Merge remote-tracking branch 'origin/dygraph' into dygraph
Showing
510 KB
581 KB
723 KB
947 KB
352 KB
1.26 MB
This image diff could not be displayed because it is too large. You can view the blob instead.
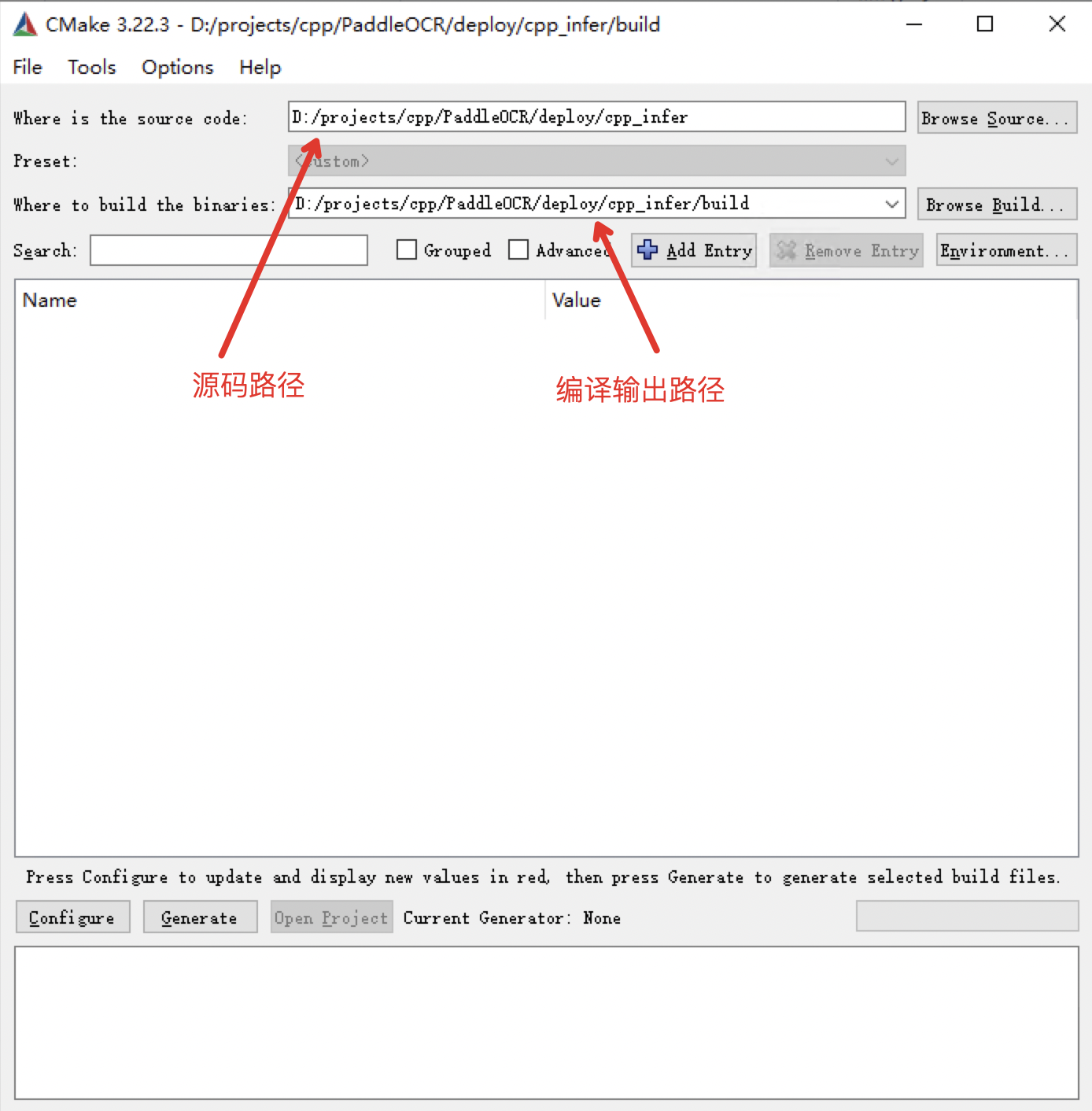
510 KB
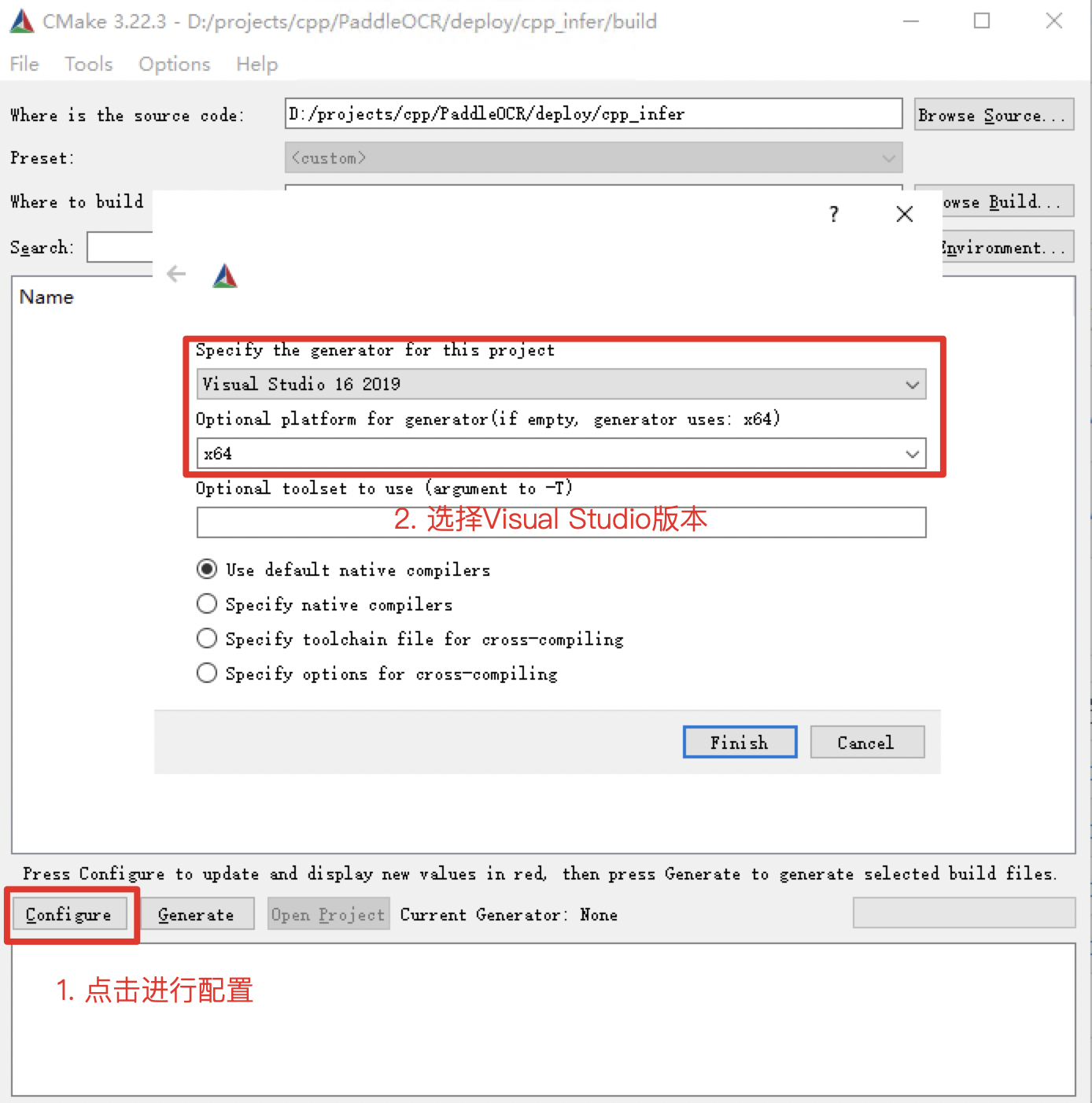
581 KB
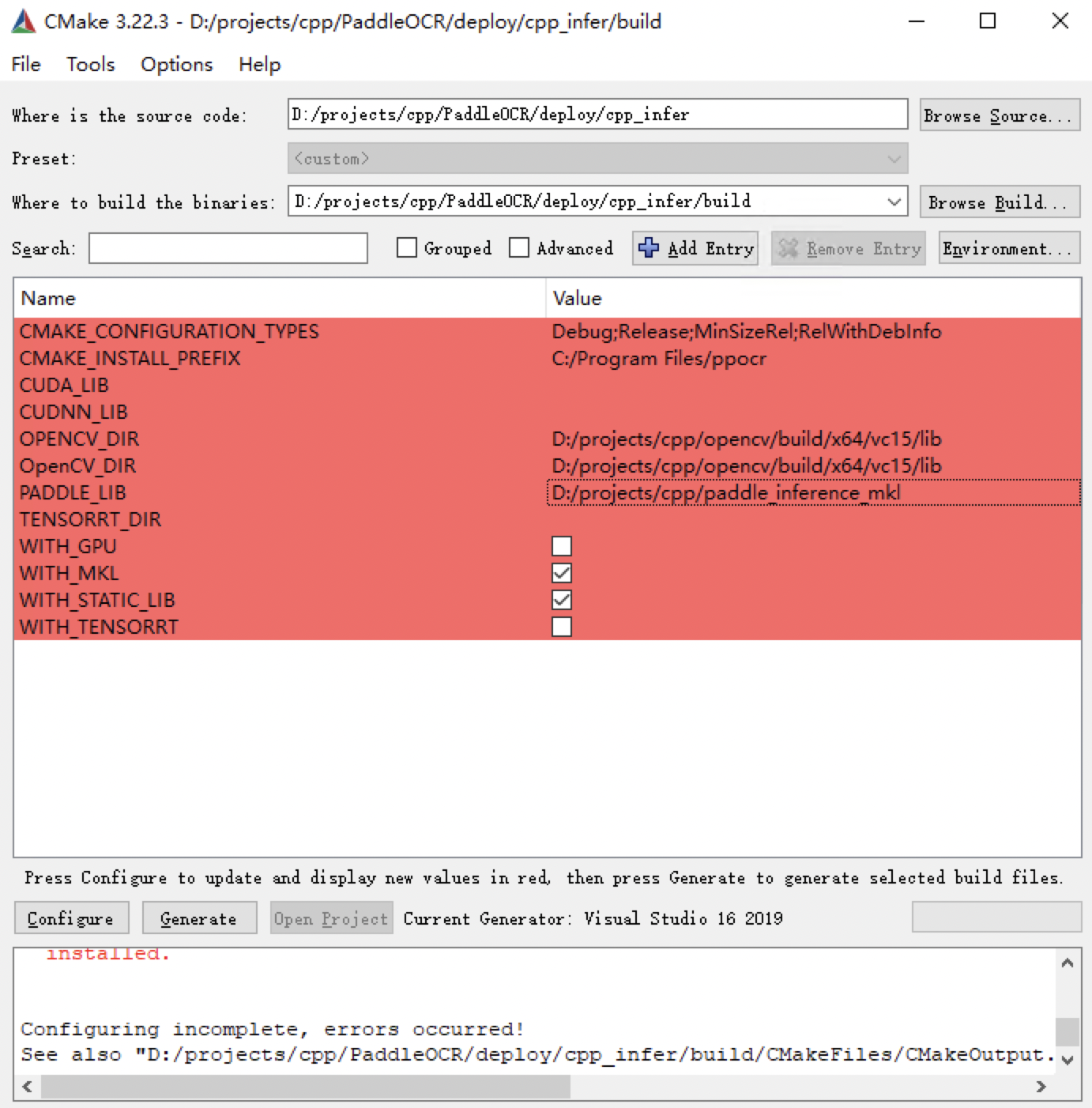
723 KB
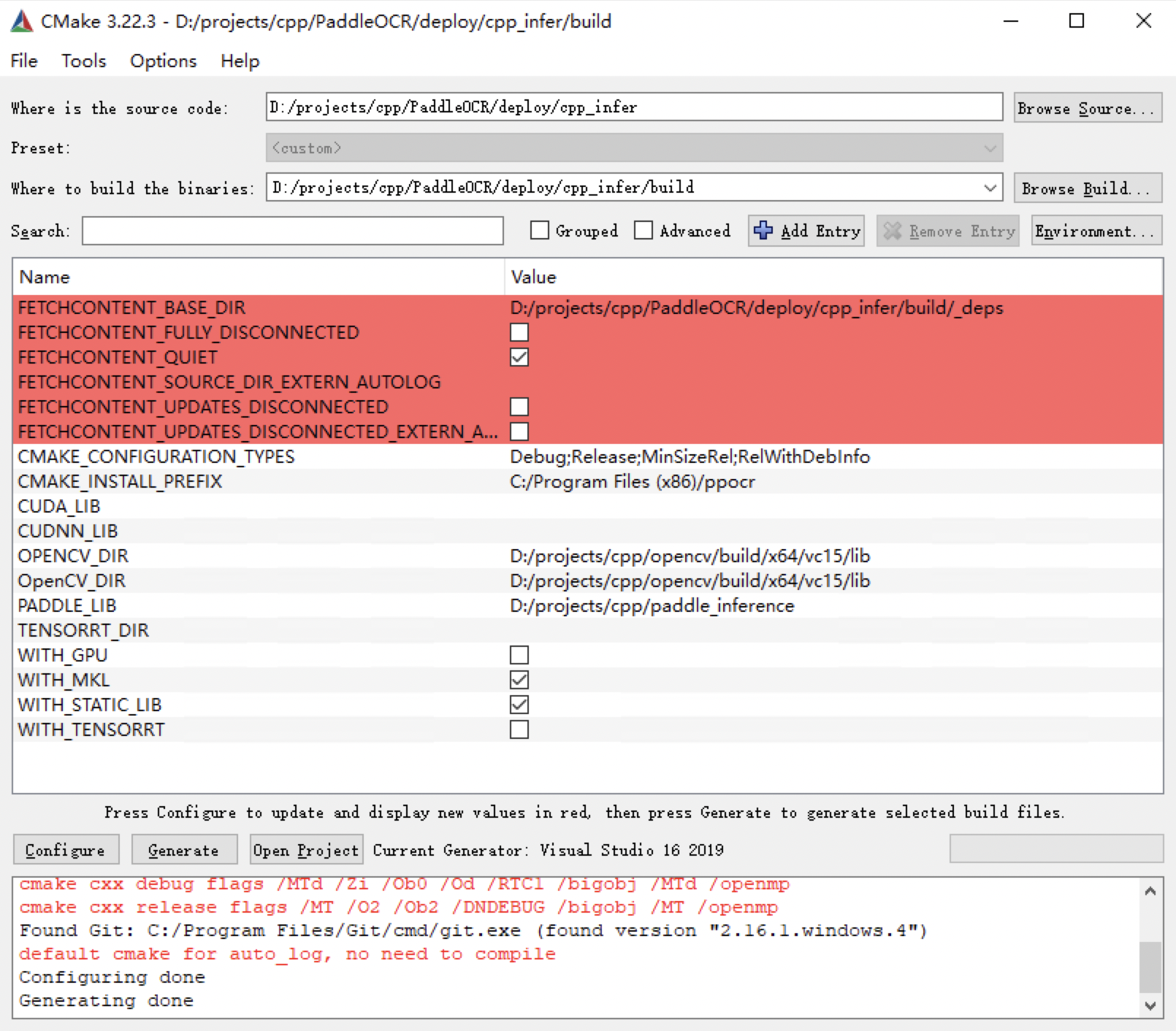
947 KB
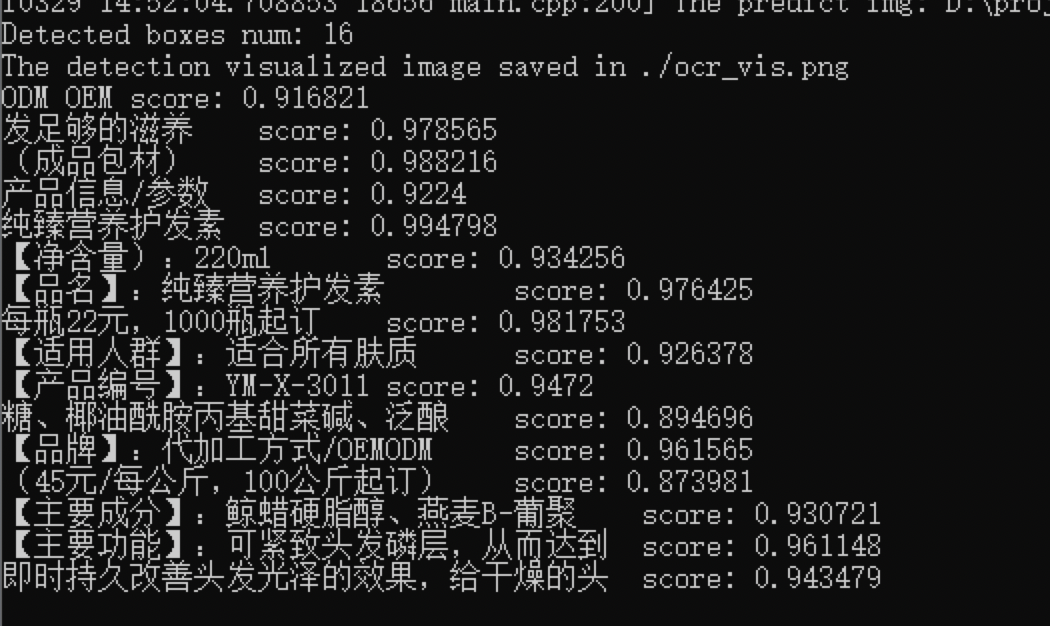
352 KB
1.26 MB