Merge pull request #200 from microsoft/master
merge master
Showing
crowdin.yml
0 → 100644
26.2 KB
30.4 KB
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


32.7 KB
6.97 KB
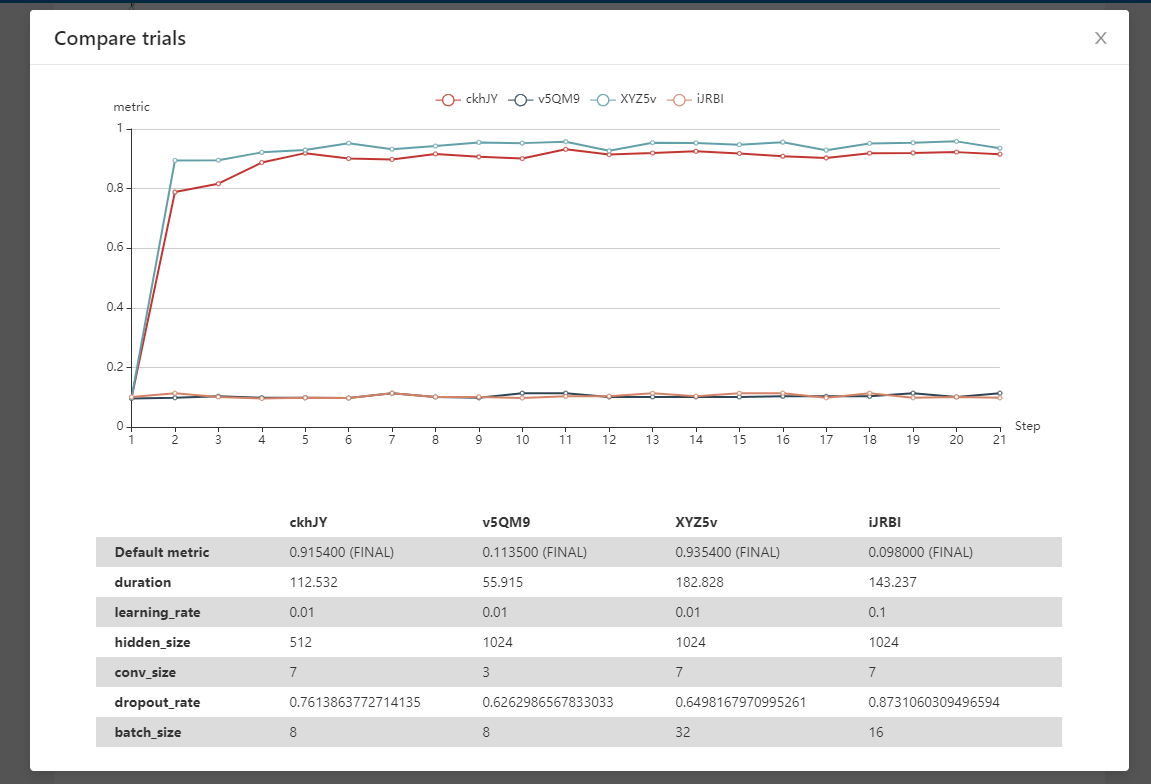
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


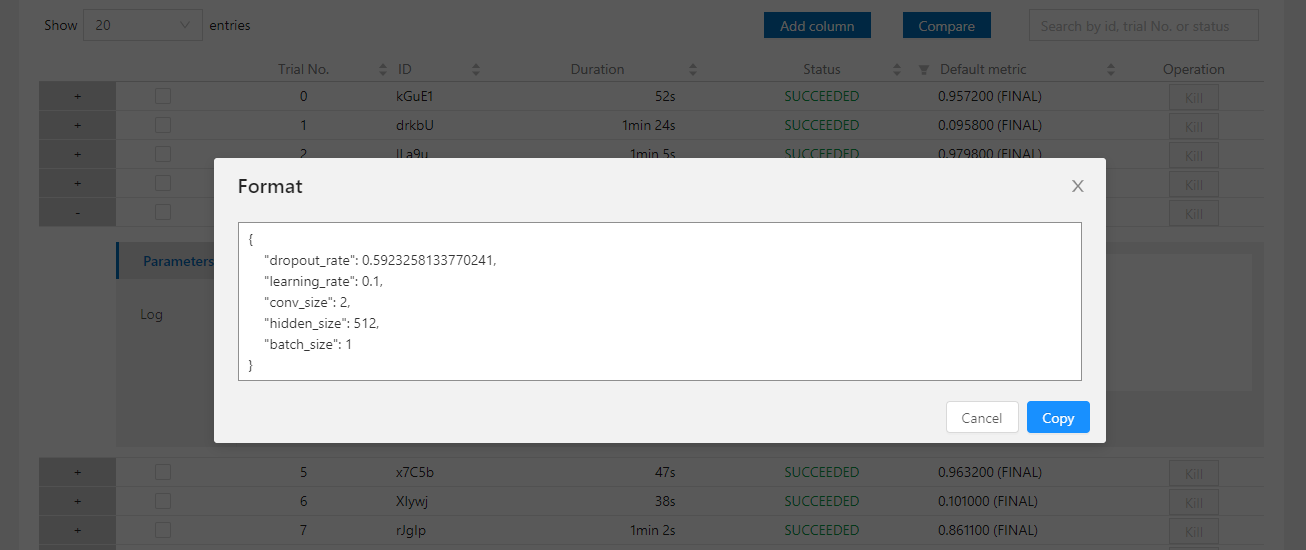
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


25.8 KB
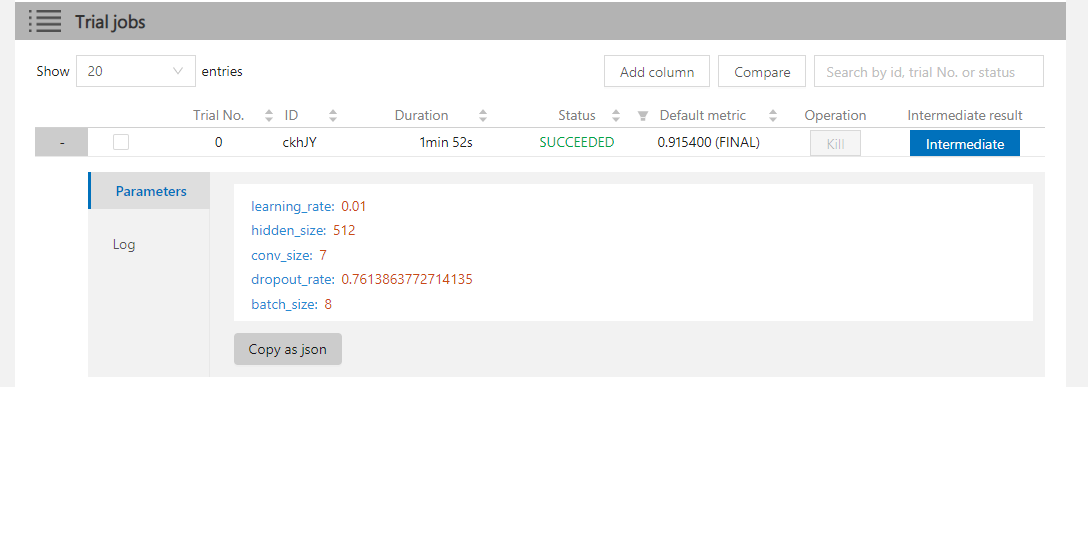
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


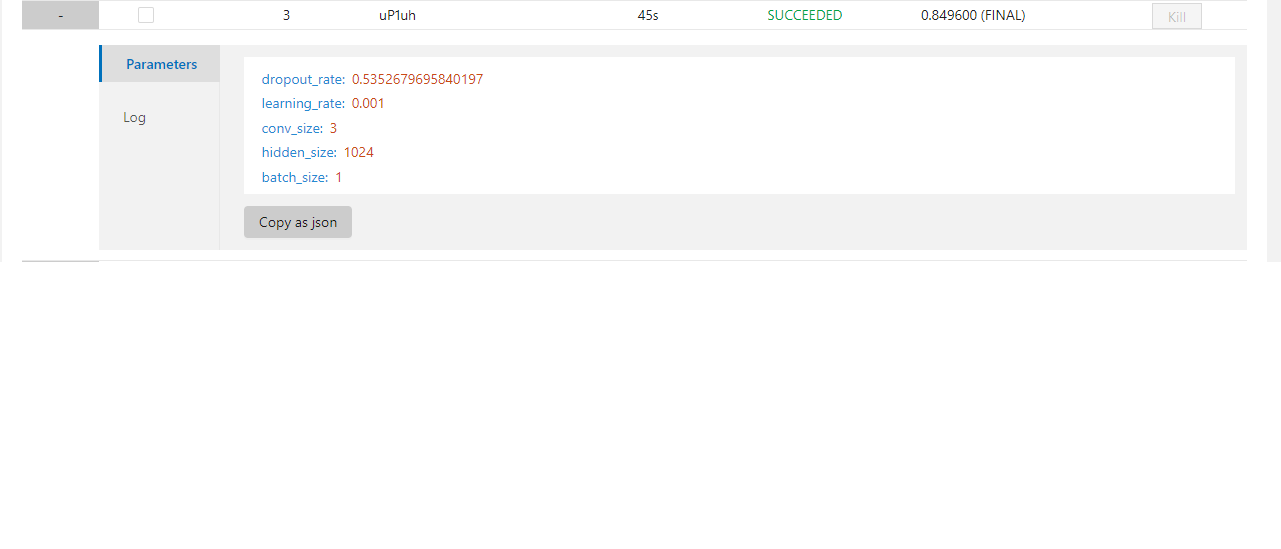
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


18.6 KB
88.7 KB