init
Showing
.gitignore
0 → 100644
.gitmodules
0 → 100644
AUTHORS
0 → 100644
LICENSE
0 → 100644
README.md
0 → 100644
README_ori.md
0 → 100644
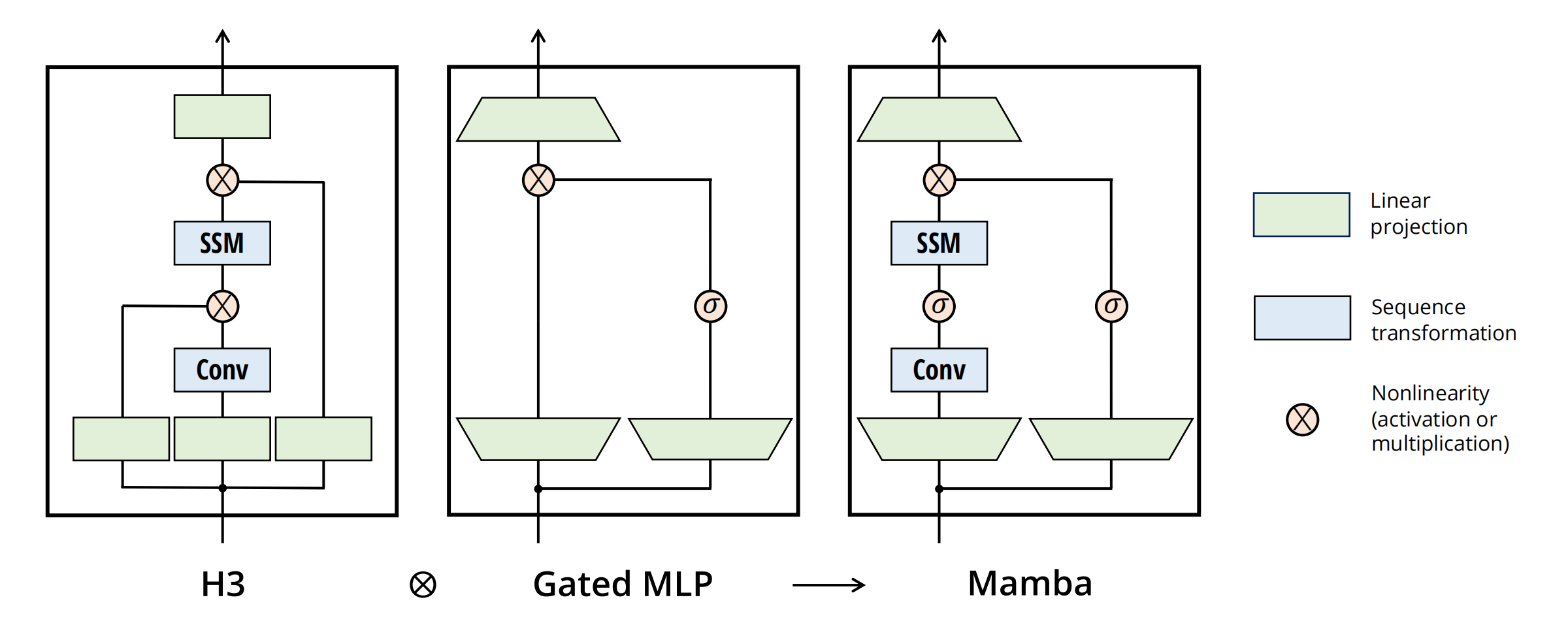
assets/mamba.png
0 → 100644
144 KB
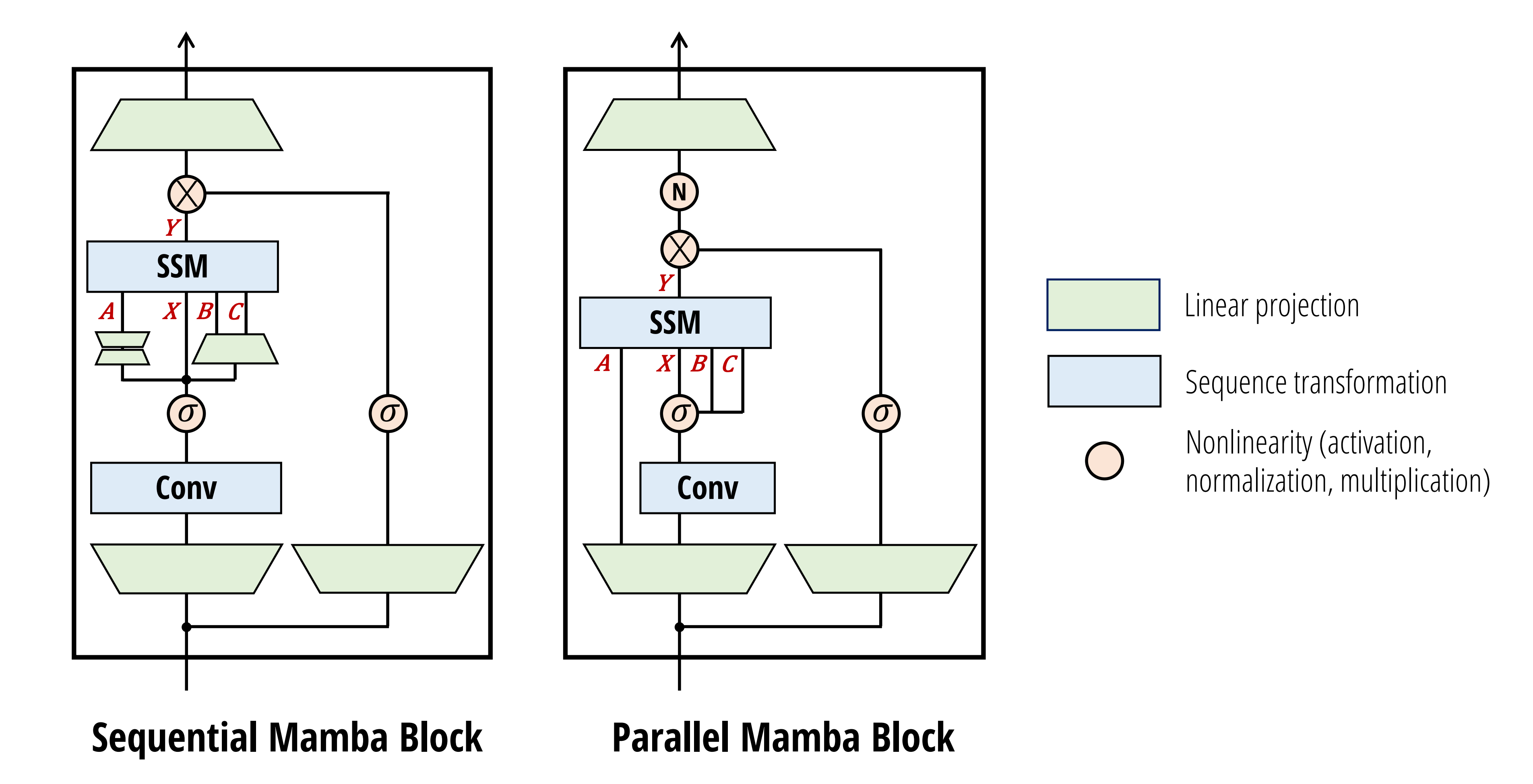
assets/mamba2.png
0 → 100644
355 KB
assets/mamba2_result.png
0 → 100644
24 KB
assets/mamba_result.png
0 → 100644
25.1 KB
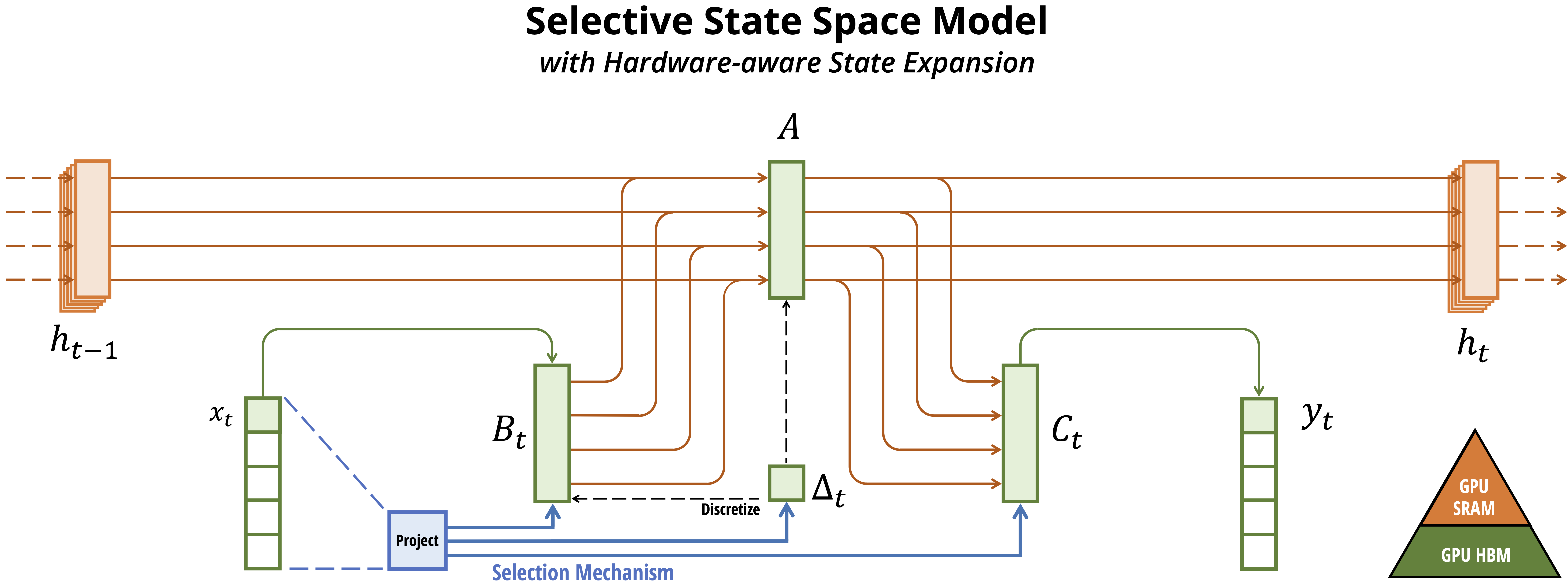
assets/selection.png
0 → 100644
799 KB
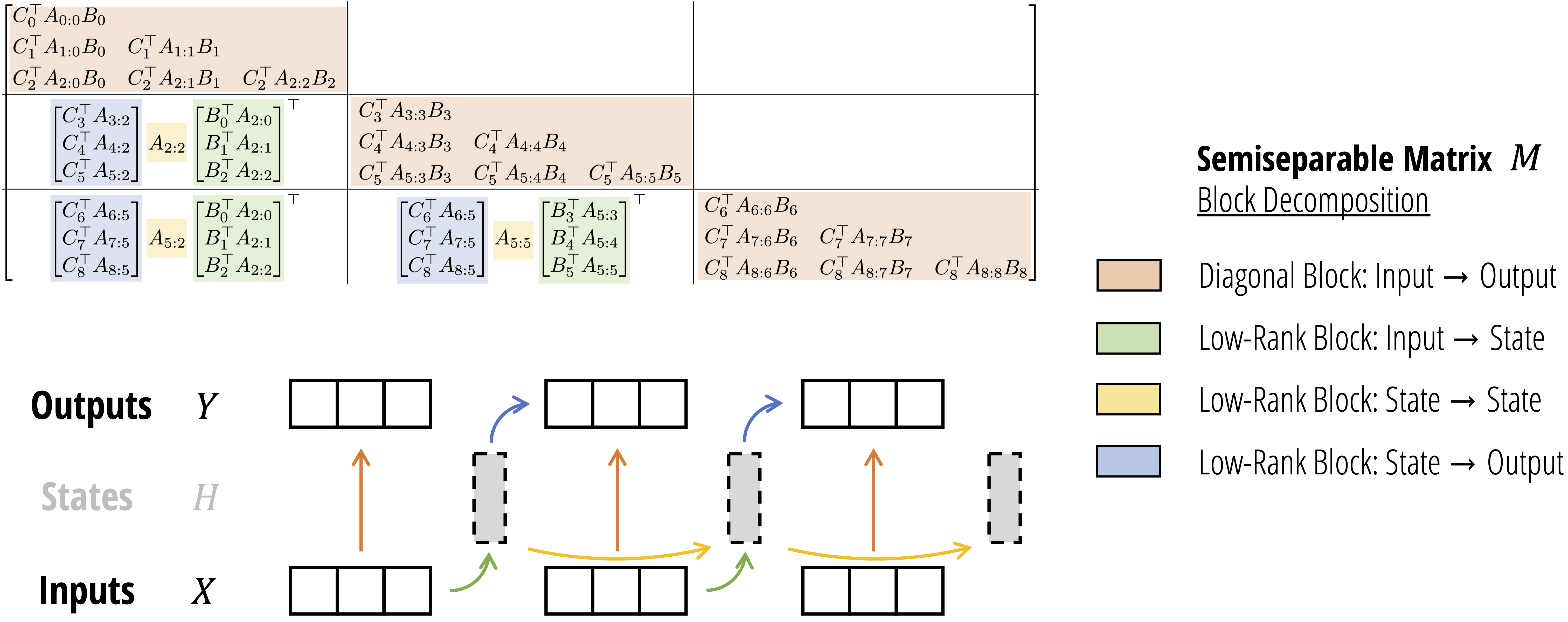
assets/ssd_algorithm.png
0 → 100644
1.07 MB
assets/ssm.png
0 → 100644
189 KB