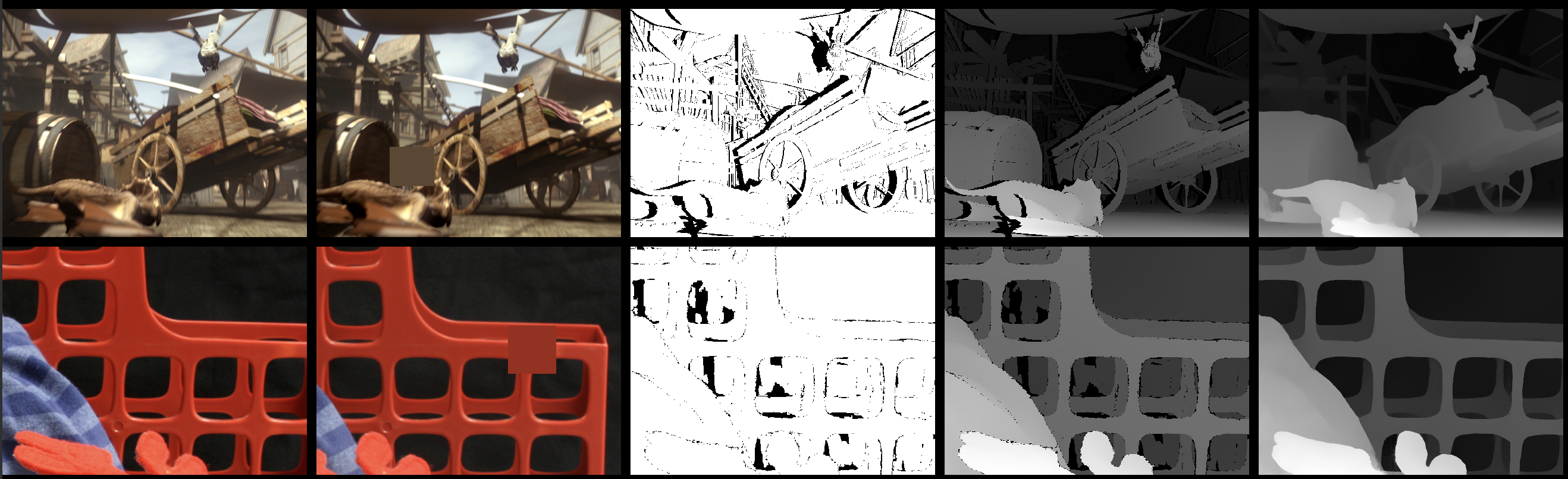
Removing prototype related things from release/0.14 branch (#6687)
* Remove test related to prototype * Remove torchvision/prototype dir * Remove references/depth/stereo because it depend on prototype * Remove prototype related entries on mypy.ini * Remove things related to prototype in pytest.ini * clean setup.py from prototype * Clean CI from prototype * Remove unused expect file
Showing
267 KB
1.28 MB
1.7 MB
314 KB