Initial commit
Showing
3rdParty/InstallRBuild.sh
0 → 100644
File added
File added
File added
File added
File added
File added
CMakeLists.txt
0 → 100644
Doc/Tutorial_Cpp.md
0 → 100644
Doc/Tutorial_Python.md
0 → 100644
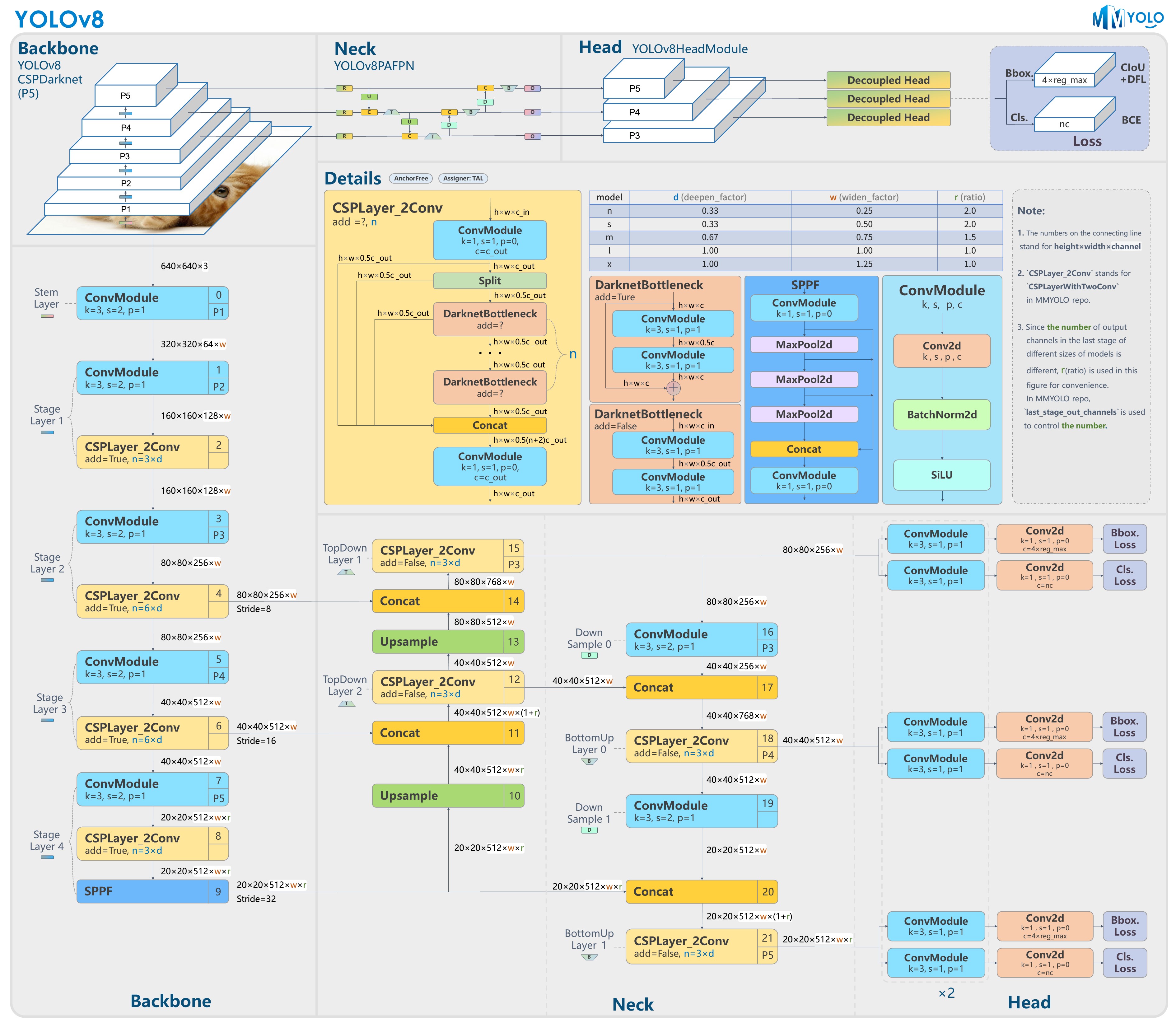
Doc/yolov8_model.jpg
0 → 100644
1.35 MB
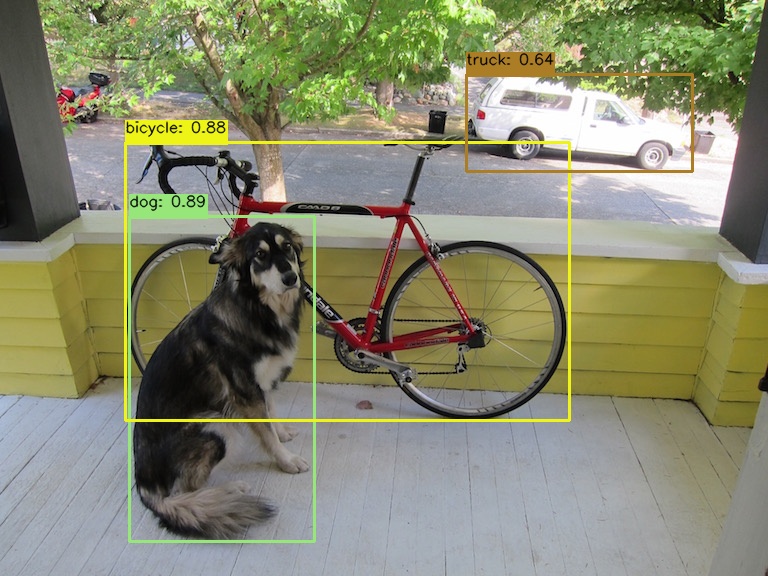
Python/Result.jpg
0 → 100644
121 KB
Python/Result0.jpg
0 → 100644
178 KB
Python/Result1.jpg
0 → 100644
478 KB
README.md
0 → 100644
Resource/Configuration.xml
0 → 100644
160 KB
476 KB