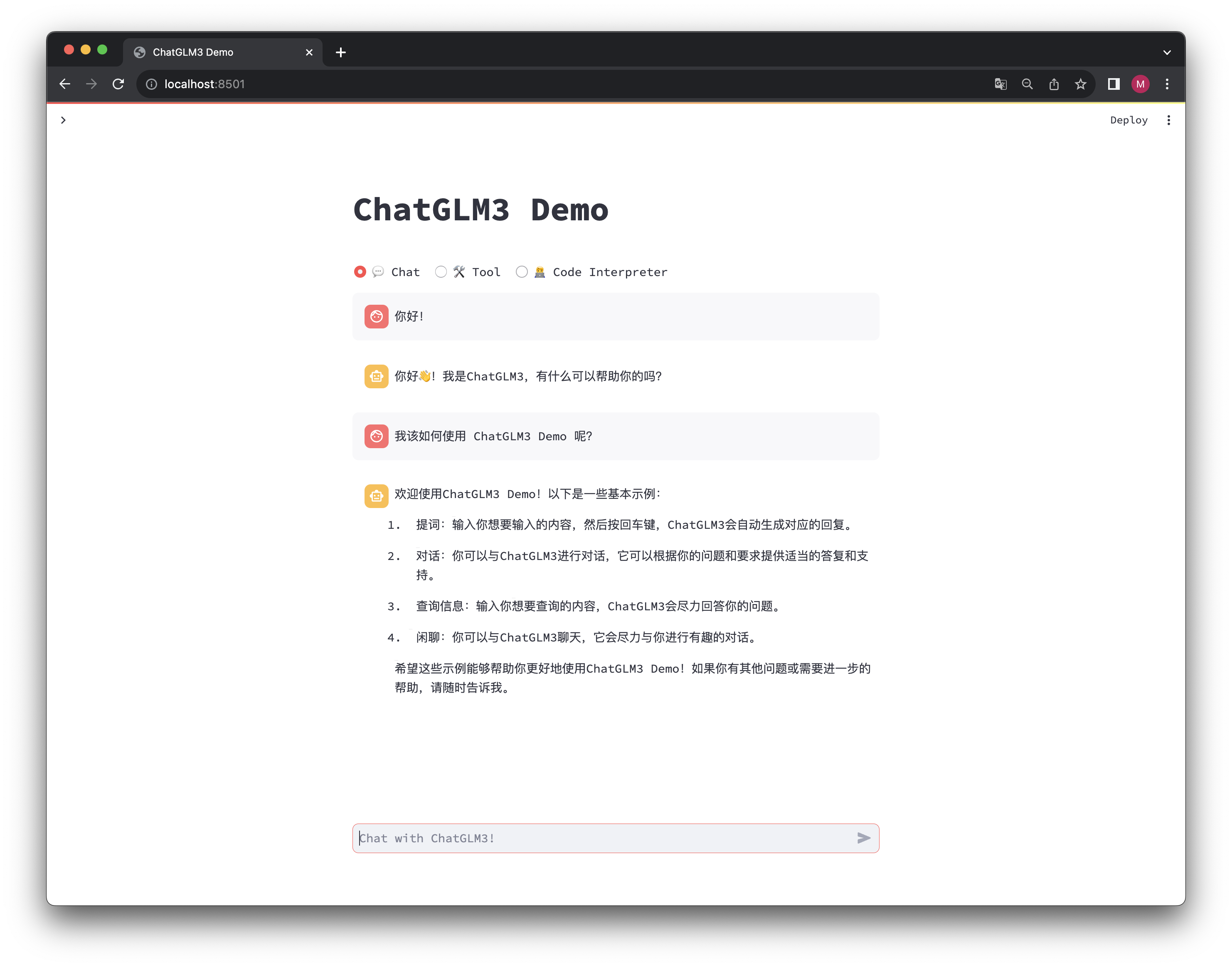
added chatglm3
Showing
DEPLOYMENT.md
0 → 100644
DEPLOYMENT_en.md
0 → 100644
Dockerfile
0 → 100644
MODEL_LICENSE
0 → 100644
PROMPT.md
0 → 100644
PROMPT_en.md
0 → 100644
README.md
0 → 100644
README_en.md
0 → 100644
README_old.md
0 → 100644
basic_demo/cli_demo.py
0 → 100644
basic_demo/infer_test.py
0 → 100644
basic_demo/utils.py
0 → 100644
basic_demo/vocab.txt
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
basic_demo/web_demo.py
0 → 100644
basic_demo/web_demo2.py
0 → 100644
composite_demo/README.md
0 → 100755
composite_demo/README_en.md
0 → 100755
740 KB