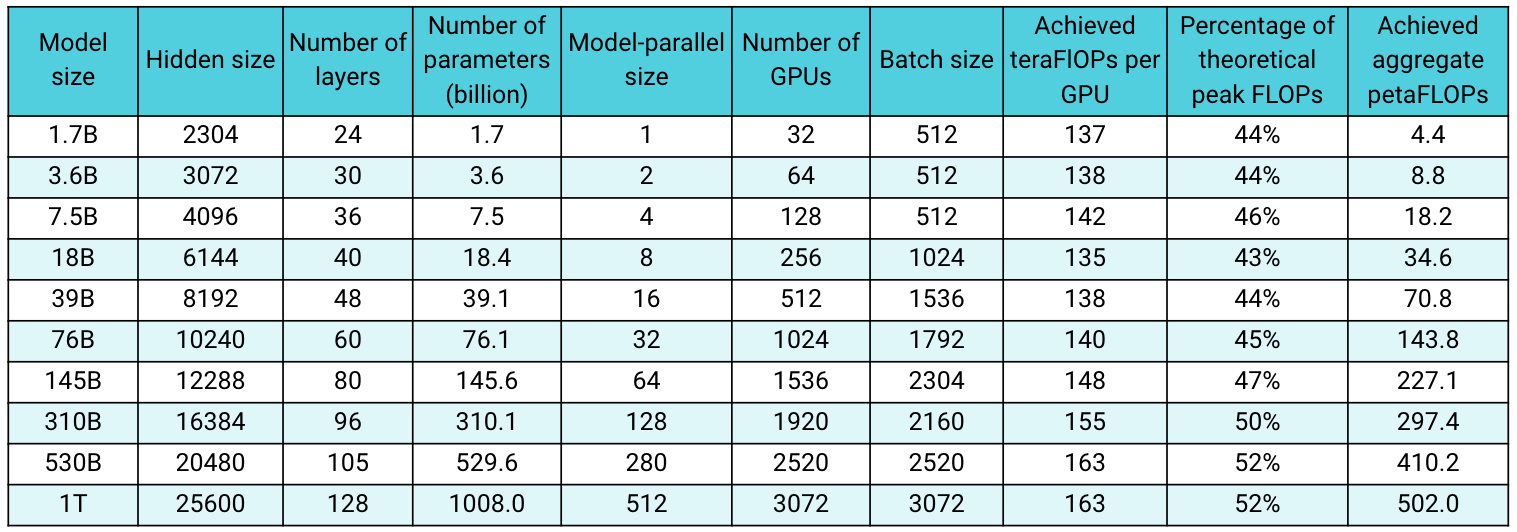
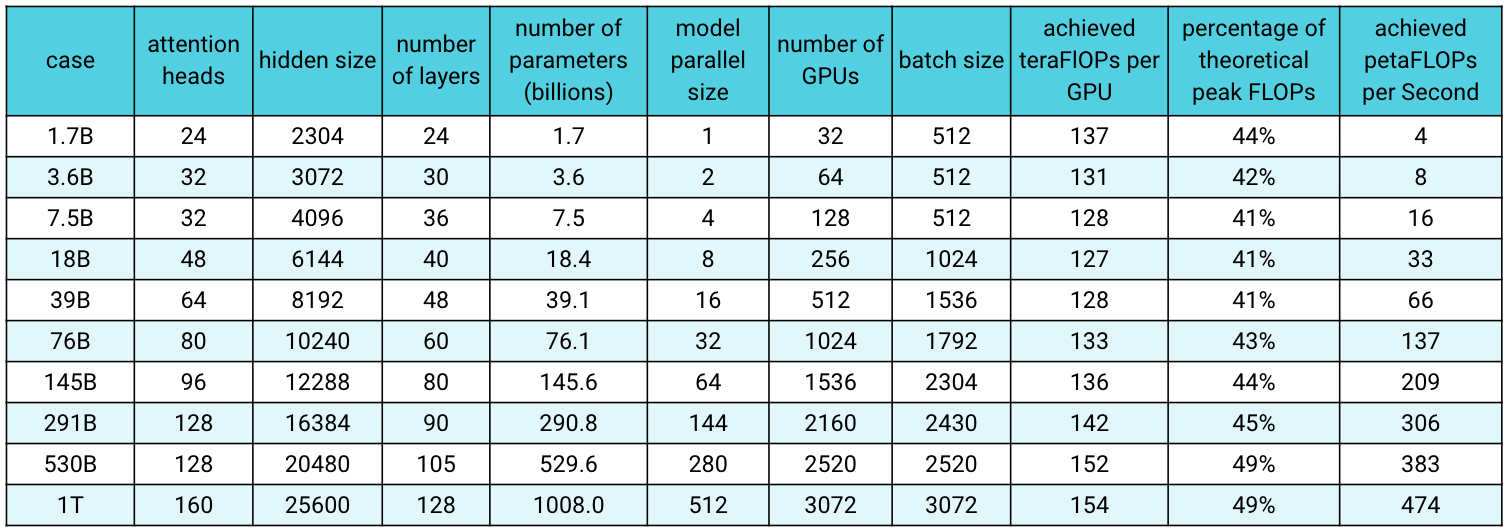
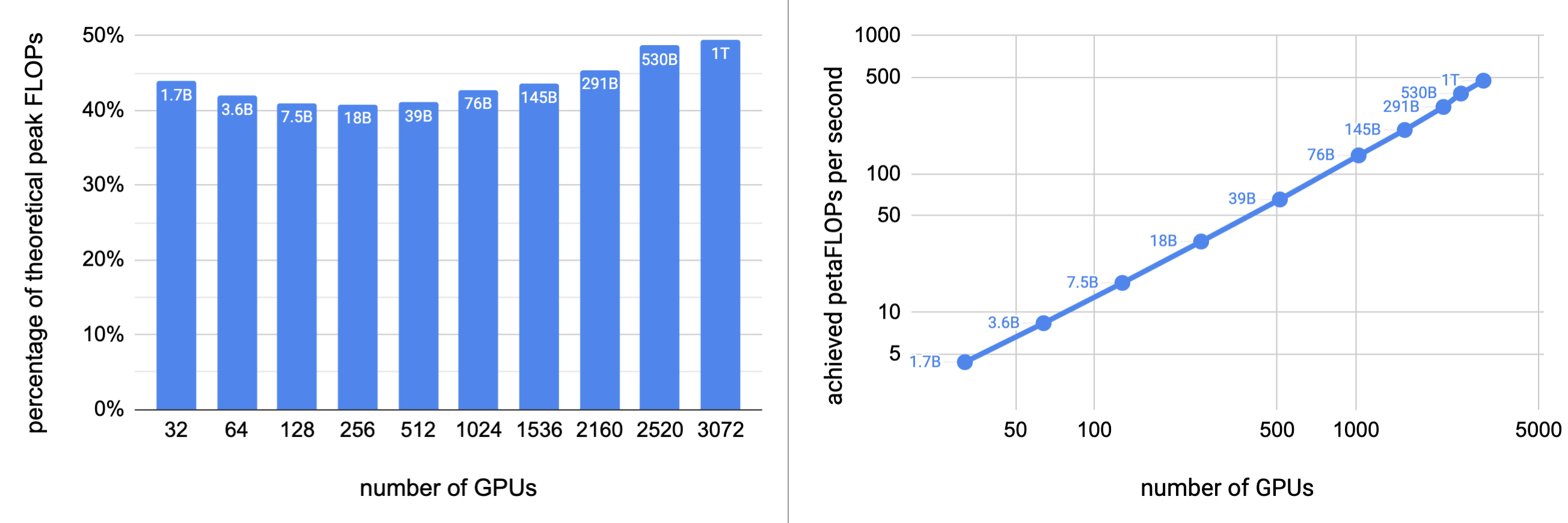
Merge branch 'main' into github-main
Showing
.gitlab-ci.yml
0 → 100644
examples/pretrain_ict.sh
0 → 100755
images/Makefile
deleted
100644 → 0
images/cases_april2021.png
0 → 100644
159 KB
150 KB
images/scaling.png
deleted
100644 → 0
280 KB
images/tables.tex
deleted
100644 → 0
This diff is collapsed.
megatron/data/autoaugment.py
0 → 100644