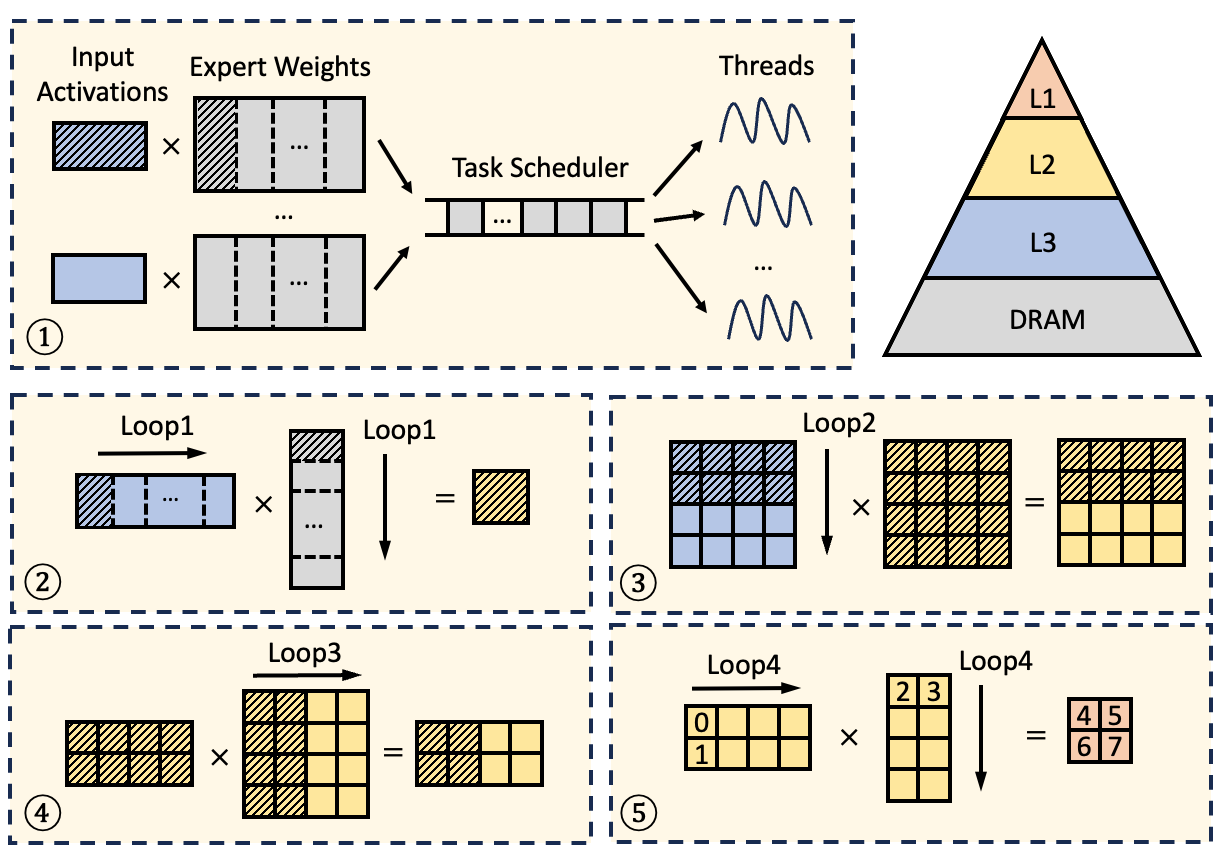
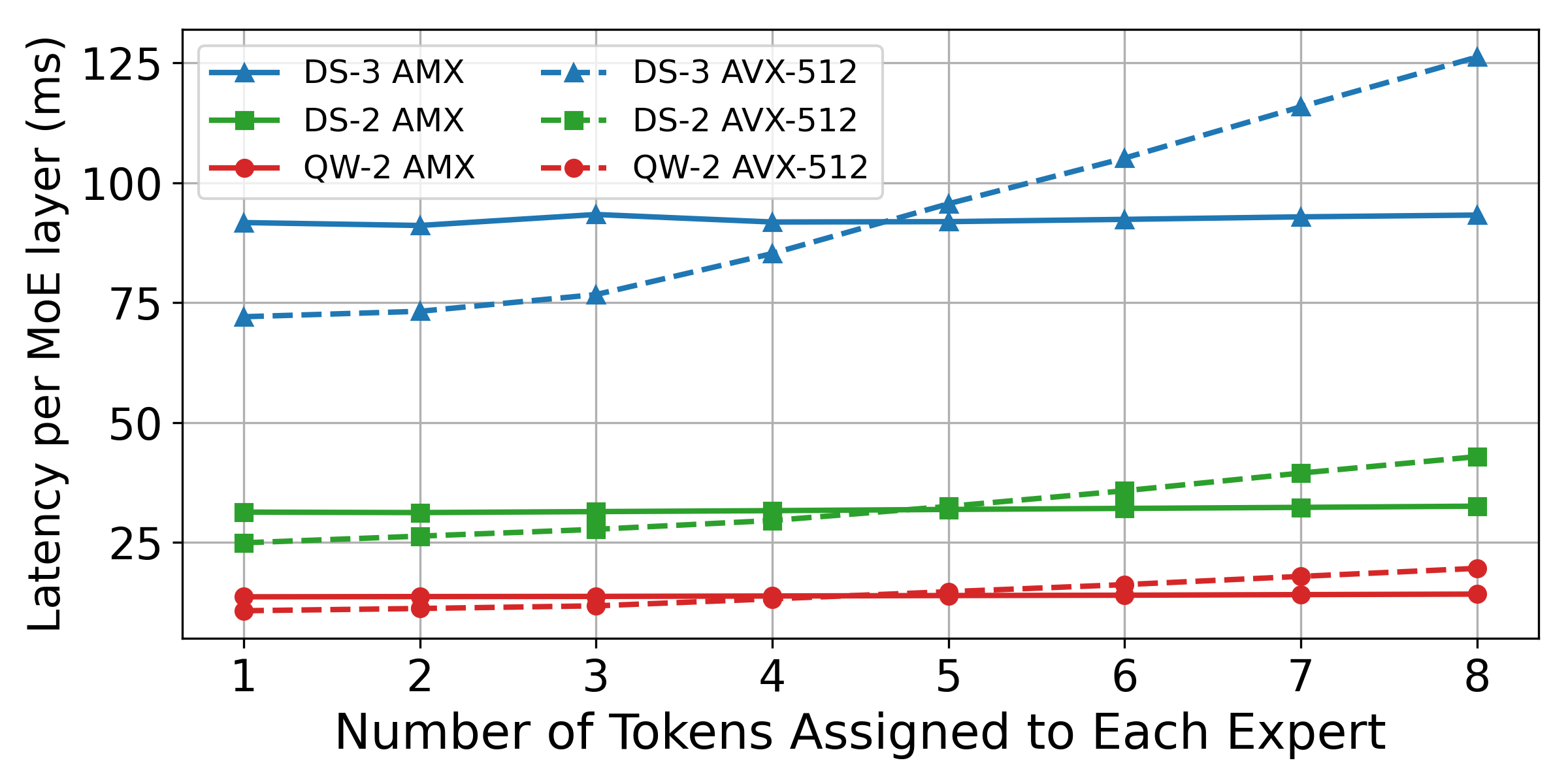
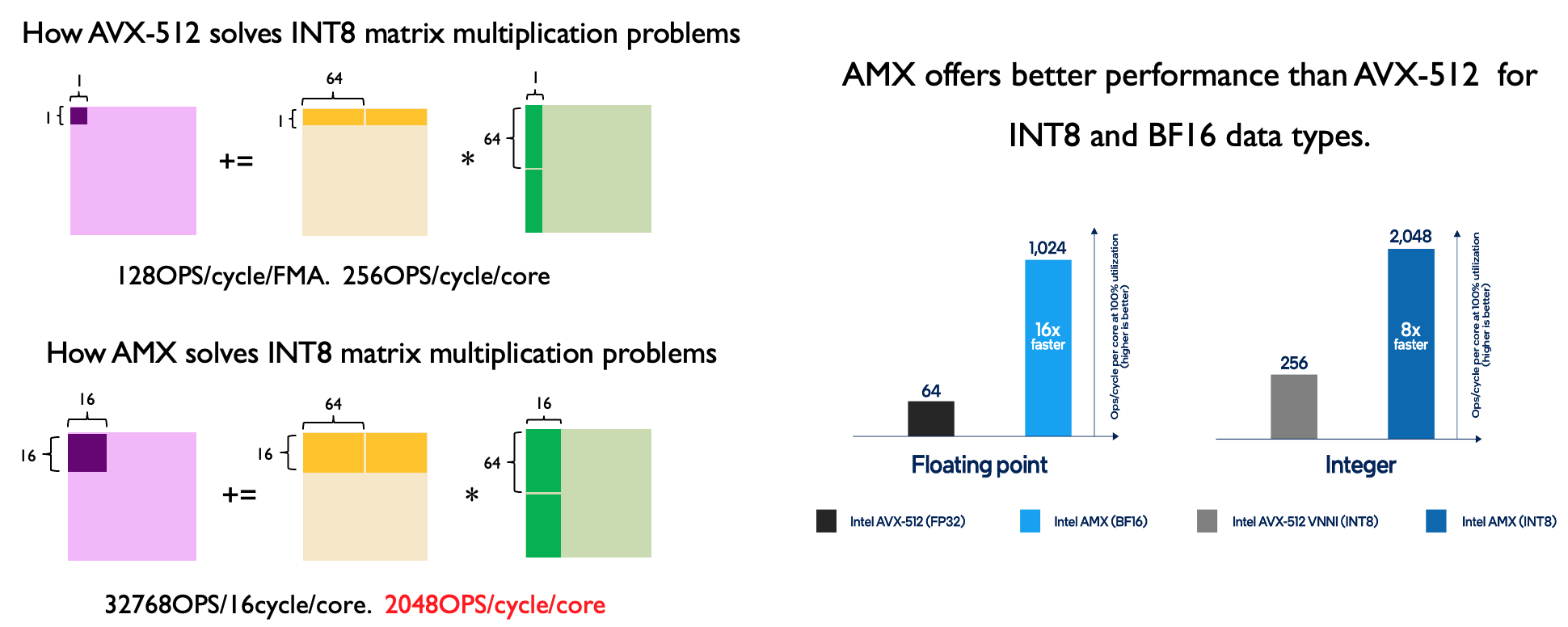
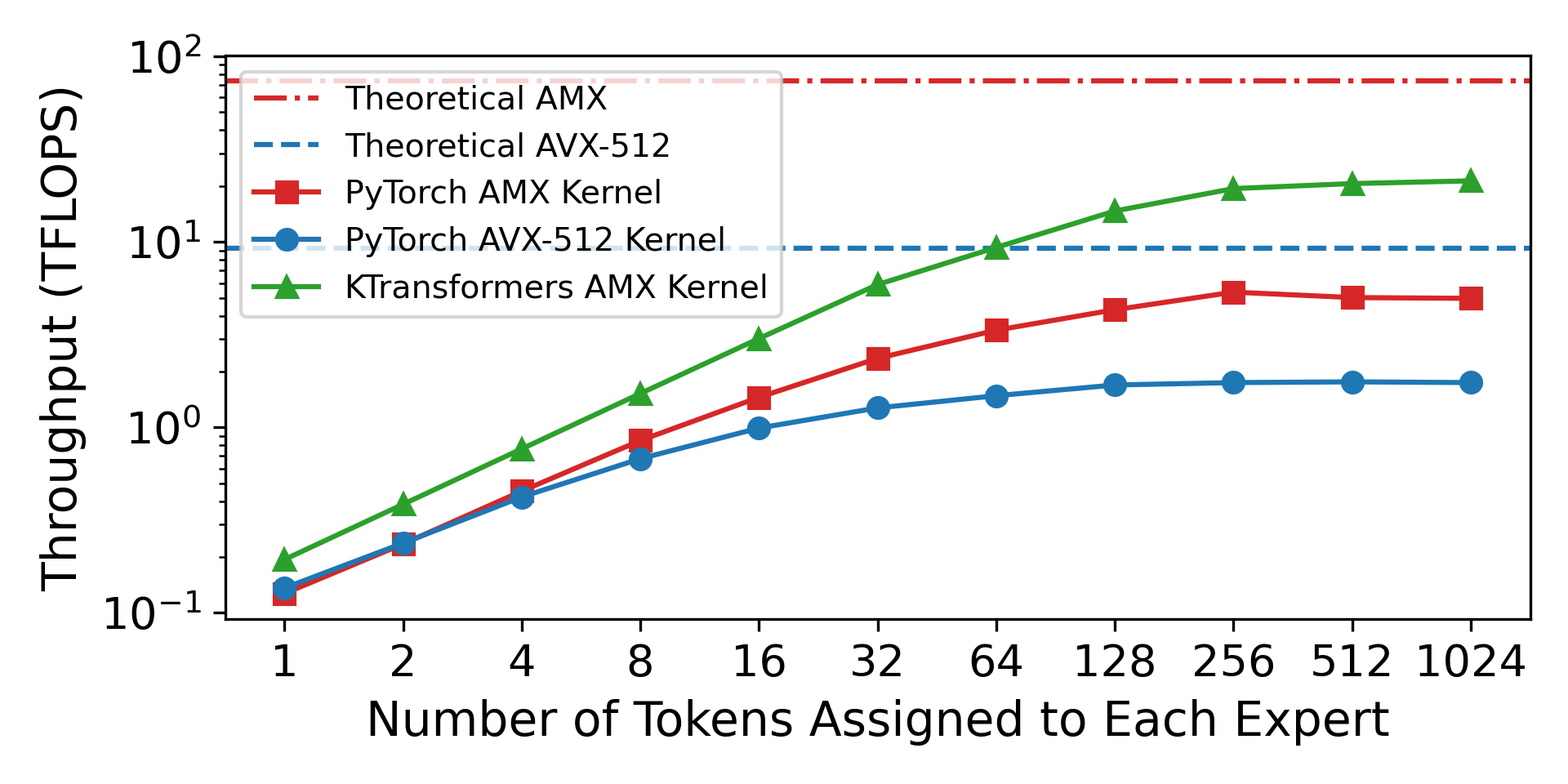
Merge remote-tracking branch 'dev/support-amx-2'
Showing
.clang-format
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
doc/assets/amx.png
0 → 100644
110 KB
doc/assets/amx_avx.png
0 → 100644
180 KB
doc/assets/amx_intro.png
0 → 100644
162 KB
doc/assets/onednn_1.png
0 → 100644
160 KB
doc/en/AMX.md
0 → 100644