added
File added