Merge remote-tracking branch 'PaddlePaddle/dygraph' into dygraph
Showing
doc/doc_ch/pgnet.md
0 → 100644
doc/doc_en/pgnet_en.md
0 → 100644
663 KB
467 KB
134 KB
337 KB
534 KB
558 KB
232 KB
249 KB
461 KB

| W: | H:
| W: | H:


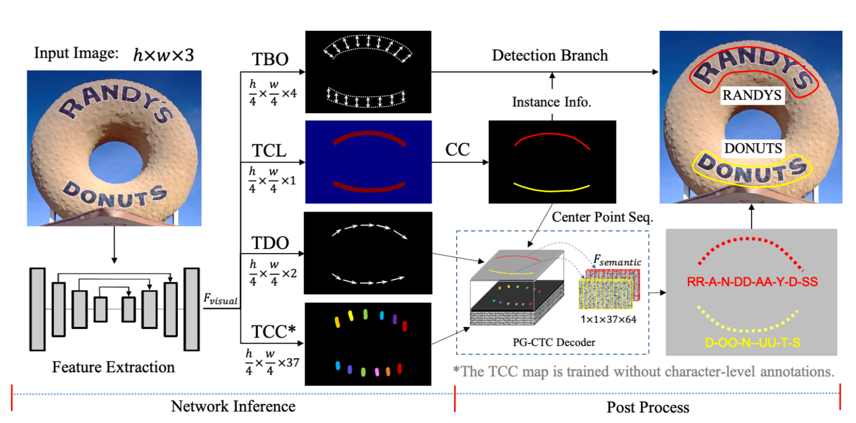
doc/pgnet_framework.png
0 → 100644
242 KB