Merge pull request #36 from kvcache-ai/develop-0.1.2
Release v0.1.2
Showing
This diff is collapsed.
104 KB
274 KB
doc/assets/multi_gpu.png
0 → 100644
102 KB
doc/en/injection_tutorial.md
0 → 100644
Release v0.1.2
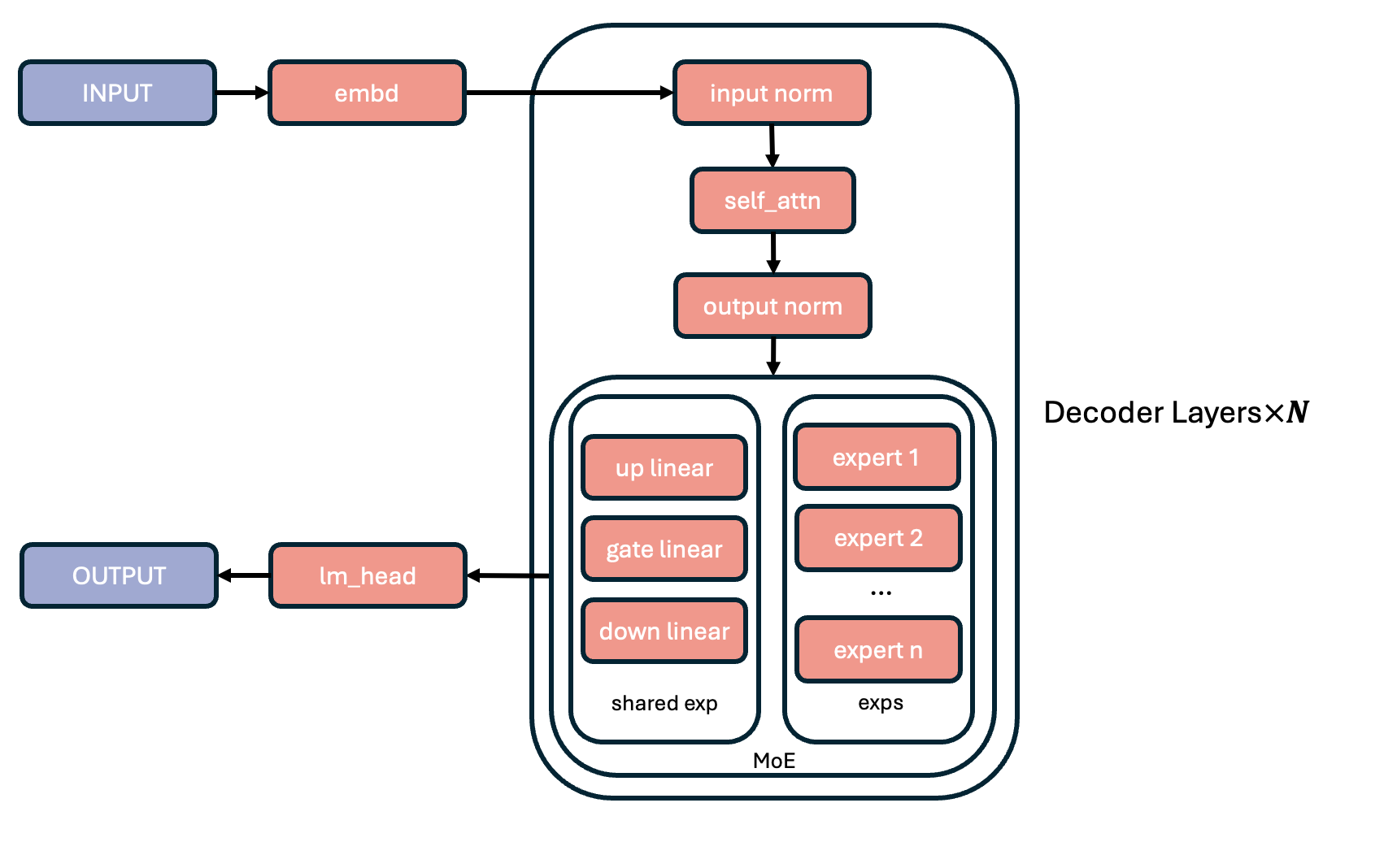
104 KB
274 KB
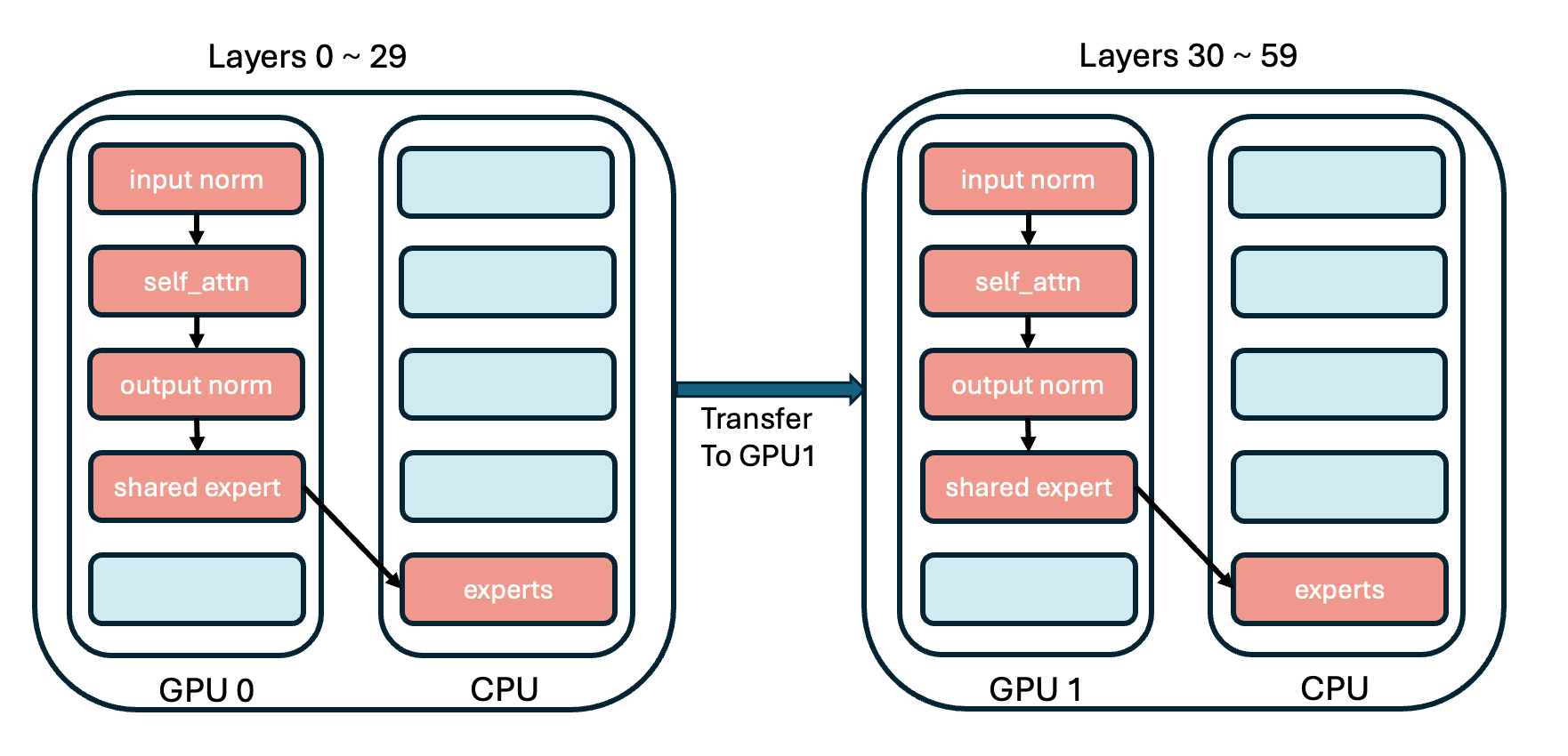
102 KB