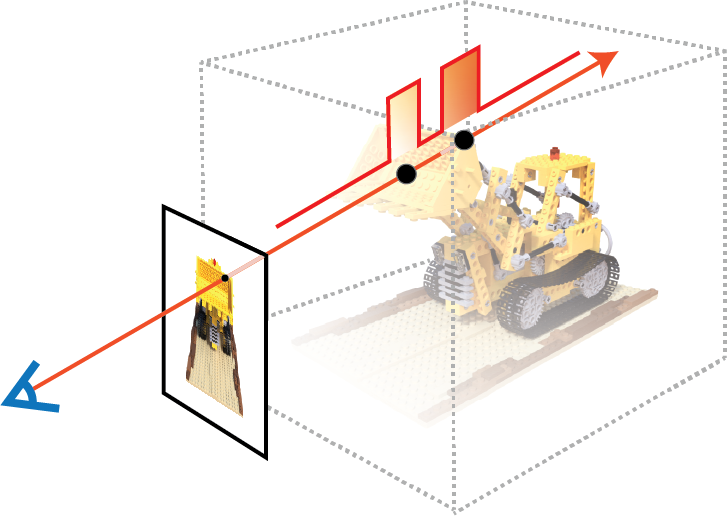
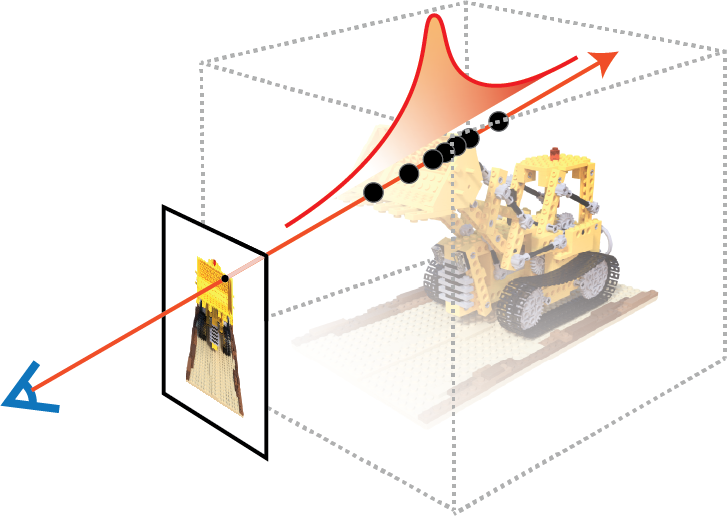
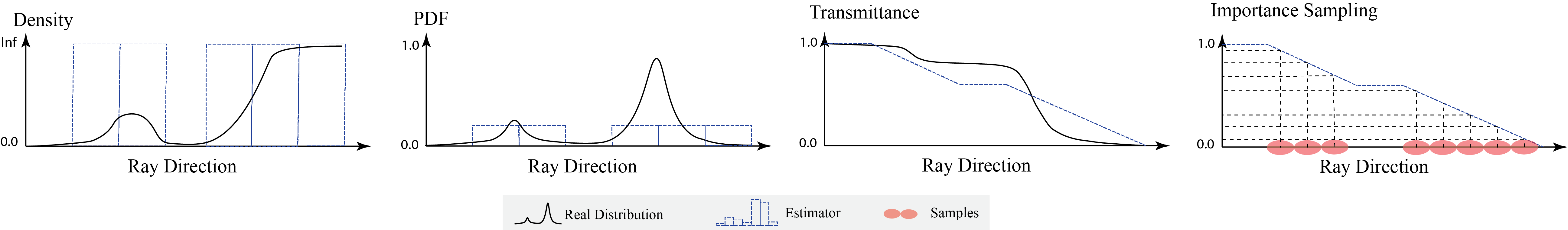
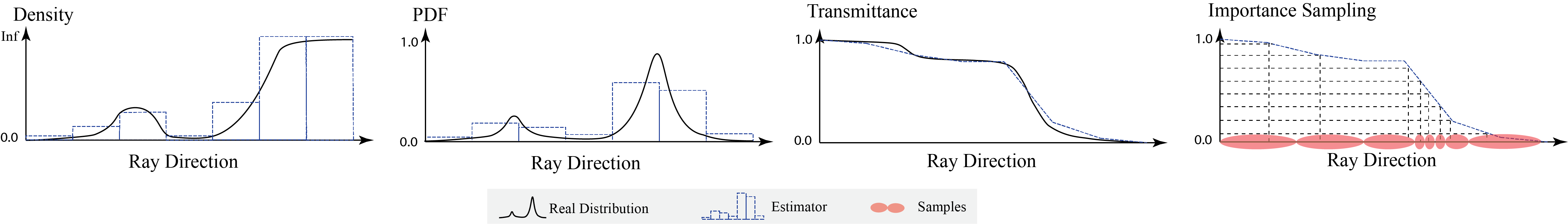
0.5.0: Rewrite all the underlying CUDA. Speedup and Benchmarking. (#182)
* importance_sampling with test * package importance_sampling * compute_intervals tested and packaged * compute_intervals_v2 * bicycle is failing * fix cut in compute_intervals_v2, test pass for rendering * hacky way to get opaque_bkgd work * reorg ING * PackedRaySegmentsSpec * chunk_ids -> ray_ids * binary -> occupied * test_traverse_grid_basic checked * fix traverse_grid with step size, checked * support max_step_size, not verified * _cuda and cuda; upgrade ray_marching * inclusive scan * test_exclusive_sum but seems to have numeric error * inclusive_sum_backward verified * exclusive sum backward * merge fwd and bwd for scan * inclusive & exclusive prod verified * support normal scan with torch funcs * rendering and tests * a bit clean up * importance_sampling verified * stratified for importance_sampling * importance_sampling in pdf.py * RaySegmentsSpec in data_specs; fix various bugs * verified with _proposal_packed.py * importance sampling support batch input/output. need to verify * prop script with batch samples * try to use cumsum instead of cumprod * searchsorted * benchmarking prop * ray_aabb_intersect untested * update prop benchmark numbers * minor fixes * batched ray_aabb_intersect * ray_aabb_intersect and traverse with grid(s) * tiny optimize for traverse_grids kernels * traverse_grids return intervals and samples * cub not verified * cleanup * propnet and occgrid as estimators * training print iters 10k * prop is good now * benchmark in google sheet. * really cleanup: scan.py and test * pack.py and test * rendering and test * data_specs.py and pdf.py docs * data_specs.py and pdf.py docs * init and headers * grid.py and test for it * occ grid docs * generated docs * example docs for pack and scan function. * doc fix for volrend.py * doc fix for pdf.py * fix doc for rendering function * docs * propnet docs * update scripts * docs: index.rst * methodology docs * docs for examples * mlp nerf script * update t-nerf script * rename dnerf to tnerf * misc update * bug fix: pdf_loss with test * minor fix * update readme with submodules * fix format * update gitingore file * fix doc failure. teaser png to jpg * docs in examples/
Showing
148 KB
150 KB
116 KB
116 KB
1.08 MB