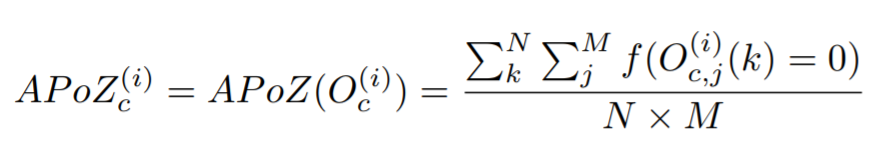"git@developer.sourcefind.cn:gaoqiong/composable_kernel.git" did not exist on "bc26a2faea287cec6ceca03d6b8d4bbcc2e9a635"
Add network trimming pruning algorithm and fix bias mask(testing) (#1867)
Showing
docs/img/apoz.png
0 → 100644
36.1 KB
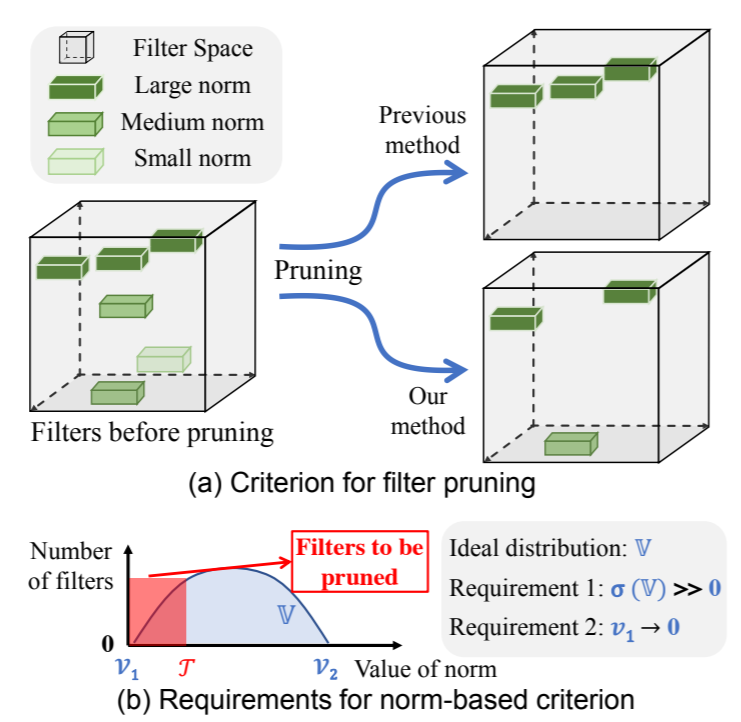
docs/img/fpgm_fig1.png
0 → 100644
111 KB
This diff is collapsed.