Initial commit
parents
Showing
3rdParty/InstallRBuild.sh
0 → 100644
File added
File added
File added
File added
File added
CMakeLists.txt
0 → 100644
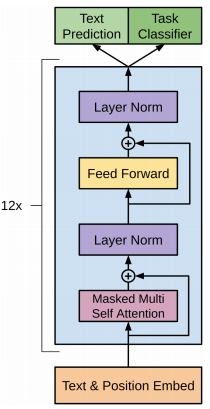
Doc/Images/GPT_01.png
0 → 100644
28.5 KB
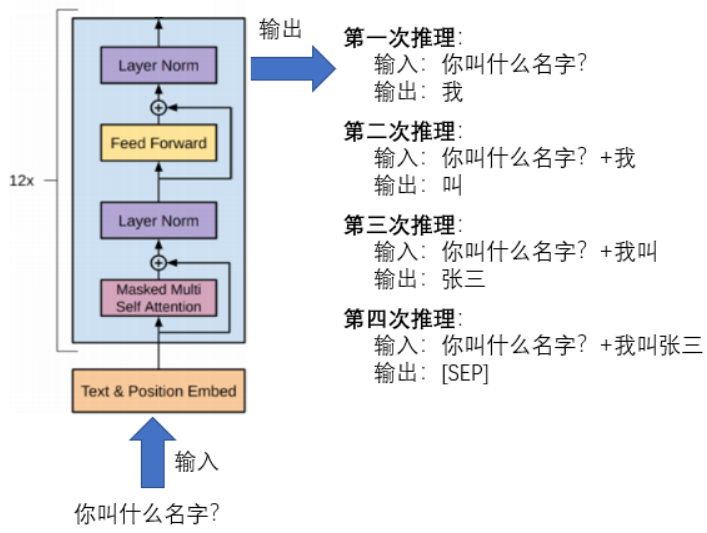
Doc/Images/GPT_02.png
0 → 100644
104 KB
Doc/Tutorial_Cpp.md
0 → 100644
Doc/Tutorial_Python.md
0 → 100644
Python/gpt2.py
0 → 100644
Python/requirements.txt
0 → 100644
README.md
0 → 100644
Resource/vocab_shici.txt
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
Src/GPT2.cpp
0 → 100644
Src/GPT2.h
0 → 100644
Src/Utility/Filesystem.cpp
0 → 100644
Src/Utility/Filesystem.h
0 → 100644
Src/Utility/SimpleLog.h
0 → 100644