Merge branch 'dygraph' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR into update_requirements
Showing
26.2 KB
119 KB
195 KB
deploy/slim/prune/README.md
0 → 100644
doc/doc_ch/pgnet.md
0 → 100644
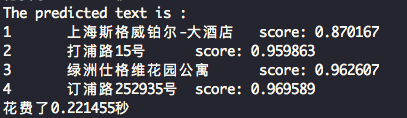
26.2 KB

119 KB
195 KB