
MIGraphX Samples教程
v2.4.2
2023.02.06
# 目录
[TOC]
# C++ Samples
## 分类器
### 模型简介
本示例使用了经典的mnist模型,模型下载地址:https://github.com/onnx/models/blob/main/vision/classification/mnist/model/mnist-12.onnx,模型结构如下图所示(可以通过netron (https://netron.app/) 查看),该模型的输入shape为[1,1,28,28] ,数据排布为NCHW,输出是10个类别的概率(未归一化)。

### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
1. 转换为单通道灰度图
2. resize到28x28
3. 将像素值归一化到[0.0, 1.0]
4. 转换数据排布为NCHW
本示例代码采用了OpenCV的cv::dnn::blobFromImages()函数实现了预处理操作:
```
ErrorCode Classifier::Classify(const std::vector &srcImages,std::vector> &predictions)
{
...
// 预处理
cv::Mat inputBlob;
cv::dnn::blobFromImages(srcImages,// 输入数据,支持多张图像
inputBlob, // 输出数据
scale, // 缩放系数,这里为1/255.0
inputSize, // 模型输入大小,这里为28x28
meanValue, // 均值,这里不需要减均值,所以设置为0.0
swapRB, // 单通道图像,这里设置为0
false);
...
}
```
cv::dnn::blobFromImages()函数支持多个输入图像,首先将输入图像resize到inputSize,然后减去均值meanValue,最后乘以scale并转换为NCHW,最终将转换好的数据保存到inputBlob中,然后就可以输入到模型中执行推理了。
### 推理
完成预处理后,就可以执行推理了:
```
ErrorCode Classifier::Classify(const std::vector &srcImages,std::vector> &predictions)
{
...
// 预处理
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector results = net.eval(inputData);
// 获取输出节点的属性
migraphx::argument result = results[0]; // 获取第一个输出节点的数据
...
}
```
1. inputData表示MIGraphX的输入数据,inputData是一个映射关系,每个输入节点名都会对应一个输入数据,如果有多个输入,则需要为每个输入节点名创建数据,inputName表示输入节点名,这里为Input3,migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data}表示该节点名对应的数据,这里是通过前面预处理的数据inputBlob来创建的,第一个参数表示数据的shape,第二个参数表示数据指针。
2. net.eval(inputData)返回模型的推理结果,由于这里只有一个输出节点,所以std::vector中只有一个数据,results[0]表示第一个输出节点,这里对应Plus214_Output_0节点,获取输出数据之后,就可以对输出数据进行各种操作了。
3. 由于该模型输出的是一个未归一化的概率,所以如果需要得到每一类的实际的概率值,还需要计算softmax。
### 运行示例
根据samples工程中的README.md构建成功C++ samples后,在build目录下输入如下命令运行该示例:
```
./MIGraphX_Samples 0
```
输出结果为:
```
...
========== 0 result ==========
label:0,confidence:0.000000
label:1,confidence:0.000034
label:2,confidence:0.000012
label:3,confidence:0.000169
label:4,confidence:0.000044
label:5,confidence:0.000001
label:6,confidence:0.000000
label:7,confidence:0.000725
label:8,confidence:0.000278
label:9,confidence:0.998737
```
由于示例图像为数字9,所以结果中label为9的概率最高。

## SSD检测器
### 模型简介
SSD检测器示例使用了经典的SSD算法(https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.02325),原论文作者使用Caffe框架实现,本示例采用的是于仕琪老师开源的YuFaceDetectNet人脸检测模型,最初也是采用Caffe框架实现的,从下面的commit对应的工程中可以下载到Caffe模型:https://github.com/ShiqiYu/libfacedetection/commit/54b8e036b299b4763afa6a74af2502a8b13eb0ad,模型在libfacedetection/models/caffe目录下,该目录下同时提供了训练和部署的模型结构,本示例采用了yufacedetectnet-open-v2模型。
### 模型转换
由于MIGraphX不支持YuFaceDetectNet模型中的Permute,PriorBox和DetectionOutput这几个层,所以需要对模型做一些修改,基本的思路就是让MIGraphX不支持的层在CPU上运行。

图中黄色部分为MIGraphX不支持的层,导出onnx模型的时候需要删除这些层,将这些层都放到CPU上执行。 修改Resource/Models/Detector/SSD/yufacedetectnet-open-v2.prototxt文件的时候,直接删除不支持的层即可,修改后的文件为Resource/Models/Detector/SSD/yufacedetectnet-open-v2_onnx.prototxt文件,可以使用比较工具查看修改的部分,使用yufacedetectnet-open-v2_onnx.prototxt和yufacedetectnet-open-v2.caffemodel通过caffe-onnx(https://github.com/htshinichi/caffe-onnx)这个转换工具就可以将Caffe模型转换为onnx模型了。
注意:使用Caffe训练SSD模型的时候,需要去掉Normalize层,否则使用caffe-onnx工具转换模型的时候会失败,本示例中直接将yufacedetectnet-open-v2.prototxt中的Normalize层去掉了。
### SSD参数设置
在运行模型前,需要设置SSD模型的参数,Resource/Configuration.xml文件中的DetectorSSD节点对应了本示例使用的YuFaceDetectNet检测器的参数,下面看一下是如何根据yufacedetectnet-open-v2.prototxt设置Configuration.xml中的参数的,可以使用netscope (http://ethereon.github.io/netscope/#/editor ) 可视化.prototxt文件,方便观察模型结构,在yufacedetectnet-open-v2.prototxt中一共有4个priorbox层,分别为conv3_3_norm_mbox_priorbox,conv4_3_norm_mbox_priorbox,conv5_3_norm_mbox_priorbox,conv6_3_norm_mbox_priorbox,以conv3_3_norm_mbox_priorbox为例,其prototxt文件中的代码如下:
```
layer {
name: "conv3_3_norm_mbox_priorbox"
type: "PriorBox"
bottom: "conv3_3_norm"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv3_3_norm_mbox_priorbox"
prior_box_param {
min_size: 10.0
min_size: 16.0
min_size: 24.0
clip: false
variance: 0.10000000149
variance: 0.10000000149
variance: 0.20000000298
variance: 0.20000000298
step: 8.0
offset: 0.5
}
}
```
一共有3个min_size:10,16,24,同时clip为fase且step为8,该层没有设置flip参数,所以采用默认值true(注:如果该层只有一个宽高比为1的anchor,则flip参数可以设置为false),由于该priorbox层没有设置其他宽高比,只包含一个宽高比为1的anchor,所以Configuration.xml中不需要设置宽高比,所以配置文件中对应的参数为:
```
10
16
24
0
0
8
8
```
如果你需要添加其他宽高比的anchor,在设置priorbox层参数的时候需要注意:Configuration.xml中AspectRatio参数设置的时候不需要包含1,因为程序中默认已经添加1了,同时需要忽略flip参数,比如现在有4个priorbox层,每一层的宽高比设置为0.3333和0.25且flip为true,则每一层只需要写0.3333和0.25即可,xml代码如下:
```
0.3333
0.25
0.3333
0.25
0.3333
0.25
0.3333
0.25
```
其他priorbox层参数的设置与conv3_3_norm_mbox_priorbox类似,这里需要注意:**Configuration.xml中priorbox层的顺序要与onnx文件中的输出节点顺序保持一致**,通过netron (https://netron.app/) 查看到onnx文件的输出顺序如下:

所以Configuration.xml中priorbox层的顺序为conv3_3_norm_mbox_priorbox,conv4_3_norm_mbox_priorbox,conv5_3_norm_mbox_priorbox,conv6_3_norm_mbox_priorbox,所以Configuration.xml中minisize参数设置如下:
```
10
16
24
32
48
64
96
128
192
256
```
设置好priorbox参数后,还需要设置DetectionOutput层的参数,由于本示例模型是一个人脸检测模型,所以只有两类目标(背景和人脸),所以ClassNumber为2,DetectionOutput层的其他参数可以根据实际情况做微调,本示例中采用如下设置:
```
400
200
0.3
0.9
```
### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
1. 减去均值,本示例使用的模型不需要减均值
2. 转换数据排布为NCHW
本示例代码采用了OpenCV的cv::dnn::blobFromImage()函数实现了预处理操作:
```
ErrorCode DetectorSSD::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage,std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 预处理并转换为NCHW
cv::Mat inputBlob;
blobFromImage(srcImage, // 输入数据
inputBlob, // 输出数据
scale, // 1
inputSize, // SSD输入大小,本示例为640x480
meanValue,// 本示例不需要减均值,这里设置为0
swapRB, // false
false);
...
}
```
### 推理
模型转换成功并且设置好SSD参数之后就可以执行推理了,对于MIGraphX不支持的SSD层,需要在CPU上实现,示例代码Src/Detector/DetectorSSD.h中的PermuteLayer(),PriorBoxLayer(),DetectionOutputLayer()分别实现了对应的层。
```
ErrorCode DetectorSSD::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage,std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector inferenceResults=net.eval(inputData);
vector> regressions;
vector> classifications;
for(int i=0;i regression;
migraphx::argument result0 = inferenceResults[2*i];
result0.visit([&](auto output) { regression.assign(output.begin(), output.end()); });
regression=PermuteLayer(regression,ssdParameter.priorBoxWidth[i],ssdParameter.priorBoxHeight[i],numberOfPriorBox*4);
regressions.push_back(regression);
// 分类
std::vector classification;
migraphx::argument result1 = inferenceResults[2*i+1];
result1.visit([&](auto output) { classification.assign(output.begin(), output.end()); });
classification=PermuteLayer(classification,ssdParameter.priorBoxWidth[i],ssdParameter.priorBoxHeight[i],numberOfPriorBox*ssdParameter.classNum);
classifications.push_back(classification);
}
// 对推理结果进行处理,得到最后SSD检测的结果
GetResult(classifications,regressions,resultsOfDetection);
// 转换到原图坐标
for(int i=0;i
## RetinaFace人脸检测器
### 模型简介
RetinaFace是一个经典的人脸检测模型(https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.00641),采用了SSD架构。

本示例采用了如下的开源实现:https://github.com/biubug6/Pytorch_Retinaface,作者提供了restnet50 和mobilenet0.25两个预训练模型,本示例使用了mobilenet0.25预训练模型,将mobilenet0.25预训练模型下载下来后,保存到Pytorch_Retinaface工程的weights目录。
### 模型转换
在将mobilenet0.25预训练模型转换为onnx文件的时候,本示例需要对作者提供的python代码做如下改变:
#### 修改models/retinaface.py
1. **将ClassHead类修改为如下实现**
```
class ClassHead(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,inchannels=512,num_anchors=3):
super(ClassHead,self).__init__()
self.num_anchors = num_anchors
self.conv1x1 = nn.Conv2d(inchannels,self.num_anchors*2,kernel_size=(1,1),stride=1,padding=0)
def forward(self,x):
out = self.conv1x1(x)
return out
```
由于本示例的C++推理代码已经实现了permute操作,所以这里需要去掉out.permute(0,2,3,1).contiguous()。
2. **将BboxHead类修改为如下实现**
```
class BboxHead(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,inchannels=512,num_anchors=3):
super(BboxHead,self).__init__()
self.conv1x1 = nn.Conv2d(inchannels,num_anchors*4,kernel_size=(1,1),stride=1,padding=0)
def forward(self,x):
out = self.conv1x1(x)
return out
```
与ClassHead一样,需要去掉permute操作。
3. **将RetinaFace类的forward修改为如下实现**
```
def forward(self,inputs):
out = self.body(inputs)
# FPN
fpn = self.fpn(out)
# SSH
feature1 = self.ssh1(fpn[0])
feature2 = self.ssh2(fpn[1])
feature3 = self.ssh3(fpn[2])
features = [feature1, feature2, feature3]
bbox_regressions = [self.BboxHead[i](feature) for i, feature in enumerate(features)]
classifications = [self.ClassHead[i](feature) for i, feature in enumerate(features)]
output=(bbox_regressions[0],classifications[0],bbox_regressions[1],classifications[1],bbox_regressions[2],classifications[2])
return output
```
本示例去掉了landmark检测功能,所以需要去掉forward中的landmark部分,bbox_regressions和classifications需要删除torch.cat操作,同时需要修改output为(bbox_regressions[0],classifications[0],bbox_regressions[1],classifications[1],bbox_regressions[2],classifications[2])。
#### 修改data/config.py
将cfg_mnet中的'pretrain': True,修改为'pretrain': False,
#### 修改convert_to_onnx.py
导出onnx模型的时候,需要修改原来的output_names,可以直接删除torch.onnx._export()的output_names参数或者手动指定每个输出节点的名字,如果直接删除了output_names参数,则会生成一个随机名,本示例直接删除了output_names参数,同时本示例修改了onnx文件名output_onnx,修改后的main函数如下:
```
if __name__ == '__main__':
torch.set_grad_enabled(False)
cfg = None
if args.network == "mobile0.25":
cfg = cfg_mnet
elif args.network == "resnet50":
cfg = cfg_re50
# net and model
net = RetinaFace(cfg=cfg, phase = 'test')
net = load_model(net, args.trained_model, args.cpu)
net.eval()
print('Finished loading model!')
print(net)
device = torch.device("cpu" if args.cpu else "cuda")
net = net.to(device)
# ------------------------ export -----------------------------
output_onnx = 'mobilenet0.25_Final.onnx'
print("==> Exporting model to ONNX format at '{}'".format(output_onnx))
input_names = ["input0"]
output_names = ["output0"]
inputs = torch.randn(1, 3, args.long_side, args.long_side).to(device)
torch_out = torch.onnx._export(net, inputs, output_onnx, export_params=True, verbose=False,
input_names=input_names)
```
注意:如果需要修改模型的输入大小,可以修改args.long_side参数,默认为640x640。
完成上述修改后,执行python convert_to_onnx.py命令就可以实现模型转换了,转换成功后会在当前目录生成mobilenet0.25_Final.onnx文件,下面就可以进行推理了。本示例将修改好的工程保存到了samples工程中的Resource/Models/Detector/RetinaFace目录中,在Pytorch_Retinaface目录中执行python convert_to_onnx.py命令可以直接生成onnx文件。
### 检测器参数设置
samples工程中的Resource/Configuration.xml文件的DetectorRetinaFace节点表示RetinaFace检测器的参数,这些参数是根据Pytorch_Retinaface工程中的data/config.py文件中的cfg_mnet来设置的,下面我们看一下是如何通过cfg_mnet来设置的。
2. **设置anchor大小**
cfg_mnet的min_sizes表示每一个priorbox层的anchor大小,我们可以看到该模型一共有3个priorbox层,第一层anchor大小为16和32,第二层anchor大小为64和128,第三层anchor大小为256和512,注意:**Configuration.xml中priorbox层的顺序要与onnx文件中的输出节点顺序保持一致**,通过netron (https://netron.app/) 可以看到首先输出的是467和470节点,这两个节点对应的是特征图最大的检测层,所以对应的anchor大小为16和32,最后输出的是469和472节点,这两个节点对应的是特征图最小的检测层,所以对应的anchor大小为256和512,

所以Configuration.xml配置文件中的参数设置如下:
```
3
16
32
64
128
256
512
```
3. **设置Flip和Clip**
cfg_mnet中的clip为False,所以Configuration.xml中对应的参数设置为0即可,由于只有一个宽高比为1的anchor,所以Flip设置为0。
```
0
0
0
0
0
0
```
4. **设置anchor的宽高比**
由于RetinaFace只包含宽高比为1的anchor,所以这里不需要设置宽高比。
5. **设置每个priorbox层的步长**
cfg_mnet中的steps表示每个priorbox层的步长,所以三个priorbox的步长依次为8,16,32,对应的Configuration.xml的设置如下:
```
8
16
32
8
16
32
```
6. **设置DetectionOutput层的参数**
由于本示例模型是一个人脸检测模型,所以只有两类目标(背景和人脸),所以ClassNumber为2,DetectionOutput层的其他参数可以根据实际情况做微调,本示例中采用如下设置:
```
400
200
0.3
0.9
```
### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
1. 减去均值,RetinaFace训练的时候对图像做了减均值的操作(train.py文件中的第38行),注意均值的顺序是BGR顺序。
2. 转换数据排布为NCHW
本示例代码采用了OpenCV的cv::dnn::blobFromImage()函数实现了预处理操作:
```
ErrorCode DetectorRetinaFace::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage,std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 预处理并转换为NCHW
cv::Mat inputBlob;
blobFromImage(srcImage, // 输入数据
inputBlob, // 输出数据
scale, // 1
inputSize, // SSD输入大小,本示例为640x480
meanValue,// (104,117,123)
swapRB, // false
false);
...
}
```
### 推理
模型转换成功并且设置好检测器参数之后就可以执行推理了。
```
ErrorCode DetectorRetinaFace::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage,std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector inferenceResults=net.eval(inputData);
vector> regressions;
vector> classifications;
for(int i=0;i regression;
migraphx::argument result0 = inferenceResults[2*i];
result0.visit([&](auto output) { regression.assign(output.begin(), output.end()); });
regression=PermuteLayer(regression,ssdParameter.priorBoxWidth[i],ssdParameter.priorBoxHeight[i],numberOfPriorBox*4);
regressions.push_back(regression);
// ClassHead
std::vector classification;
migraphx::argument result1 = inferenceResults[2*i+1];
result1.visit([&](auto output) { classification.assign(output.begin(), output.end()); });
classification=PermuteLayer(classification,ssdParameter.priorBoxWidth[i],ssdParameter.priorBoxHeight[i],numberOfPriorBox*ssdParameter.classNum);
classifications.push_back(classification);
}
// 对推理结果进行处理,得到最后SSD检测的结果
GetResult(classifications,regressions,resultsOfDetection);
// 转换到原图坐标
for(int i=0;i
## 动态shape(MTCNN人脸检测器)
### 模型简介
动态shape示例程序采用了MTCNN人脸检测器模型中的PNet模型(https://arxiv.org/abs/1604.02878),论文主页:https://kpzhang93.github.io/MTCNN_face_detection_alignment/index.html。MTCNN中的PNet是一个典型的动态shape模型,PNet网络结构如下图所示,PNet是一个全卷积网络,所以可以输入不同大小的图像。

MTCNN检测器在检测之前会对输入图像构建一个图像金字塔,这个图像金字塔中包含了不同尺度的图像,然后将不同尺度的图像依次输入到PNet提取人脸候选区域,经过PNet提取出来的人脸候选区域再经过RNet和ONet进一步筛选和微调得到最后的检测结果。

本示例对原始的PNet模型做了一些调整,训练的时候将输入图像大小修改为24x24,同时将第1个卷积和第3个卷积的步长修改为2。
### 模型转换
论文中作者提供的是Caffe训练好的模型,可以通过caffe-onnx这个工具(https://github.com/htshinichi/caffe-onnx)转换为onnx模型。
### 设置最大输入shape
由于PNet是一个动态shape模型,所以在推理之前需要设置最大输入shape,Resource/Configuration.xml文件中的DetectorMTCNN节点的MaxHeight和MaxWidth表示最大输入图像的高和宽,可以根据实际情况来定,本示例设置为512和512,程序中通过如下代码设置最大输入shape:
```
// 设置最大输入大小
migraphx::onnx_options onnx_options;
onnx_options.map_input_dims["input"]={1,3,maxHeight,maxWidth};
```
### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
1. 减去均值127.5并乘以系数0.0078125
2. 转换数据排布为NCHW
本示例代码采用了OpenCV的cv::dnn::blobFromImage()函数实现了预处理操作:
```
cv::Mat inputBlob = blobFromImage(inputImage, 0.0078125, cv::Size(), cv::Scalar(127.5, 127.5, 127.5), false);
```
### 推理
完成预处理后,就可以执行推理了:
```
...
// 处理图像金字塔的每一级图像
for (int k = 0; k < scales.size(); ++k)
{
// 输入图像
float scale = scales[k];
cv::Mat inputImage;
cv::Size inputSize=cv::Size(ceil(srcImage.cols*scale), ceil(srcImage.rows*scale));
resize(srcImage, inputImage,inputSize, 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
// 每次输入shape发生变化后,需要对模型进行reshape
std::vector inputShapeOfReshape={1,3,inputSize.height,inputSize.width};
std::unordered_map> inputShapeMap;
inputShapeMap[inputName] = inputShapeOfReshape;
net.reshape(inputShapeMap);
// 预处理并转换为NCHW
cv::Mat inputBlob = blobFromImage(inputImage, 0.0078125, cv::Size(), cv::Scalar(127.5, 127.5, 127.5), false);
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{migraphx::shape(inputShape.type(),inputShapeOfReshape), (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector results = net.eval(inputData);
...
}
...
```
1. for循环表示依次处理图像金字塔的每一级图像,由于每一级图像大小都不一样,所以推理之前需要对模型进行reshape操作,每一级图像经过预处理操作之后就可以输入到模型中执行推理了。
2. results表示推理返回的结果,这里表示conv4-2_Y和prob1_Y节点,results中的顺序与onnx中输出节点保持一致,可以通过netron (https://netron.app/) 查看,可以看出results中依次表示conv4-2_Y,prob1_Y节点,

返回的结果需要经过进一步的后处理操作才能得到最后的人脸候选区域。
### 运行示例
根据samples工程中的README.md构建成功C++ samples后,在build目录下输入如下命令运行该示例:
```
# 设置动态shape模式
export MIGRAPHX_DYNAMIC_SHAPE=1
# 运行示例
./MIGraphX_Samples 3
```
会在当前目录生成检测结果图像Result.jpg

## YOLOV3检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV3是由Joseph Redmon和Ali Farhadi在《YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement》论文中提出的单阶段检测模型,算法首先通过特征提取网络对输入提取特征,backbone部分由YOLOV2时期的Darknet19进化至Darknet53加深了网络层数,引入了Resnet中的跨层加和操作;然后结合不同卷积层的特征实现多尺度训练,一共有13x13、26x26、52x52三种分辨率,分别用来预测大、中、小的物体;每种分辨率的特征图将输入图像分成不同数量的格子,每个格子预测B个bounding box,每个bounding box预测内容包括: Location(x, y, w, h)、Confidence Score和C个类别的概率,因此YOLOv3输出层的channel数为B*(5 + C)。YOLOv3的loss函数也有三部分组成:Location误差,Confidence误差和分类误差。
 本示例采用如下的开源实现:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3, 作者在V9.6.0版本中提供多种不同的YOLOV3预训练模型,其中包括yolov3、yolov3-fixed、yolov3-spp、yolov3-tiny四个版本。本示例选择yolov3-tiny.pt预训练模型进行构建MIGraphX推理,下载YOLOV3的预训练模型yolov3-tiny.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV3工程的weights目录。
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV3源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov3-tiny.pt转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV3工程根目录
cd
# 环境配置,torch、torchvision手动安装
pip install -r requirements.txt
# 导出onnx模型
python export.py --weights yolov3.pt --imgsz 416 416 --include onnx
```
注意:官方源码提供的模型转换的程序中包含更多的功能,例如动态shape模型的导出,可根据需要进行添加相关参数。
### 检测器参数设置
samples工程中的Resource/Configuration.xml文件的DetectorYOLOV3节点表示YOLOV3检测器的参数,相关参数主要依据官方推理示例进行设置。各个参数含义如下:
- ModelPath:yolov3模型存放路径
- ClassNameFile:coco数据集类别文件存放路径
- UseFP16:是否使用FP16推理模式
- NumberOfClasses:检测类别数量
- ConfidenceThreshold:置信度阈值,用于判断anchor内的物体是否为正样本
- NMSThreshold:非极大值抑制阈值,用于消除重复框
- ObjectThreshold:用于判断anchor内部是否有物体
```
"../Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV3/yolov3-tiny.onnx"
"../Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV3/coco.names"
0
80
0.2
0.4
0.4
```
### 模型初始化
模型初始化首先通过parse_onnx()函数加载YOLOV3的onnx模型,并可以通过program的get_parameter_shapes()函数获取网络的输入属性。完成模型加载之后需要使用compile()方法编译模型,编译模式使用migraphx::gpu::target{}设为GPU模式,编译过程主要基于MIGraphX IR完成各种优化。同时如果需要使用低精度量化进行推理,可以使用quantize_fp16()函数实现。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV3::Initialize(InitializationParameterOfDetector initializationParameterOfDetector)
{
...
//模型加载
net = migraphx::parse_onnx(modelPath);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to load model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
// 获取模型输入属性
std::pair inputAttribute=*(net.get_parameter_shapes().begin());
inputName=inputAttribute.first;
inputShape=inputAttribute.second;
inputSize=cv::Size(inputShape.lens()[3],inputShape.lens()[2]);// NCHW
// 设置模型为GPU模式
migraphx::target gpuTarget = migraphx::gpu::target{};
// 量化
if(useFP16)
{
migraphx::quantize_fp16(net);
}
// 编译模型
migraphx::compile_options options;
options.device_id=0; // 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备(>=1.2版本中支持)
options.offload_copy=true; // 设置offload_copy
net.compile(gpuTarget,options);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to compile model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
...
}
```
### 模型推理
#### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
- 转换数据排布为NCHW
- 归一化[0.0, 1.0]
- 将输入数据的尺寸变换到YOLOV3输入大小(1,3,416,416)
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV3::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 预处理并转换为NCHW
cv::Mat inputBlob;
blobFromImage(srcImage, // 输入数据
inputBlob, // 输出数据
1 / 255.0, //归一化
inputSize, //YOLOV3输入尺寸,本示例为416x416
Scalar(0, 0, 0), //未减去均值
true, //转换RB通道
false);
...
}
```
#### 前向推理
完成图像预处理以及YOLOV3目标检测相关参数设置之后开始执行推理,利用migraphx推理计算得到YOLOV3模型的输出数据。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV3::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector inferenceResults = net.eval(inputData);
// 获取推理结果
std::vector outs;
migraphx::argument result = inferenceResults[0];
// 转换为cv::Mat
migraphx::shape outputShape = result.get_shape();
int shape[]={outputShape.lens()[0],outputShape.lens()[1],outputShape.lens()[2]};
cv::Mat out(3,shape,CV_32F);
memcpy(out.data,result.data(),sizeof(float)*outputShape.elements());
outs.push_back(out);
...
}
```
YOLOV3的MIGraphX推理结果inferenceResults是一个std::vector< migraphx::argument >类型,YOLOV3的onnx模型包含一个输出,所以result等于inferenceResults[0],result包含三个维度:outputShape.lens()[0]=1表示batch信息,outputShape.lens()[1]=10647表示生成anchor数量,outputShape.lens()[2]=85表示对每个anchor的预测信息。同时可将85拆分为4+1+80,前4个参数用于判断每一个特征点的回归参数,回归参数调整后可以获得预测框,第5个参数用于判断每一个特征点是否包含物体,最后80个参数用于判断每一个特征点所包含的物体种类。获取上述信息之后进行anchors筛选,筛选过程分为两个步骤:
- 第一步根据objectThreshold阈值进行筛选,大于该阈值则判断当前anchor内包含物体,小于该阈值则判断无物体;
- 第二步根据confidenceThreshold阈值进行筛选,当满足第一步阈值anchor的最大置信度得分maxClassScore大于该阈值,则进一步获取当前anchor的坐标信息和预测物体类别信息,小于该阈值则不做处理。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV3::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
//获取先验框的个数numProposal=10647
int numProposal = outs[0].size[1];
//获取每个anchor的预测信息数量numOut=85
int numOut = outs[0].size[2];
//变换输出的维度
outs[0] = outs[0].reshape(0, numProposal);
//生成先验框
std::vector confidences;
std::vector boxes;
std::vector classIds;
//原图尺寸与模型输入尺寸的缩放比例
float ratioh = (float)srcImage.rows / inputSize.height, ratiow = (float)srcImage.cols / inputSize.width;
//计算cx,cy,w,h,box_sore,class_sore
int n = 0, rowInd = 0;
float* pdata = (float*)outs[0].data;
for (n = 0; n < numProposal; n++)
{
//获取当前anchor是否包含物体的概率值
float boxScores = pdata[4];
//第一次筛选,判断anchor内是否包含物体
if (boxScores > yolov3Parameter.objectThreshold)
{
//获取每个anchor内部预测的80个类别概率信息
cv::Mat scores = outs[0].row(rowInd).colRange(5, numOut);
cv::Point classIdPoint;
double maxClassScore;
/获取80个类别中最大概率值和对应的类别ID
cv::minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &maxClassScore, 0, &classIdPoint);
maxClassScore *= boxScores;
//第二次筛选,判断当前anchor的最大置信度得分是否满足阈值
if (maxClassScore > yolov3Parameter.confidenceThreshold)
{
const int classIdx = classIdPoint.x;
//将每个anchor坐标按缩放比例映射到原图
float cx = pdata[0] * ratiow;
float cy = pdata[1] * ratioh;
float w = pdata[2] * ratiow;
float h = pdata[3] * ratioh;
//获取anchor的左上角坐标
int left = int(cx - 0.5 * w);
int top = int(cy - 0.5 * h);
confidences.push_back((float)maxClassScore);
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(left, top, (int)(w), (int)(h)));
classIds.push_back(classIdx);
}
}
rowInd++;
pdata += numOut;
}
...
}
```
为了消除重叠锚框,输出最终的YOLOV3目标检测结果,执行非极大值抑制对筛选之后的anchor进行处理,最后保存检测结果到resultsOfDetection中。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV3::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
//执行non maximum suppression消除冗余重叠boxes
std::vector indices;
dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, yolov3Parameter.confidenceThreshold, yolov3Parameter.nmsThreshold, indices);
for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i)
{
int idx = indices[i];
int classID=classIds[idx];
string className=classNames[classID];
float confidence=confidences[idx];
cv::Rect box = boxes[idx];、
//保存每个最终预测anchor的坐标值、置信度分数、类别ID
ResultOfDetection result;
result.boundingBox=box;
result.confidence=confidence;// confidence
result.classID=classID; // label
result.className=className;
resultsOfDetection.push_back(result);
}
...
}
```
### 运行示例
根据samples工程中的README.md构建成功C++ samples后,在build目录下输入如下命令运行该示例:
```
./MIGraphX_Samples 4
```
会在当前目录生成检测结果图像Result.jpg。

## YOLOV5检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV5是一种单阶段目标检测算法,该算法在YOLOV4的基础上添加了一些新的改进思路,使其速度与精度都得到了极大的性能提升。具体包括:输入端的Mosaic数据增强、自适应锚框计算、自适应图片缩放操作;主干网络的Focus结构与CSP结构;Neck端的FPN+PAN结构;输出端的损失函数GIOU_Loss以及预测框筛选的DIOU_nms。网络结构如图所示。

YOLOV5的官方源码地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5, 官方源码中具有YOLOV5n、YOLOV5s、YOLOV5m、YOLOV5l等不同的版本。本示例采用YOLOV5s版本进行MIGraphX推理示例构建,下载YOLOV5s的预训练模型yolov5s.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV5工程的weights目录。
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV5源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov5s.pt预训练模型转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV5工程根目录
cd
# 环境配置,torch、torchvision手动安装
pip install -r requirement.txt
# 转换模型
python export.py --weights ./weights/yolov5s.pt --imgsz 608 608 --include onnx
```
注意:官方源码提供的模型转换的程序中包含更多的功能,例如动态shape模型的导出,可根据需要进行添加相关参数。
### 检测器参数设置
samples工程中的Resource/Configuration.xml文件的DetectorYOLOV5节点表示YOLOV5检测器的参数,相关参数主要依据官方推理示例进行设置。各个参数含义如下:
- ModelPath:yolov5模型存放路径
- ClassNameFile:coco数据集类别文件存放路径
- UseFP16:是否使用FP16推理模式
- NumberOfClasses:检测类别数量
- ConfidenceThreshold:置信度阈值,用于判断anchor内的物体是否为正样本
- NMSThreshold:非极大值抑制阈值,用于消除重复框
- ObjectThreshold:用于判断anchor内部是否有物体
```
"../Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV5/YOLOV5s.onnx"
"../Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV5/coco.names"
0
80
0.25
0.5
0.5
```
### 模型初始化
模型初始化首先通过parse_onnx()函数加载YOLOV5的onnx模型,并可以通过program的get_parameter_shapes()函数获取网络的输入属性。完成模型加载之后需要使用compile()方法编译模型,编译模式使用migraphx::gpu::target{}设为GPU模式,编译过程主要基于MIGraphX IR完成各种优化。同时如果需要使用低精度量化进行推理,可以使用quantize_fp16()函数实现。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV5::Initialize(InitializationParameterOfDetector initializationParameterOfDetector)
{
...
//模型加载
net = migraphx::parse_onnx(modelPath);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to load model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
// 获取模型输入属性
std::pair inputAttribute=*(net.get_parameter_shapes().begin());
inputName=inputAttribute.first;
inputShape=inputAttribute.second;
inputSize=cv::Size(inputShape.lens()[3],inputShape.lens()[2]);// NCHW
// 设置模型为GPU模式
migraphx::target gpuTarget = migraphx::gpu::target{};
// 量化
if(useFP16)
{
migraphx::quantize_fp16(net);
}
// 编译模型
migraphx::compile_options options;
options.device_id=0; // 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备(>=1.2版本中支持)
options.offload_copy=true; // 设置offload_copy
net.compile(gpuTarget,options);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to compile model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
...
}
```
### 模型推理
#### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
1. 转换数据排布为NCHW
2. 归一化[0.0, 1.0]
3. 将输入数据的尺寸变换到YOLOV5输入大小(1,3,608,608)
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV5::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 预处理并转换为NCHW
cv::Mat inputBlob;
blobFromImage(srcImage, // 输入数据
inputBlob, // 输出数据
1 / 255.0, //归一化
inputSize, //YOLOV5输入尺寸,本示例为608x608
Scalar(0, 0, 0), //未减去均值
true, //转换RB通道
false);
...
}
```
#### 前向推理
完成图像预处理以及YOLOV5目标检测相关参数设置之后开始执行推理,利用migraphx推理计算得到YOLOV5模型的输出。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV5::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector inferenceResults = net.eval(inputData);
// 获取推理结果
std::vector outs;
migraphx::argument result = inferenceResults[0];
// 转换为cv::Mat
migraphx::shape outputShape = result.get_shape();
int shape[]={outputShape.lens()[0],outputShape.lens()[1],outputShape.lens()[2]};
cv::Mat out(3,shape,CV_32F);
memcpy(out.data,result.data(),sizeof(float)*outputShape.elements());
outs.push_back(out);
...
}
```
YOLOV5的MIGraphX推理结果inferenceResults是一个std::vector< migraphx::argument >类型,YOLOV5的onnx模型包含一个输出,所以result等于inferenceResults[0],result包含三个维度:outputShape.lens()[0]=1表示batch信息,outputShape.lens()[1]=22743表示生成anchor数量,outputShape.lens()[2]=85表示对每个anchor的预测信息。同时可将85拆分为4+1+80,前4个参数用于判断每一个特征点的回归参数,回归参数调整后可以获得预测框,第5个参数用于判断每一个特征点是否包含物体,最后80个参数用于判断每一个特征点所包含的物体种类。获取上述信息之后进行anchors筛选,筛选过程分为两个步骤:
- 第一步根据objectThreshold阈值进行筛选,大于该阈值则判断当前anchor内包含物体,小于该阈值则判断无物体
- 第二步根据confidenceThreshold阈值进行筛选,当满足第一步阈值anchor的最大置信度得分maxClassScore大于该阈值,则进一步获取当前anchor的坐标信息和预测物体类别信息,小于该阈值则不做处理。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV5::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
//获取先验框的个数numProposal=22743
numProposal = outs[0].size[1];
//每个anchor的预测信息数量numOut=85
numOut = outs[0].size[2];
outs[0] = outs[0].reshape(0, numProposal);
std::vector confidences;
std::vector boxes;
std::vector classIds;
//原图尺寸与模型输入尺寸的缩放比例
float ratioh = (float)srcImage.rows / inputSize.height, ratiow = (float)srcImage.cols / inputSize.width;
//计算cx,cy,w,h,box_sore,class_sore
int n = 0, rowInd = 0;
float* pdata = (float*)outs[0].data;
for (n = 0; n < numProposal; n++)
{
//获取当前anchor是否包含物体的概率值
float boxScores = pdata[4];
//第一次筛选,判断anchor内是否包含物体
if (boxScores > yolov5Parameter.objectThreshold)
{
//获取每个anchor内部预测的80个类别概率信息
cv::Mat scores = outs[0].row(rowInd).colRange(5, numOut);
cv::Point classIdPoint;
double maxClassScore;
//获取80个类别中最大概率值和对应的类别ID
cv::minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &maxClassScore, 0, &classIdPoint);
maxClassScore *= boxScores;
//第二次筛选,判断当前anchor的最大置信度得分是否满足阈值
if (maxClassScore > yolov5Parameter.confidenceThreshold)
{
const int classIdx = classIdPoint.x;
//将每个anchor坐标按缩放比例映射到原图
float cx = pdata[0] * ratiow;
float cy = pdata[1] * ratioh;
float w = pdata[2] * ratiow;
float h = pdata[3] * ratioh;
//获取anchor的左上角坐标
int left = int(cx - 0.5 * w);
int top = int(cy - 0.5 * h);
confidences.push_back((float)maxClassScore);
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(left, top, (int)(w), (int)(h)));
classIds.push_back(classIdx);
}
}
rowInd++;
pdata += numOut;
}
...
}
```
为了消除重叠锚框,输出最终的YOLOV5目标检测结果,执行非极大值抑制对筛选之后的anchor进行处理,最后保存检测结果到resultsOfDetection中。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV5::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 执行non maximum suppression消除冗余重叠boxes
std::vector indices;
dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, yolov5Parameter.confidenceThreshold, yolov5Parameter.nmsThreshold, indices);
for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i)
{
int idx = indices[i];
int classID=classIds[idx];
string className=classNames[classID];
float confidence=confidences[idx];
cv::Rect box = boxes[idx];
//保存每个最终预测anchor的坐标值、置信度分数、类别ID
ResultOfDetection result;
result.boundingBox=box;
result.confidence=confidence;// confidence
result.classID=classID; // label
result.className=className;
resultsOfDetection.push_back(result);
}
...
}
```
### 运行示例
根据samples工程中的README.md构建成功C++ samples后,在build目录下输入如下命令运行该示例:
```
./MIGraphX_Samples 5
```
会在当前目录生成检测结果图像Result.jpg。
本示例采用如下的开源实现:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3, 作者在V9.6.0版本中提供多种不同的YOLOV3预训练模型,其中包括yolov3、yolov3-fixed、yolov3-spp、yolov3-tiny四个版本。本示例选择yolov3-tiny.pt预训练模型进行构建MIGraphX推理,下载YOLOV3的预训练模型yolov3-tiny.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV3工程的weights目录。
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV3源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov3-tiny.pt转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV3工程根目录
cd
# 环境配置,torch、torchvision手动安装
pip install -r requirements.txt
# 导出onnx模型
python export.py --weights yolov3.pt --imgsz 416 416 --include onnx
```
注意:官方源码提供的模型转换的程序中包含更多的功能,例如动态shape模型的导出,可根据需要进行添加相关参数。
### 检测器参数设置
samples工程中的Resource/Configuration.xml文件的DetectorYOLOV3节点表示YOLOV3检测器的参数,相关参数主要依据官方推理示例进行设置。各个参数含义如下:
- ModelPath:yolov3模型存放路径
- ClassNameFile:coco数据集类别文件存放路径
- UseFP16:是否使用FP16推理模式
- NumberOfClasses:检测类别数量
- ConfidenceThreshold:置信度阈值,用于判断anchor内的物体是否为正样本
- NMSThreshold:非极大值抑制阈值,用于消除重复框
- ObjectThreshold:用于判断anchor内部是否有物体
```
"../Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV3/yolov3-tiny.onnx"
"../Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV3/coco.names"
0
80
0.2
0.4
0.4
```
### 模型初始化
模型初始化首先通过parse_onnx()函数加载YOLOV3的onnx模型,并可以通过program的get_parameter_shapes()函数获取网络的输入属性。完成模型加载之后需要使用compile()方法编译模型,编译模式使用migraphx::gpu::target{}设为GPU模式,编译过程主要基于MIGraphX IR完成各种优化。同时如果需要使用低精度量化进行推理,可以使用quantize_fp16()函数实现。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV3::Initialize(InitializationParameterOfDetector initializationParameterOfDetector)
{
...
//模型加载
net = migraphx::parse_onnx(modelPath);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to load model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
// 获取模型输入属性
std::pair inputAttribute=*(net.get_parameter_shapes().begin());
inputName=inputAttribute.first;
inputShape=inputAttribute.second;
inputSize=cv::Size(inputShape.lens()[3],inputShape.lens()[2]);// NCHW
// 设置模型为GPU模式
migraphx::target gpuTarget = migraphx::gpu::target{};
// 量化
if(useFP16)
{
migraphx::quantize_fp16(net);
}
// 编译模型
migraphx::compile_options options;
options.device_id=0; // 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备(>=1.2版本中支持)
options.offload_copy=true; // 设置offload_copy
net.compile(gpuTarget,options);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to compile model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
...
}
```
### 模型推理
#### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
- 转换数据排布为NCHW
- 归一化[0.0, 1.0]
- 将输入数据的尺寸变换到YOLOV3输入大小(1,3,416,416)
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV3::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 预处理并转换为NCHW
cv::Mat inputBlob;
blobFromImage(srcImage, // 输入数据
inputBlob, // 输出数据
1 / 255.0, //归一化
inputSize, //YOLOV3输入尺寸,本示例为416x416
Scalar(0, 0, 0), //未减去均值
true, //转换RB通道
false);
...
}
```
#### 前向推理
完成图像预处理以及YOLOV3目标检测相关参数设置之后开始执行推理,利用migraphx推理计算得到YOLOV3模型的输出数据。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV3::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector inferenceResults = net.eval(inputData);
// 获取推理结果
std::vector outs;
migraphx::argument result = inferenceResults[0];
// 转换为cv::Mat
migraphx::shape outputShape = result.get_shape();
int shape[]={outputShape.lens()[0],outputShape.lens()[1],outputShape.lens()[2]};
cv::Mat out(3,shape,CV_32F);
memcpy(out.data,result.data(),sizeof(float)*outputShape.elements());
outs.push_back(out);
...
}
```
YOLOV3的MIGraphX推理结果inferenceResults是一个std::vector< migraphx::argument >类型,YOLOV3的onnx模型包含一个输出,所以result等于inferenceResults[0],result包含三个维度:outputShape.lens()[0]=1表示batch信息,outputShape.lens()[1]=10647表示生成anchor数量,outputShape.lens()[2]=85表示对每个anchor的预测信息。同时可将85拆分为4+1+80,前4个参数用于判断每一个特征点的回归参数,回归参数调整后可以获得预测框,第5个参数用于判断每一个特征点是否包含物体,最后80个参数用于判断每一个特征点所包含的物体种类。获取上述信息之后进行anchors筛选,筛选过程分为两个步骤:
- 第一步根据objectThreshold阈值进行筛选,大于该阈值则判断当前anchor内包含物体,小于该阈值则判断无物体;
- 第二步根据confidenceThreshold阈值进行筛选,当满足第一步阈值anchor的最大置信度得分maxClassScore大于该阈值,则进一步获取当前anchor的坐标信息和预测物体类别信息,小于该阈值则不做处理。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV3::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
//获取先验框的个数numProposal=10647
int numProposal = outs[0].size[1];
//获取每个anchor的预测信息数量numOut=85
int numOut = outs[0].size[2];
//变换输出的维度
outs[0] = outs[0].reshape(0, numProposal);
//生成先验框
std::vector confidences;
std::vector boxes;
std::vector classIds;
//原图尺寸与模型输入尺寸的缩放比例
float ratioh = (float)srcImage.rows / inputSize.height, ratiow = (float)srcImage.cols / inputSize.width;
//计算cx,cy,w,h,box_sore,class_sore
int n = 0, rowInd = 0;
float* pdata = (float*)outs[0].data;
for (n = 0; n < numProposal; n++)
{
//获取当前anchor是否包含物体的概率值
float boxScores = pdata[4];
//第一次筛选,判断anchor内是否包含物体
if (boxScores > yolov3Parameter.objectThreshold)
{
//获取每个anchor内部预测的80个类别概率信息
cv::Mat scores = outs[0].row(rowInd).colRange(5, numOut);
cv::Point classIdPoint;
double maxClassScore;
/获取80个类别中最大概率值和对应的类别ID
cv::minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &maxClassScore, 0, &classIdPoint);
maxClassScore *= boxScores;
//第二次筛选,判断当前anchor的最大置信度得分是否满足阈值
if (maxClassScore > yolov3Parameter.confidenceThreshold)
{
const int classIdx = classIdPoint.x;
//将每个anchor坐标按缩放比例映射到原图
float cx = pdata[0] * ratiow;
float cy = pdata[1] * ratioh;
float w = pdata[2] * ratiow;
float h = pdata[3] * ratioh;
//获取anchor的左上角坐标
int left = int(cx - 0.5 * w);
int top = int(cy - 0.5 * h);
confidences.push_back((float)maxClassScore);
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(left, top, (int)(w), (int)(h)));
classIds.push_back(classIdx);
}
}
rowInd++;
pdata += numOut;
}
...
}
```
为了消除重叠锚框,输出最终的YOLOV3目标检测结果,执行非极大值抑制对筛选之后的anchor进行处理,最后保存检测结果到resultsOfDetection中。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV3::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
//执行non maximum suppression消除冗余重叠boxes
std::vector indices;
dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, yolov3Parameter.confidenceThreshold, yolov3Parameter.nmsThreshold, indices);
for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i)
{
int idx = indices[i];
int classID=classIds[idx];
string className=classNames[classID];
float confidence=confidences[idx];
cv::Rect box = boxes[idx];、
//保存每个最终预测anchor的坐标值、置信度分数、类别ID
ResultOfDetection result;
result.boundingBox=box;
result.confidence=confidence;// confidence
result.classID=classID; // label
result.className=className;
resultsOfDetection.push_back(result);
}
...
}
```
### 运行示例
根据samples工程中的README.md构建成功C++ samples后,在build目录下输入如下命令运行该示例:
```
./MIGraphX_Samples 4
```
会在当前目录生成检测结果图像Result.jpg。

## YOLOV5检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV5是一种单阶段目标检测算法,该算法在YOLOV4的基础上添加了一些新的改进思路,使其速度与精度都得到了极大的性能提升。具体包括:输入端的Mosaic数据增强、自适应锚框计算、自适应图片缩放操作;主干网络的Focus结构与CSP结构;Neck端的FPN+PAN结构;输出端的损失函数GIOU_Loss以及预测框筛选的DIOU_nms。网络结构如图所示。

YOLOV5的官方源码地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5, 官方源码中具有YOLOV5n、YOLOV5s、YOLOV5m、YOLOV5l等不同的版本。本示例采用YOLOV5s版本进行MIGraphX推理示例构建,下载YOLOV5s的预训练模型yolov5s.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV5工程的weights目录。
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV5源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov5s.pt预训练模型转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV5工程根目录
cd
# 环境配置,torch、torchvision手动安装
pip install -r requirement.txt
# 转换模型
python export.py --weights ./weights/yolov5s.pt --imgsz 608 608 --include onnx
```
注意:官方源码提供的模型转换的程序中包含更多的功能,例如动态shape模型的导出,可根据需要进行添加相关参数。
### 检测器参数设置
samples工程中的Resource/Configuration.xml文件的DetectorYOLOV5节点表示YOLOV5检测器的参数,相关参数主要依据官方推理示例进行设置。各个参数含义如下:
- ModelPath:yolov5模型存放路径
- ClassNameFile:coco数据集类别文件存放路径
- UseFP16:是否使用FP16推理模式
- NumberOfClasses:检测类别数量
- ConfidenceThreshold:置信度阈值,用于判断anchor内的物体是否为正样本
- NMSThreshold:非极大值抑制阈值,用于消除重复框
- ObjectThreshold:用于判断anchor内部是否有物体
```
"../Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV5/YOLOV5s.onnx"
"../Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV5/coco.names"
0
80
0.25
0.5
0.5
```
### 模型初始化
模型初始化首先通过parse_onnx()函数加载YOLOV5的onnx模型,并可以通过program的get_parameter_shapes()函数获取网络的输入属性。完成模型加载之后需要使用compile()方法编译模型,编译模式使用migraphx::gpu::target{}设为GPU模式,编译过程主要基于MIGraphX IR完成各种优化。同时如果需要使用低精度量化进行推理,可以使用quantize_fp16()函数实现。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV5::Initialize(InitializationParameterOfDetector initializationParameterOfDetector)
{
...
//模型加载
net = migraphx::parse_onnx(modelPath);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to load model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
// 获取模型输入属性
std::pair inputAttribute=*(net.get_parameter_shapes().begin());
inputName=inputAttribute.first;
inputShape=inputAttribute.second;
inputSize=cv::Size(inputShape.lens()[3],inputShape.lens()[2]);// NCHW
// 设置模型为GPU模式
migraphx::target gpuTarget = migraphx::gpu::target{};
// 量化
if(useFP16)
{
migraphx::quantize_fp16(net);
}
// 编译模型
migraphx::compile_options options;
options.device_id=0; // 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备(>=1.2版本中支持)
options.offload_copy=true; // 设置offload_copy
net.compile(gpuTarget,options);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to compile model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
...
}
```
### 模型推理
#### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
1. 转换数据排布为NCHW
2. 归一化[0.0, 1.0]
3. 将输入数据的尺寸变换到YOLOV5输入大小(1,3,608,608)
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV5::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 预处理并转换为NCHW
cv::Mat inputBlob;
blobFromImage(srcImage, // 输入数据
inputBlob, // 输出数据
1 / 255.0, //归一化
inputSize, //YOLOV5输入尺寸,本示例为608x608
Scalar(0, 0, 0), //未减去均值
true, //转换RB通道
false);
...
}
```
#### 前向推理
完成图像预处理以及YOLOV5目标检测相关参数设置之后开始执行推理,利用migraphx推理计算得到YOLOV5模型的输出。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV5::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector inferenceResults = net.eval(inputData);
// 获取推理结果
std::vector outs;
migraphx::argument result = inferenceResults[0];
// 转换为cv::Mat
migraphx::shape outputShape = result.get_shape();
int shape[]={outputShape.lens()[0],outputShape.lens()[1],outputShape.lens()[2]};
cv::Mat out(3,shape,CV_32F);
memcpy(out.data,result.data(),sizeof(float)*outputShape.elements());
outs.push_back(out);
...
}
```
YOLOV5的MIGraphX推理结果inferenceResults是一个std::vector< migraphx::argument >类型,YOLOV5的onnx模型包含一个输出,所以result等于inferenceResults[0],result包含三个维度:outputShape.lens()[0]=1表示batch信息,outputShape.lens()[1]=22743表示生成anchor数量,outputShape.lens()[2]=85表示对每个anchor的预测信息。同时可将85拆分为4+1+80,前4个参数用于判断每一个特征点的回归参数,回归参数调整后可以获得预测框,第5个参数用于判断每一个特征点是否包含物体,最后80个参数用于判断每一个特征点所包含的物体种类。获取上述信息之后进行anchors筛选,筛选过程分为两个步骤:
- 第一步根据objectThreshold阈值进行筛选,大于该阈值则判断当前anchor内包含物体,小于该阈值则判断无物体
- 第二步根据confidenceThreshold阈值进行筛选,当满足第一步阈值anchor的最大置信度得分maxClassScore大于该阈值,则进一步获取当前anchor的坐标信息和预测物体类别信息,小于该阈值则不做处理。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV5::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
//获取先验框的个数numProposal=22743
numProposal = outs[0].size[1];
//每个anchor的预测信息数量numOut=85
numOut = outs[0].size[2];
outs[0] = outs[0].reshape(0, numProposal);
std::vector confidences;
std::vector boxes;
std::vector classIds;
//原图尺寸与模型输入尺寸的缩放比例
float ratioh = (float)srcImage.rows / inputSize.height, ratiow = (float)srcImage.cols / inputSize.width;
//计算cx,cy,w,h,box_sore,class_sore
int n = 0, rowInd = 0;
float* pdata = (float*)outs[0].data;
for (n = 0; n < numProposal; n++)
{
//获取当前anchor是否包含物体的概率值
float boxScores = pdata[4];
//第一次筛选,判断anchor内是否包含物体
if (boxScores > yolov5Parameter.objectThreshold)
{
//获取每个anchor内部预测的80个类别概率信息
cv::Mat scores = outs[0].row(rowInd).colRange(5, numOut);
cv::Point classIdPoint;
double maxClassScore;
//获取80个类别中最大概率值和对应的类别ID
cv::minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &maxClassScore, 0, &classIdPoint);
maxClassScore *= boxScores;
//第二次筛选,判断当前anchor的最大置信度得分是否满足阈值
if (maxClassScore > yolov5Parameter.confidenceThreshold)
{
const int classIdx = classIdPoint.x;
//将每个anchor坐标按缩放比例映射到原图
float cx = pdata[0] * ratiow;
float cy = pdata[1] * ratioh;
float w = pdata[2] * ratiow;
float h = pdata[3] * ratioh;
//获取anchor的左上角坐标
int left = int(cx - 0.5 * w);
int top = int(cy - 0.5 * h);
confidences.push_back((float)maxClassScore);
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(left, top, (int)(w), (int)(h)));
classIds.push_back(classIdx);
}
}
rowInd++;
pdata += numOut;
}
...
}
```
为了消除重叠锚框,输出最终的YOLOV5目标检测结果,执行非极大值抑制对筛选之后的anchor进行处理,最后保存检测结果到resultsOfDetection中。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV5::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 执行non maximum suppression消除冗余重叠boxes
std::vector indices;
dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, yolov5Parameter.confidenceThreshold, yolov5Parameter.nmsThreshold, indices);
for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i)
{
int idx = indices[i];
int classID=classIds[idx];
string className=classNames[classID];
float confidence=confidences[idx];
cv::Rect box = boxes[idx];
//保存每个最终预测anchor的坐标值、置信度分数、类别ID
ResultOfDetection result;
result.boundingBox=box;
result.confidence=confidence;// confidence
result.classID=classID; // label
result.className=className;
resultsOfDetection.push_back(result);
}
...
}
```
### 运行示例
根据samples工程中的README.md构建成功C++ samples后,在build目录下输入如下命令运行该示例:
```
./MIGraphX_Samples 5
```
会在当前目录生成检测结果图像Result.jpg。
 ## YOLOV7检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV7是2022年最新出现的一种YOLO系列目标检测模型,在论文 [YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.02696)中提出。
## YOLOV7检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV7是2022年最新出现的一种YOLO系列目标检测模型,在论文 [YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.02696)中提出。
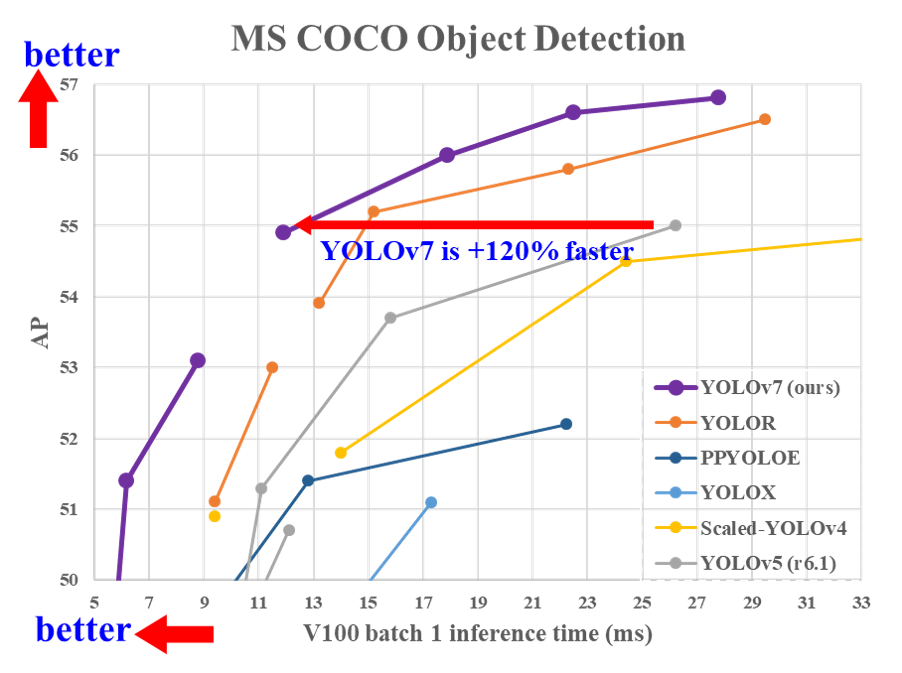 本示例采用YOLOv7的官方源码:https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7, 作者提供了多个预训练模型,本示例使用yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型,将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型下载下来后,保存到Pytorch_YOLOV7工程的weights目录。
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV7源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV7工程根目录
cd
# 安装程序运行的依赖,torch、torchvision需要手动安装
pip install -r requirement.txt
# 转换模型
python export.py --weights ./weight/yolov7-tiny.pt --img-size 640 640
```
注意:如果需要修改onnx模型的输入大小,可以调整--img-size参数,同时模型输入batch默认为1,若想修改可以通过添加--batch-size设置,程序运行结束后,在当前目录下会生成onnx格式的YOLOV7模型,并将该模型保存到了samples工程中的Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV7目录中,可以用来MIGraphX加载推理。
### 检测器参数设置
samples工程中的Resource/Configuration.xml文件的DetectorYOLOV7节点表示YOLOV7检测器的参数,相关参数主要依据官方推理示例进行设置。其中包括模型存放路径、类别名称文件、检测类别数量、置信度阈值、非极大值抑制阈值和判断先验框是否有物体阈值。
- ModelPath:yolov7模型存放路径
- ClassNameFile:coco数据集类别文件存放路径
- UseFP16:是否使用FP16推理模式
- NumberOfClasses:检测类别数量
- ConfidenceThreshold:置信度阈值,用于判断anchor内的物体是否为正样本
- NMSThreshold:非极大值抑制阈值,用于消除重复框
- ObjectThreshold:用于判断anchor内部是否有物体
```
"../Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV7/yolov7-tiny.onnx"
"../Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV7/coco.names"
0
80
0.25
0.5
0.5
```
### 模型初始化
模型初始化首先通过parse_onnx()函数加载YOLOV7的onnx模型,并可以通过program的get_parameter_shapes()函数获取网络的输入属性。完成模型加载之后需要使用compile()方法编译模型,编译模式使用migraphx::gpu::target{}设为GPU模式,编译过程主要基于MIGraphX IR完成各种优化。同时如果需要使用低精度量化进行推理,可以使用quantize_fp16()函数实现。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV7::Initialize(InitializationParameterOfDetector initializationParameterOfDetector)
{
...
//模型加载
net = migraphx::parse_onnx(modelPath);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to load model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
// 获取模型输入属性
std::pair inputAttribute=*(net.get_parameter_shapes().begin());
inputName=inputAttribute.first;
inputShape=inputAttribute.second;
inputSize=cv::Size(inputShape.lens()[3],inputShape.lens()[2]);// NCHW
// 设置模型为GPU模式
migraphx::target gpuTarget = migraphx::gpu::target{};
// 量化
if(useFP16)
{
migraphx::quantize_fp16(net);
}
// 编译模型
migraphx::compile_options options;
options.device_id=0; // 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备(>=1.2版本中支持)
options.offload_copy=true; // 设置offload_copy
net.compile(gpuTarget,options);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to compile model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
...
}
```
### 模型推理
#### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
- 转换数据排布为NCHW
- 归一化到[0.0, 1.0]
- 将输入数据的尺寸变换到YOLOV7输入大小(1,3,640,640)
```c++
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV7::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 预处理并转换为NCHW
cv::Mat inputBlob;
blobFromImage(srcImage, //输入数据
inputBlob, //输出数据
1 / 255.0, //缩放系数,这里为1/255.0
inputSize, //YOLOV7输入尺寸(640,640)
Scalar(0, 0, 0), // 均值,这里不需要减均值,所以设置为0.0
true, //转换RB通道
false);
...
}
```
#### 前向推理
完成图像预处理以及yolov7目标检测相关参数设置之后开始执行推理,获取migraphx推理结果。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV7::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector inferenceResults=net.eval(inputData);
// 获取推理结果
std::vector outs;
migraphx::argument result = inferenceResults[0];
// 转换为cv::Mat
migraphx::shape outputShape = result.get_shape();
int shape[]={outputShape.lens()[0],outputShape.lens()[1],outputShape.lens()[2]};
cv::Mat out(4,shape,CV_32F);
memcpy(out.data,result.data(),sizeof(float)*outputShape.elements());
outs.push_back(out);
...
}
```
YOLOV7的MIGraphX推理结果inferenceResults是一个std::vector< migraphx::argument >类型,YOLOV7的onnx模型包含一个输出,所以result等于inferenceResults[0],result包含三个维度:outputShape.lens()[0]=1表示batch信息,outputShape.lens()[1]=25200表示生成anchor数量,outputShape.lens()[2]=85表示对每个anchor的预测信息。同时可将85拆分为4+1+80,前4个参数用于判断每一个特征点的回归参数,回归参数调整后可以获得预测框,第5个参数用于判断每一个特征点是否包含物体,最后80个参数用于判断每一个特征点所包含的物体种类。获取上述信息之后进行anchors筛选,筛选过程分为两个步骤:
- 第一步根据objectThreshold阈值进行筛选,大于该阈值则判断当前anchor内包含物体,小于该阈值则判断无物体
- 第二步根据confidenceThreshold阈值进行筛选,当满足第一步阈值anchor的最大置信度得分maxClassScore大于该阈值,则进一步获取当前anchor内部的物体类别和坐标信息,小于该阈值则不做处理。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV7::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
//获取先验框的个数numProposal=25200
int numProposal = outs[0].size[1];
//每个anchor的预测信息数量numOut=85
int numOut = outs[0].size[2];
outs[0] = outs[0].reshape(0, numProposal);
std::vector confidence;
std::vector boxes
std::vector classIds
//原图尺寸与模型输入尺寸的缩放比例
float ratioh = (float)srcImage.rows / inputSize.height, ratiow = (float)srcImage.cols / inputSize.width;
//计算cx,cy,w,h,box_sore,class_sore
int n = 0, rowInd = 0;
float* pdata = (float*)outs[0].data;
for (n = 0; n < numProposal; n++)
{
//获取是否包含物体的概率值
float boxScores = pdata[4];
//第一次筛选,判断anchor内是否包含物体
if (boxScores > yolov7Parameter.objectThreshold)
{
//获取每个anchor内部预测的80个类别概率信息
cv::Mat scores = outs[0].row(rowInd).colRange(5, numOut);
cv::Point classIdPoint;
double maxClassScore;
//获取80个类别中最大概率值和对应的类别ID
cv::minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &maxClassScore, 0, &classIdPoint);
maxClassScore *= boxScores;
//第二次筛选,判断当前anchor的最大置信度得分是否满足阈值
if (maxClassScore > yolov7Parameter.confidenceThreshold)
{
const int classIdx = classIdPoint.x;
//将每个anchor坐标按缩放比例映射到原图
float cx = pdata[0] * ratiow;
float cy = pdata[1] * ratioh;
float w = pdata[2] * ratiow;
float h = pdata[3] * ratioh;
//获取anchor的左上角坐标
int left = int(cx - 0.5 * w);
int top = int(cy - 0.5 * h);
confidences.push_back((float)maxClassScore);
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(left, top, (int)(w), (int)(h)));
classIds.push_back(classIdx);
}
}
rowInd++;
pdata += numOut;
}
...
}
```
为了消除重叠锚框,输出最终的YOLOV7目标检测结果,执行非极大值抑制对筛选之后的anchor进行处理,最后保存检测结果到resultsOfDetection中。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV7::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
//执行non maximum suppression消除冗余重叠boxes
std::vector indices;
dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, yolov7Parameter.confidenceThreshold, yolov7Parameter.nmsThreshold, indices);
for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i)
{
int idx = indices[i];
int classID=classIds[idx];
string className=classNames[classID];
float confidence=confidences[idx];
cv::Rect box = boxes[idx];
//保存每个最终预测anchor的坐标值、置信度分数、类别ID
ResultOfDetection result;
result.boundingBox=box;
result.confidence=confidence;// confidence
result.classID=classID; // label
result.className=className;
resultsOfDetection.push_back(result);
}
...
}
```
### 运行示例
根据samples工程中的README.md构建成功C++ samples后,在build目录下输入如下命令运行该示例:
```
./MIGraphX_Samples 6
```
会在当前目录生成检测结果图像Result.jpg。
本示例采用YOLOv7的官方源码:https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7, 作者提供了多个预训练模型,本示例使用yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型,将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型下载下来后,保存到Pytorch_YOLOV7工程的weights目录。
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV7源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV7工程根目录
cd
# 安装程序运行的依赖,torch、torchvision需要手动安装
pip install -r requirement.txt
# 转换模型
python export.py --weights ./weight/yolov7-tiny.pt --img-size 640 640
```
注意:如果需要修改onnx模型的输入大小,可以调整--img-size参数,同时模型输入batch默认为1,若想修改可以通过添加--batch-size设置,程序运行结束后,在当前目录下会生成onnx格式的YOLOV7模型,并将该模型保存到了samples工程中的Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV7目录中,可以用来MIGraphX加载推理。
### 检测器参数设置
samples工程中的Resource/Configuration.xml文件的DetectorYOLOV7节点表示YOLOV7检测器的参数,相关参数主要依据官方推理示例进行设置。其中包括模型存放路径、类别名称文件、检测类别数量、置信度阈值、非极大值抑制阈值和判断先验框是否有物体阈值。
- ModelPath:yolov7模型存放路径
- ClassNameFile:coco数据集类别文件存放路径
- UseFP16:是否使用FP16推理模式
- NumberOfClasses:检测类别数量
- ConfidenceThreshold:置信度阈值,用于判断anchor内的物体是否为正样本
- NMSThreshold:非极大值抑制阈值,用于消除重复框
- ObjectThreshold:用于判断anchor内部是否有物体
```
"../Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV7/yolov7-tiny.onnx"
"../Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV7/coco.names"
0
80
0.25
0.5
0.5
```
### 模型初始化
模型初始化首先通过parse_onnx()函数加载YOLOV7的onnx模型,并可以通过program的get_parameter_shapes()函数获取网络的输入属性。完成模型加载之后需要使用compile()方法编译模型,编译模式使用migraphx::gpu::target{}设为GPU模式,编译过程主要基于MIGraphX IR完成各种优化。同时如果需要使用低精度量化进行推理,可以使用quantize_fp16()函数实现。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV7::Initialize(InitializationParameterOfDetector initializationParameterOfDetector)
{
...
//模型加载
net = migraphx::parse_onnx(modelPath);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to load model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
// 获取模型输入属性
std::pair inputAttribute=*(net.get_parameter_shapes().begin());
inputName=inputAttribute.first;
inputShape=inputAttribute.second;
inputSize=cv::Size(inputShape.lens()[3],inputShape.lens()[2]);// NCHW
// 设置模型为GPU模式
migraphx::target gpuTarget = migraphx::gpu::target{};
// 量化
if(useFP16)
{
migraphx::quantize_fp16(net);
}
// 编译模型
migraphx::compile_options options;
options.device_id=0; // 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备(>=1.2版本中支持)
options.offload_copy=true; // 设置offload_copy
net.compile(gpuTarget,options);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to compile model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
...
}
```
### 模型推理
#### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
- 转换数据排布为NCHW
- 归一化到[0.0, 1.0]
- 将输入数据的尺寸变换到YOLOV7输入大小(1,3,640,640)
```c++
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV7::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 预处理并转换为NCHW
cv::Mat inputBlob;
blobFromImage(srcImage, //输入数据
inputBlob, //输出数据
1 / 255.0, //缩放系数,这里为1/255.0
inputSize, //YOLOV7输入尺寸(640,640)
Scalar(0, 0, 0), // 均值,这里不需要减均值,所以设置为0.0
true, //转换RB通道
false);
...
}
```
#### 前向推理
完成图像预处理以及yolov7目标检测相关参数设置之后开始执行推理,获取migraphx推理结果。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV7::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector inferenceResults=net.eval(inputData);
// 获取推理结果
std::vector outs;
migraphx::argument result = inferenceResults[0];
// 转换为cv::Mat
migraphx::shape outputShape = result.get_shape();
int shape[]={outputShape.lens()[0],outputShape.lens()[1],outputShape.lens()[2]};
cv::Mat out(4,shape,CV_32F);
memcpy(out.data,result.data(),sizeof(float)*outputShape.elements());
outs.push_back(out);
...
}
```
YOLOV7的MIGraphX推理结果inferenceResults是一个std::vector< migraphx::argument >类型,YOLOV7的onnx模型包含一个输出,所以result等于inferenceResults[0],result包含三个维度:outputShape.lens()[0]=1表示batch信息,outputShape.lens()[1]=25200表示生成anchor数量,outputShape.lens()[2]=85表示对每个anchor的预测信息。同时可将85拆分为4+1+80,前4个参数用于判断每一个特征点的回归参数,回归参数调整后可以获得预测框,第5个参数用于判断每一个特征点是否包含物体,最后80个参数用于判断每一个特征点所包含的物体种类。获取上述信息之后进行anchors筛选,筛选过程分为两个步骤:
- 第一步根据objectThreshold阈值进行筛选,大于该阈值则判断当前anchor内包含物体,小于该阈值则判断无物体
- 第二步根据confidenceThreshold阈值进行筛选,当满足第一步阈值anchor的最大置信度得分maxClassScore大于该阈值,则进一步获取当前anchor内部的物体类别和坐标信息,小于该阈值则不做处理。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV7::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
//获取先验框的个数numProposal=25200
int numProposal = outs[0].size[1];
//每个anchor的预测信息数量numOut=85
int numOut = outs[0].size[2];
outs[0] = outs[0].reshape(0, numProposal);
std::vector confidence;
std::vector boxes
std::vector classIds
//原图尺寸与模型输入尺寸的缩放比例
float ratioh = (float)srcImage.rows / inputSize.height, ratiow = (float)srcImage.cols / inputSize.width;
//计算cx,cy,w,h,box_sore,class_sore
int n = 0, rowInd = 0;
float* pdata = (float*)outs[0].data;
for (n = 0; n < numProposal; n++)
{
//获取是否包含物体的概率值
float boxScores = pdata[4];
//第一次筛选,判断anchor内是否包含物体
if (boxScores > yolov7Parameter.objectThreshold)
{
//获取每个anchor内部预测的80个类别概率信息
cv::Mat scores = outs[0].row(rowInd).colRange(5, numOut);
cv::Point classIdPoint;
double maxClassScore;
//获取80个类别中最大概率值和对应的类别ID
cv::minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &maxClassScore, 0, &classIdPoint);
maxClassScore *= boxScores;
//第二次筛选,判断当前anchor的最大置信度得分是否满足阈值
if (maxClassScore > yolov7Parameter.confidenceThreshold)
{
const int classIdx = classIdPoint.x;
//将每个anchor坐标按缩放比例映射到原图
float cx = pdata[0] * ratiow;
float cy = pdata[1] * ratioh;
float w = pdata[2] * ratiow;
float h = pdata[3] * ratioh;
//获取anchor的左上角坐标
int left = int(cx - 0.5 * w);
int top = int(cy - 0.5 * h);
confidences.push_back((float)maxClassScore);
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(left, top, (int)(w), (int)(h)));
classIds.push_back(classIdx);
}
}
rowInd++;
pdata += numOut;
}
...
}
```
为了消除重叠锚框,输出最终的YOLOV7目标检测结果,执行非极大值抑制对筛选之后的anchor进行处理,最后保存检测结果到resultsOfDetection中。
```
ErrorCode DetectorYOLOV7::Detect(const cv::Mat &srcImage, std::vector &resultsOfDetection)
{
...
//执行non maximum suppression消除冗余重叠boxes
std::vector indices;
dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, yolov7Parameter.confidenceThreshold, yolov7Parameter.nmsThreshold, indices);
for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i)
{
int idx = indices[i];
int classID=classIds[idx];
string className=classNames[classID];
float confidence=confidences[idx];
cv::Rect box = boxes[idx];
//保存每个最终预测anchor的坐标值、置信度分数、类别ID
ResultOfDetection result;
result.boundingBox=box;
result.confidence=confidence;// confidence
result.classID=classID; // label
result.className=className;
resultsOfDetection.push_back(result);
}
...
}
```
### 运行示例
根据samples工程中的README.md构建成功C++ samples后,在build目录下输入如下命令运行该示例:
```
./MIGraphX_Samples 6
```
会在当前目录生成检测结果图像Result.jpg。
 ## 图像分割
本示例采用了经典的Unet模型进行图像分割,模型下载地址:https://www.dropbox.com/s/3ntkhyk30x05uuv/unet_13_256.onnx,将unet_13_256.onnx文件保存在Resource\Models\Segmentation文件夹下。模型结构如下图所示(可以通过netron工具(https://netron.app/)查看具体的模型结构),该模型的输入shape为[batch_size,3,256,256],输出shape为[batch_size,1,256,256],数据排布为NCHW。

### 参数设置
samples工程中的Resource/Configuration.xml文件的Unet节点表示图像分割模型Unet的参数,主要包括模型存放路径。
```xml
"../Resource/Models/Segmentation/unet_13_256.onnx"
```
### 模型初始化
首先,通过parse_onnx()函数加载图像分割Unet的onnx模型,并可以通过program的get_parameter_shapes()函数获取网络的输入属性。完成模型加载之后需要使用compile()方法编译模型,编译模式使用migraphx::gpu::target{}设为GPU模式,编译过程主要基于MIGraphX IR完成各种优化。
```C++
ErrorCode Unet::Initialize(InitializationParameterOfSegmentation initParamOfSegmentationUnet)
{
...
// 加载模型
net = migraphx::parse_onnx(modelPath); // 根据提供的模型地址,去加载模型文件
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to load model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
// 获取模型输入属性
std::pair inputAttribute=*(net.get_parameter_shapes().begin());
inputName=inputAttribute.first;
inputShape=inputAttribute.second;
inputSize=cv::Size(inputShape.lens()[3],inputShape.lens()[2]);
// 设置模型为GPU模式
migraphx::target gpuTarget = migraphx::gpu::target{};
// 编译模型
migraphx::compile_options options;
options.device_id=0; // 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备(>=1.2版本中支持)
options.offload_copy=true; // 设置offload_copy
net.compile(gpuTarget,options);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to compile model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
...
}
```
### 预处理
完成模型初始化之后,需要将输入数据进行如下预处理:
1.尺度变换,将图像resize到256x256大小
2.归一化,将数据归一化到[0.0, 1.0]之间
3.数据排布,将数据从HWC转换为NCHW
本示例代码主要通过opencv实现预处理操作:
```C++
ErrorCode Unet::Segmentation(const cv::Mat &srcImage, cv::Mat &maskImage)
{
...
// 图像预处理,将图像resize到(256x256)大小,并转换为NCHW
cv::Mat inputBlob;
cv::dnn::blobFromImage(srcImage, // 输入数据,支持多张图像
inputBlob, // 输出数据
1 / 255.0, // 缩放系数
inputSize, // 模型输入大小,这里为256x256
Scalar(0, 0, 0), // 均值,这里不需要减均值,所以设置为0
true, // 通道转换,B通道与R通道互换,所以为true
false);
...
}
```
1.cv::dnn::blobFromImage()函数支持多个输入图像,首先将输入图像resize到inputSize大小,然后减去均值,其次乘以缩放系数1/255.0并转换为NCHW,最终将转换好的数据保存到inputBlob作为输入数据执行推理。
### 推理
完成图像预处理后,就可以执行推理,得到推理结果。
```c++
ErrorCode Unet::Segmentation(const cv::Mat &srcImage, cv::Mat &maskImage)
{
...
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector results = net.eval(inputData);
// 获取输出节点的属性
migraphx::argument result = results[0]; // 获取第一个输出节点的数据
migraphx::shape outputShape=result.get_shape(); // 输出节点的shape
std::vector outputSize=outputShape.lens(); // 每一维大小,维度顺序为(N,C,H,W)
int numberOfOutput=outputShape.elements(); // 输出节点元素的个数
float *data = (float *)result.data(); // 输出节点数据指针
// 计算sigmoid值,并且当大于0.996时,值为1,当小于0.996时,值为0,存储在value_mask[]数组中
int value_mask[numberOfOutput];
for(int i=0; i 0.996)
{
value_mask[i] = 1;
}
else
{
value_mask[i] = 0;
}
}
// 将对应的value_mask[]数组中的值依次赋值到outputImage对应位置处
cv::Mat outputImage = cv::Mat_(Size(outputShape.lens()[3], outputShape.lens()[2]), CV_32S);
for(int i=0;i(i,j)=value_mask[256*i+j]; // 其中,256代表了outputShape.lens()[3]的值
}
}
// 将32S格式的数据转换为8U格式的数据
outputImage.convertTo(maskImage, CV_8U, 255.0);
...
}
```
1.inputData表示MIGraphX的输入数据,这里表示为图像数据,inputName表示输入节点名,migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data}表示该节点名对应的数据,这里是通过前面预处理的数据inputBlob来创建的,第一个参数表示数据的shape,第二个参数表示数据指针。
2.net.eval(inputData)返回模型的推理结果,由于这里只有一个输出节点,所以std::vector中只有一个数据,results[0]表示第一个输出节点,获取输出数据之后,就可以对输出数据执行相关后处理操作。
3.模型得到的推理结果并不能直接作为分割结果。首先,对推理结果计算sigmoid值,当计算值大于0.996时值为1,小于等于0.996时值为0,保存在数组value_mask中。其次,创建一个cv::Mat将value_mask数组中的值按行依次赋值到对应的位置。最后,将32S格式的数据转换为8U格式的数据,对应位置乘以255,得到最终的分割图像。
注:本次采用的模型权重onnx文件是通过使用具有普通背景的汽车图像来训练的。因此,“现实世界“图像的分割结果不完美是意料之中的。为了获得更好的结果,建议对现实世界示例数据集上的模型进行微调。
### 运行示例
根据samples工程中的README.md构建成功C++ samples后,在build目录下输入如下命令运行该示例:
```c++
./ MIGraphX_Samples 8
```
会在当前目录中生成分割结果图像Result.jpg
输出结果为:

## 超分辨率重建
### 模型简介
图像超分辨率重建技术是指设计并采用某种算法,使得可以通过观测到的低分辨率(Low Resolution, LR)图像重建出近似真实高分辨率(High Resolution , HR)图像的方法。本次部署的超分辨率模型是2016提出的ESPCN网络,主要通过一系列卷积层不断提取图像特征,最后通过sub-pixel亚像素卷积层提高图像分辨率,从而实现图像超分辨率的方法。ESPCN网络结构如下图所示

本示例采用onnx官方提供的ESPCN模型示例:https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/main/vision/super_resolution/sub_pixel_cnn_2016,将super.onnx文件保存在Resource\Models\Super_Resolution文件夹下。
### 参数设置
samples工程中的Resource/Configuration.xml文件的Espcn节点表示超分辨率模型Espcn的参数,主要包括模型存放路径。
```xml
"../Resource/Models/Super_Resolution/super.onnx"
```
### 模型初始化
首先,通过parse_onnx()函数加载图像超分辨率ESPCN的onnx模型,并可以通过program的get_parameter_shapes()函数获取网络的输入属性。完成模型加载之后需要使用compile()方法编译模型,编译模式使用migraphx::gpu::target{}设为GPU模式,编译过程主要基于MIGraphX IR完成各种优化。
```C++
ErrorCode Espcn::Initialize(InitializationParameterOfSuperresolution initParamOfSuperresolutionESPCN)
{
...
// 加载模型
net = migraphx::parse_onnx(modelPath); // 根据提供的模型地址,去加载模型文件
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to load model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
// 获取模型输入属性
std::pair inputAttribute=*(net.get_parameter_shapes().begin());
inputName=inputAttribute.first;
inputShape=inputAttribute.second;
inputSize=cv::Size(inputShape.lens()[3],inputShape.lens()[2]);
// 设置模型为GPU模式
migraphx::target gpuTarget = migraphx::gpu::target{};
// 编译模型
migraphx::compile_options options;
options.device_id=0; // 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备(>=1.2版本中支持)
options.offload_copy=true; // 设置offload_copy
net.compile(gpuTarget,options);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to compile model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
...
}
```
### 预处理
完成模型初始化之后,需要将输入数据进行如下预处理:
1.分离图像通道,变为B、G、R三个通道图像;
2.BGR格式通过公式转换为YCbCr格式,得到Y、Cb、Cr三通道图像;
3.Y通道图像resize到224x224,变为浮点型数据,并转换数据排布为NCHW;
本示例代码主要采用如下方式完成预处理操作:
```c++
ErrorCode Espcn::Super(const cv::Mat &srcImage, cv::Mat &superImage)
{
...
// 图像预处理(分离图像通道,只处理Y通道的图像,进行模型推理)
// 分离图像通道
std::vector channels;
cv::split(srcImage, channels); // B通道=channels[0],G通道=channels[1],R通道=channels[2]
// 将BGR格式转换为YCbCr格式,采用opencv官方转换公式
cv::Mat Y_channels = 0.299*channels[2] + 0.587*channels[1] + 0.114*channels[0];
cv::Mat Cb_channels = (channels[0]-Y_channels) * 0.564 + 128;
cv::Mat Cr_channels = (channels[2]-Y_channels) * 0.713 + 128;
// 将Y通道图像resize为224x224,变为浮点型数据,并转换数据排布为NCHW
cv::Mat inputBlob;
cv::dnn::blobFromImage(Y_channels, // 输入数据,支持多张图像
inputBlob, // 输出数据
1/255.0, // 缩放系数
inputSize, // 模型输入大小,这里为672x672
Scalar(0, 0, 0), // 均值,这里不需要减均值,所以设置为0
false, // 通道转换,因为只处理Y通道数据,不需要通道转换,所以设置为false
false);
...
}
```
1.在预处理过程中,重要的是BGR格式转换为YCbCr格式,主要是因为相较于色差,人类视觉对亮度变化更为敏感。因此,在处理的过程中感兴趣的不是颜色变化(存储在 CbCr 通道中的信息),而只是其亮度(Y 通道),所以需要将BGR转换为YCbCr,转换公式采用的是opencv官方提供的公式,链接:https://docs.opencv.org/3.4.11/de/d25/imgproc_color_conversions.html。
2.得到Y通道图像后,需要resize为固定尺寸并转换为NCHW,主要采用cv::dnn::blobFromImage()函数。首先将输入图像resize到inputSize,然后减去均值,其次乘以缩放系数1/255.0并转换为NCHW,最终将转换好的数据保存到inputBlob作为输入数据执行推理。
### 推理
完成图像预处理后,就可以执行推理,得到推理结果。
```C++
ErrorCode Espcn::Super(const cv::Mat &srcImage, cv::Mat &superImage)
{
...
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector results = net.eval(inputData);
// 获取输出节点的属性
migraphx::argument result = results[0]; // 获取第一个输出节点的数据
migraphx::shape outputShape=result.get_shape(); // 输出节点的shape
std::vector outputSize=outputShape.lens(); // 每一维大小,维度顺序为(N,C,H,W)
int numberOfOutput=outputShape.elements(); // 输出节点元素的个数
float *data = (float *)result.data(); // 输出节点数据指针
// 获取推理结果,是重建后每个像素点的像素值,创建一个cv::Mat,依次在对应位置处赋予像素值。
cv::Mat output_Y = cv::Mat_(Size(outputShape.lens()[3], outputShape.lens()[2]), CV_32F); //规定尺寸大小
for(int i=0;i(i,j)=data[672*i+j]; // 其中,672代表了outputShape.lens()[3]的值
}
}
// 将32F格式的数据变为8U格式的数据
cv::Mat output_Y8;
output_Y.convertTo(output_Y8, CV_8U, 255.0); // 转换为无符号8位像素数据类型,0-255是大多数图像和视频格式的正常范围
...
// 将YCbCr转换为BGR
cv::Mat B_output = output_Y8 + 1.773 * (Cb_output - 128);
cv::Mat G_output = output_Y8 - 0.714 * (Cr_output - 128) - 0.344 * (Cb_output - 128);
cv::Mat R_output = output_Y8 + 1.403 * (Cr_output - 128);
// 将BGR三通道图像合并到一起
std::vector channels2;
channels2.push_back(B_output);
channels2.push_back(G_output);
channels2.push_back(R_output);
cv::merge(channels2, superImage);
return SUCCESS;
}
```
1.inputData表示MIGraphX的输入数据,这里表示为Y通道图像数据,inputName表示输入节点名,migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data}表示该节点名对应的数据,这里通过前面的预处理数据inputBlob来创建的,第一个参数表示数据的shape,第二个参数表示数据指针。
2.net.eval(inputData)返回模型的推理结果,由于这里只有一个输出节点,所以std::vector中只有一个数据,results[0]表示第一个输出节点,获取输出数据之后,就可以对输出数据执行相关后处理操作。
3.推理结果为重建后的图像像素点值,创建一个cv::Mat,尺寸为672x672,通过output_Y.at(i,j)=data[672*i+j]按行赋相应像素值。最后,将YCbCr转换为BGR,并将三通道合并到一起,得到最终的重建图像。
### 运行示例
根据samples工程中的README.md构建成功C++ samples后,在build目录下输入如下命令运行该示例:
```Python
./ MIGraphX_Samples 7
```
会在当前目录中生成检测结果图像Result.jpg。
结果如下,左图为原图,有图为重建过后的图像,分辨率提高了三倍。

# Python Samples
## 分类器
本示例使用了经典的mnist模型,模型下载地址:https://github.com/onnx/models/blob/main/vision/classification/mnist/model/mnist-12.onnx,模型结构如下图所示(可以通过netron (https://netron.app/) 查看),该模型的输入shape为[1,1,28,28] ,数据排布为NCHW,输出是10个类别的概率(未归一化)。

### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
1. 转换为单通道灰度图
2. resize到28x28
3. 将像素值归一化到[0.0, 1.0]
4. 转换数据排布为NCHW
本示例代码采用了OpenCV实现了预处理操作:
```
def Preprocessing(pathOfImage):
gray = cv2.imread(pathOfImage,cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
gray = cv2.resize(gray, (28,28)).astype(np.float32)/255
input = np.reshape(gray, (1,1,28,28))
return input
```
### 推理
完成预处理后,就可以执行推理了:
```
if __name__ == '__main__':
...
# 预处理
pathOfImage ="../../Resource/Images/9.jpg"
image = Preprocessing(pathOfImage)
# 推理
results = model.run({inputName: migraphx.argument(image)}) # 推理结果,list类型
# 获取输出节点属性
result=results[0] # 获取第一个输出节点的数据,migraphx.argument类型
outputShape=result.get_shape() # 输出节点的shape,migraphx.shape类型
outputSize=outputShape.lens() # 每一维大小,维度顺序为(N,C,H,W),list类型
numberOfOutput=outputShape.elements() # 输出节点元素的个数
# 计算softmax
result=results[0].tolist() # 将migraphx.argument转换为list
result=np.array(result)
scores=Softmax(result)
# 打印10个类别的概率
print(scores)
```
1. Preprocessing()函数返回输入数据(numpy类型),然后通过{inputName: migraphx.argument(image)}构造一个字典输入模型执行推理,如果模型有多个输入,则在字典中需要添加多个输入数据。
2. model.run()返回模型的推理结果,返回结果是一个list类型,results[0]表示第一个输出节点的输出,是一个migraphx.argument类型,由于示例模型只有一个输出节点,所以results[0]对应Plus214_Output_0节点,如果想将migraphx.argument类型转换为list类型,可以通过tolist()方法实现。
3. 由于该模型输出的是一个未归一化的概率,所以如果需要得到每一类的实际的概率值,还需要计算softmax。
### 运行示例
1. 参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2. 安装依赖:
```
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
# 进入示例程序目录
cd Python/Classifier
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
3. 在Python/Classifier目录下执行如下命令运行该示例程序:
```
# 运行示例
python Classifier.py
```
输出结果为:
```
...
[1.59622257e-07 3.41601745e-05 1.17416399e-05 1.69055674e-04
4.37055434e-05 1.19463621e-06 5.51138837e-11 7.25694010e-04
2.78295036e-04 9.98735994e-01]
```
输出结果中,每个值分别对应每个label的实际概率,比如1.59622257e-07表示label为0的概率,由于示例图像为数字9,所以结果中label为9的概率最高。

## RetinaFace人脸检测器
### 模型简介
RetinaFace是一个经典的人脸检测模型(https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.00641),采用了SSD架构。

本示例采用了如下的开源实现:https://github.com/biubug6/Pytorch_Retinaface,作者提供了restnet50 和mobilenet0.25两个预训练模型,本示例使用了mobilenet0.25预训练模型,将mobilenet0.25预训练模型下载下来后,保存到Pytorch_Retinaface工程的weights目录。
### 模型转换
通过下面的步骤可以将mobilenet0.25预训练转换成onnx文件:
1. 修改data/config.py:将cfg_mnet中的'pretrain': True,修改为'pretrain': False,
2. 执行如下命令就可以将weights目录下的mobilenet0.25_Final.pth模型转换为onnx文件了
```
# 进入Pytorch_Retinaface工程根目录
cd
# 转换模型
python convert_to_onnx.py
```
注意:如果需要修改模型的输入大小,可以修改args.long_side参数,默认为640x640。
模型转换成功后,会在当前目录生成FaceDetector.onnx文件,利用该模型就可以使用MIGraphX进行推理了,本示例在samples工程中的Python/RetinaFace目录中提供了已经修改好的代码,在该目录下执行python convert_to_onnx.py可以直接生成onnx文件。
### 推理
Pytorch_Retinaface工程提供了原始Pytorch版本的推理测试代码detect.py,我们只需要将其中使用Pytorch推理的部分转换为MIGraphX推理就可以了,samples工程中的Python/RetinaFace/detect.py文件为已经转换好的推理代码,下面我们看一下是如何转换的:
1. 将加载模型部分修改为migraphx的方式加载
```
# 加载模型
model = migraphx.parse_onnx("./FaceDetector.onnx")
```
2. 模型加载成功后,需要通过model.compile进行编译,可以通过device_id设置使用哪一块设备
```
model.compile(t=migraphx.get_target("gpu"),device_id=0)
```
3. 编译成功后,就可以输入图像进行推理了,由于本示例使用的onnx模型的输入大小是640x640,所以对于输入图像需要先resize到640x640
```
# resize到onnx模型输入大小
image_path = "./curve/test.jpg"
img_raw = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
img_raw = cv2.resize(img_raw, (640,640))
```
4. 预处理部分跟作者的代码保持一致即可,这部分不需要修改
5. 下面是最关键的一步,将pytorch推理net(img)转换为MIGraphX推理migraphx_run(model,args.cpu,img),其中migraphx_run实现如下:
```
def migraphx_run(model,cpu,data_tensor):
# 将输入的tensor数据转换为numpy
if cpu:
data_numpy=data_tensor.cpu().numpy()
device = torch.device("cpu")
else:
data_numpy=data_tensor.detach().cpu().numpy()
device = torch.device("cuda")
img_data = np.zeros(data_numpy.shape).astype("float32")
for i in range(data_numpy.shape[0]):
img_data[i, :, :, :] = data_numpy[i, :, :, :]
# 执行推理
result = model.run({model.get_parameter_names()[0]: migraphx.argument(img_data)})
# 将结果转换为tensor
result0=torch.from_numpy(np.array(result[0], copy=False)).to(device)
result1=torch.from_numpy(np.array(result[1], copy=False)).to(device)
result2=torch.from_numpy(np.array(result[2], copy=False)).to(device)
return (result0,result1,result2)
```
首先需要将tensor数据转换为numpy,转换好的数据保存在img_data中,然后通过{model.get_parameter_names()[0]: migraphx.argument(img_data)}创建MIGraphX的输入数据,并使用model.run执行推理,result为推理返回的结果,然后通过torch.from_numpy的方式转换为tensor类型并返回,为了保持与Pytorch推理结果的格式一致,转换的时候需要注意输出结果的顺序,MIGraphX的输出结果顺序与onnx中保持一致,可以通过netron (https://netron.app/) 查看:

所以第一个输出结果对应pytorch结果中的loc,第二个对应conf, 第三个对应landms,所以返回的结果是(result0,result1,result2)。
6. 推理执行成功后,需要执行后处理才能得到最终的检测结果,由于我们模型推理输出的格式与原始的Pytorch模型输出是一致的,所以后处理可以直接使用原来的,不需要修改。
### 运行示例
1. 参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2. 安装Pytorch
3. 安装依赖:
```
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
# 进入示例程序目录
cd Python/RetinaFace
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
4. 运行示例:
```
python detect.py
```
会在当前目录生成检测结果图像test.jpg

## YOLOV3检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV3是由Joseph Redmon和Ali Farhadi在《YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement》论文中提出的单阶段检测模型,算法基本思想首先通过特征提取网络对输入提取特征,backbone部分由YOLOV2时期的Darknet19进化至Darknet53加深了网络层数,引入了Resnet中的跨层加和操作;然后结合不同卷积层的特征实现多尺度训练,一共有13x13、26x26、52x52三种分辨率,分别用来预测大、中、小的物体;每种分辨率的特征图将输入图像分成不同数量的格子,每个格子预测B个bounding box,每个bounding box预测内容包括: Location(x, y, w, h)、Confidence Score和C个类别的概率,因此YOLOv3输出层的channel数为B*(5 + C)。YOLOv3的loss函数也有三部分组成:Location误差,Confidence误差和分类误差。
## 图像分割
本示例采用了经典的Unet模型进行图像分割,模型下载地址:https://www.dropbox.com/s/3ntkhyk30x05uuv/unet_13_256.onnx,将unet_13_256.onnx文件保存在Resource\Models\Segmentation文件夹下。模型结构如下图所示(可以通过netron工具(https://netron.app/)查看具体的模型结构),该模型的输入shape为[batch_size,3,256,256],输出shape为[batch_size,1,256,256],数据排布为NCHW。

### 参数设置
samples工程中的Resource/Configuration.xml文件的Unet节点表示图像分割模型Unet的参数,主要包括模型存放路径。
```xml
"../Resource/Models/Segmentation/unet_13_256.onnx"
```
### 模型初始化
首先,通过parse_onnx()函数加载图像分割Unet的onnx模型,并可以通过program的get_parameter_shapes()函数获取网络的输入属性。完成模型加载之后需要使用compile()方法编译模型,编译模式使用migraphx::gpu::target{}设为GPU模式,编译过程主要基于MIGraphX IR完成各种优化。
```C++
ErrorCode Unet::Initialize(InitializationParameterOfSegmentation initParamOfSegmentationUnet)
{
...
// 加载模型
net = migraphx::parse_onnx(modelPath); // 根据提供的模型地址,去加载模型文件
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to load model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
// 获取模型输入属性
std::pair inputAttribute=*(net.get_parameter_shapes().begin());
inputName=inputAttribute.first;
inputShape=inputAttribute.second;
inputSize=cv::Size(inputShape.lens()[3],inputShape.lens()[2]);
// 设置模型为GPU模式
migraphx::target gpuTarget = migraphx::gpu::target{};
// 编译模型
migraphx::compile_options options;
options.device_id=0; // 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备(>=1.2版本中支持)
options.offload_copy=true; // 设置offload_copy
net.compile(gpuTarget,options);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to compile model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
...
}
```
### 预处理
完成模型初始化之后,需要将输入数据进行如下预处理:
1.尺度变换,将图像resize到256x256大小
2.归一化,将数据归一化到[0.0, 1.0]之间
3.数据排布,将数据从HWC转换为NCHW
本示例代码主要通过opencv实现预处理操作:
```C++
ErrorCode Unet::Segmentation(const cv::Mat &srcImage, cv::Mat &maskImage)
{
...
// 图像预处理,将图像resize到(256x256)大小,并转换为NCHW
cv::Mat inputBlob;
cv::dnn::blobFromImage(srcImage, // 输入数据,支持多张图像
inputBlob, // 输出数据
1 / 255.0, // 缩放系数
inputSize, // 模型输入大小,这里为256x256
Scalar(0, 0, 0), // 均值,这里不需要减均值,所以设置为0
true, // 通道转换,B通道与R通道互换,所以为true
false);
...
}
```
1.cv::dnn::blobFromImage()函数支持多个输入图像,首先将输入图像resize到inputSize大小,然后减去均值,其次乘以缩放系数1/255.0并转换为NCHW,最终将转换好的数据保存到inputBlob作为输入数据执行推理。
### 推理
完成图像预处理后,就可以执行推理,得到推理结果。
```c++
ErrorCode Unet::Segmentation(const cv::Mat &srcImage, cv::Mat &maskImage)
{
...
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector results = net.eval(inputData);
// 获取输出节点的属性
migraphx::argument result = results[0]; // 获取第一个输出节点的数据
migraphx::shape outputShape=result.get_shape(); // 输出节点的shape
std::vector outputSize=outputShape.lens(); // 每一维大小,维度顺序为(N,C,H,W)
int numberOfOutput=outputShape.elements(); // 输出节点元素的个数
float *data = (float *)result.data(); // 输出节点数据指针
// 计算sigmoid值,并且当大于0.996时,值为1,当小于0.996时,值为0,存储在value_mask[]数组中
int value_mask[numberOfOutput];
for(int i=0; i 0.996)
{
value_mask[i] = 1;
}
else
{
value_mask[i] = 0;
}
}
// 将对应的value_mask[]数组中的值依次赋值到outputImage对应位置处
cv::Mat outputImage = cv::Mat_(Size(outputShape.lens()[3], outputShape.lens()[2]), CV_32S);
for(int i=0;i(i,j)=value_mask[256*i+j]; // 其中,256代表了outputShape.lens()[3]的值
}
}
// 将32S格式的数据转换为8U格式的数据
outputImage.convertTo(maskImage, CV_8U, 255.0);
...
}
```
1.inputData表示MIGraphX的输入数据,这里表示为图像数据,inputName表示输入节点名,migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data}表示该节点名对应的数据,这里是通过前面预处理的数据inputBlob来创建的,第一个参数表示数据的shape,第二个参数表示数据指针。
2.net.eval(inputData)返回模型的推理结果,由于这里只有一个输出节点,所以std::vector中只有一个数据,results[0]表示第一个输出节点,获取输出数据之后,就可以对输出数据执行相关后处理操作。
3.模型得到的推理结果并不能直接作为分割结果。首先,对推理结果计算sigmoid值,当计算值大于0.996时值为1,小于等于0.996时值为0,保存在数组value_mask中。其次,创建一个cv::Mat将value_mask数组中的值按行依次赋值到对应的位置。最后,将32S格式的数据转换为8U格式的数据,对应位置乘以255,得到最终的分割图像。
注:本次采用的模型权重onnx文件是通过使用具有普通背景的汽车图像来训练的。因此,“现实世界“图像的分割结果不完美是意料之中的。为了获得更好的结果,建议对现实世界示例数据集上的模型进行微调。
### 运行示例
根据samples工程中的README.md构建成功C++ samples后,在build目录下输入如下命令运行该示例:
```c++
./ MIGraphX_Samples 8
```
会在当前目录中生成分割结果图像Result.jpg
输出结果为:

## 超分辨率重建
### 模型简介
图像超分辨率重建技术是指设计并采用某种算法,使得可以通过观测到的低分辨率(Low Resolution, LR)图像重建出近似真实高分辨率(High Resolution , HR)图像的方法。本次部署的超分辨率模型是2016提出的ESPCN网络,主要通过一系列卷积层不断提取图像特征,最后通过sub-pixel亚像素卷积层提高图像分辨率,从而实现图像超分辨率的方法。ESPCN网络结构如下图所示

本示例采用onnx官方提供的ESPCN模型示例:https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/main/vision/super_resolution/sub_pixel_cnn_2016,将super.onnx文件保存在Resource\Models\Super_Resolution文件夹下。
### 参数设置
samples工程中的Resource/Configuration.xml文件的Espcn节点表示超分辨率模型Espcn的参数,主要包括模型存放路径。
```xml
"../Resource/Models/Super_Resolution/super.onnx"
```
### 模型初始化
首先,通过parse_onnx()函数加载图像超分辨率ESPCN的onnx模型,并可以通过program的get_parameter_shapes()函数获取网络的输入属性。完成模型加载之后需要使用compile()方法编译模型,编译模式使用migraphx::gpu::target{}设为GPU模式,编译过程主要基于MIGraphX IR完成各种优化。
```C++
ErrorCode Espcn::Initialize(InitializationParameterOfSuperresolution initParamOfSuperresolutionESPCN)
{
...
// 加载模型
net = migraphx::parse_onnx(modelPath); // 根据提供的模型地址,去加载模型文件
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to load model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
// 获取模型输入属性
std::pair inputAttribute=*(net.get_parameter_shapes().begin());
inputName=inputAttribute.first;
inputShape=inputAttribute.second;
inputSize=cv::Size(inputShape.lens()[3],inputShape.lens()[2]);
// 设置模型为GPU模式
migraphx::target gpuTarget = migraphx::gpu::target{};
// 编译模型
migraphx::compile_options options;
options.device_id=0; // 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备(>=1.2版本中支持)
options.offload_copy=true; // 设置offload_copy
net.compile(gpuTarget,options);
LOG_INFO(logFile,"succeed to compile model: %s\n",GetFileName(modelPath).c_str());
...
}
```
### 预处理
完成模型初始化之后,需要将输入数据进行如下预处理:
1.分离图像通道,变为B、G、R三个通道图像;
2.BGR格式通过公式转换为YCbCr格式,得到Y、Cb、Cr三通道图像;
3.Y通道图像resize到224x224,变为浮点型数据,并转换数据排布为NCHW;
本示例代码主要采用如下方式完成预处理操作:
```c++
ErrorCode Espcn::Super(const cv::Mat &srcImage, cv::Mat &superImage)
{
...
// 图像预处理(分离图像通道,只处理Y通道的图像,进行模型推理)
// 分离图像通道
std::vector channels;
cv::split(srcImage, channels); // B通道=channels[0],G通道=channels[1],R通道=channels[2]
// 将BGR格式转换为YCbCr格式,采用opencv官方转换公式
cv::Mat Y_channels = 0.299*channels[2] + 0.587*channels[1] + 0.114*channels[0];
cv::Mat Cb_channels = (channels[0]-Y_channels) * 0.564 + 128;
cv::Mat Cr_channels = (channels[2]-Y_channels) * 0.713 + 128;
// 将Y通道图像resize为224x224,变为浮点型数据,并转换数据排布为NCHW
cv::Mat inputBlob;
cv::dnn::blobFromImage(Y_channels, // 输入数据,支持多张图像
inputBlob, // 输出数据
1/255.0, // 缩放系数
inputSize, // 模型输入大小,这里为672x672
Scalar(0, 0, 0), // 均值,这里不需要减均值,所以设置为0
false, // 通道转换,因为只处理Y通道数据,不需要通道转换,所以设置为false
false);
...
}
```
1.在预处理过程中,重要的是BGR格式转换为YCbCr格式,主要是因为相较于色差,人类视觉对亮度变化更为敏感。因此,在处理的过程中感兴趣的不是颜色变化(存储在 CbCr 通道中的信息),而只是其亮度(Y 通道),所以需要将BGR转换为YCbCr,转换公式采用的是opencv官方提供的公式,链接:https://docs.opencv.org/3.4.11/de/d25/imgproc_color_conversions.html。
2.得到Y通道图像后,需要resize为固定尺寸并转换为NCHW,主要采用cv::dnn::blobFromImage()函数。首先将输入图像resize到inputSize,然后减去均值,其次乘以缩放系数1/255.0并转换为NCHW,最终将转换好的数据保存到inputBlob作为输入数据执行推理。
### 推理
完成图像预处理后,就可以执行推理,得到推理结果。
```C++
ErrorCode Espcn::Super(const cv::Mat &srcImage, cv::Mat &superImage)
{
...
// 输入数据
migraphx::parameter_map inputData;
inputData[inputName]= migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data};
// 推理
std::vector results = net.eval(inputData);
// 获取输出节点的属性
migraphx::argument result = results[0]; // 获取第一个输出节点的数据
migraphx::shape outputShape=result.get_shape(); // 输出节点的shape
std::vector outputSize=outputShape.lens(); // 每一维大小,维度顺序为(N,C,H,W)
int numberOfOutput=outputShape.elements(); // 输出节点元素的个数
float *data = (float *)result.data(); // 输出节点数据指针
// 获取推理结果,是重建后每个像素点的像素值,创建一个cv::Mat,依次在对应位置处赋予像素值。
cv::Mat output_Y = cv::Mat_(Size(outputShape.lens()[3], outputShape.lens()[2]), CV_32F); //规定尺寸大小
for(int i=0;i(i,j)=data[672*i+j]; // 其中,672代表了outputShape.lens()[3]的值
}
}
// 将32F格式的数据变为8U格式的数据
cv::Mat output_Y8;
output_Y.convertTo(output_Y8, CV_8U, 255.0); // 转换为无符号8位像素数据类型,0-255是大多数图像和视频格式的正常范围
...
// 将YCbCr转换为BGR
cv::Mat B_output = output_Y8 + 1.773 * (Cb_output - 128);
cv::Mat G_output = output_Y8 - 0.714 * (Cr_output - 128) - 0.344 * (Cb_output - 128);
cv::Mat R_output = output_Y8 + 1.403 * (Cr_output - 128);
// 将BGR三通道图像合并到一起
std::vector channels2;
channels2.push_back(B_output);
channels2.push_back(G_output);
channels2.push_back(R_output);
cv::merge(channels2, superImage);
return SUCCESS;
}
```
1.inputData表示MIGraphX的输入数据,这里表示为Y通道图像数据,inputName表示输入节点名,migraphx::argument{inputShape, (float*)inputBlob.data}表示该节点名对应的数据,这里通过前面的预处理数据inputBlob来创建的,第一个参数表示数据的shape,第二个参数表示数据指针。
2.net.eval(inputData)返回模型的推理结果,由于这里只有一个输出节点,所以std::vector中只有一个数据,results[0]表示第一个输出节点,获取输出数据之后,就可以对输出数据执行相关后处理操作。
3.推理结果为重建后的图像像素点值,创建一个cv::Mat,尺寸为672x672,通过output_Y.at(i,j)=data[672*i+j]按行赋相应像素值。最后,将YCbCr转换为BGR,并将三通道合并到一起,得到最终的重建图像。
### 运行示例
根据samples工程中的README.md构建成功C++ samples后,在build目录下输入如下命令运行该示例:
```Python
./ MIGraphX_Samples 7
```
会在当前目录中生成检测结果图像Result.jpg。
结果如下,左图为原图,有图为重建过后的图像,分辨率提高了三倍。

# Python Samples
## 分类器
本示例使用了经典的mnist模型,模型下载地址:https://github.com/onnx/models/blob/main/vision/classification/mnist/model/mnist-12.onnx,模型结构如下图所示(可以通过netron (https://netron.app/) 查看),该模型的输入shape为[1,1,28,28] ,数据排布为NCHW,输出是10个类别的概率(未归一化)。

### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
1. 转换为单通道灰度图
2. resize到28x28
3. 将像素值归一化到[0.0, 1.0]
4. 转换数据排布为NCHW
本示例代码采用了OpenCV实现了预处理操作:
```
def Preprocessing(pathOfImage):
gray = cv2.imread(pathOfImage,cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
gray = cv2.resize(gray, (28,28)).astype(np.float32)/255
input = np.reshape(gray, (1,1,28,28))
return input
```
### 推理
完成预处理后,就可以执行推理了:
```
if __name__ == '__main__':
...
# 预处理
pathOfImage ="../../Resource/Images/9.jpg"
image = Preprocessing(pathOfImage)
# 推理
results = model.run({inputName: migraphx.argument(image)}) # 推理结果,list类型
# 获取输出节点属性
result=results[0] # 获取第一个输出节点的数据,migraphx.argument类型
outputShape=result.get_shape() # 输出节点的shape,migraphx.shape类型
outputSize=outputShape.lens() # 每一维大小,维度顺序为(N,C,H,W),list类型
numberOfOutput=outputShape.elements() # 输出节点元素的个数
# 计算softmax
result=results[0].tolist() # 将migraphx.argument转换为list
result=np.array(result)
scores=Softmax(result)
# 打印10个类别的概率
print(scores)
```
1. Preprocessing()函数返回输入数据(numpy类型),然后通过{inputName: migraphx.argument(image)}构造一个字典输入模型执行推理,如果模型有多个输入,则在字典中需要添加多个输入数据。
2. model.run()返回模型的推理结果,返回结果是一个list类型,results[0]表示第一个输出节点的输出,是一个migraphx.argument类型,由于示例模型只有一个输出节点,所以results[0]对应Plus214_Output_0节点,如果想将migraphx.argument类型转换为list类型,可以通过tolist()方法实现。
3. 由于该模型输出的是一个未归一化的概率,所以如果需要得到每一类的实际的概率值,还需要计算softmax。
### 运行示例
1. 参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2. 安装依赖:
```
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
# 进入示例程序目录
cd Python/Classifier
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
3. 在Python/Classifier目录下执行如下命令运行该示例程序:
```
# 运行示例
python Classifier.py
```
输出结果为:
```
...
[1.59622257e-07 3.41601745e-05 1.17416399e-05 1.69055674e-04
4.37055434e-05 1.19463621e-06 5.51138837e-11 7.25694010e-04
2.78295036e-04 9.98735994e-01]
```
输出结果中,每个值分别对应每个label的实际概率,比如1.59622257e-07表示label为0的概率,由于示例图像为数字9,所以结果中label为9的概率最高。

## RetinaFace人脸检测器
### 模型简介
RetinaFace是一个经典的人脸检测模型(https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.00641),采用了SSD架构。

本示例采用了如下的开源实现:https://github.com/biubug6/Pytorch_Retinaface,作者提供了restnet50 和mobilenet0.25两个预训练模型,本示例使用了mobilenet0.25预训练模型,将mobilenet0.25预训练模型下载下来后,保存到Pytorch_Retinaface工程的weights目录。
### 模型转换
通过下面的步骤可以将mobilenet0.25预训练转换成onnx文件:
1. 修改data/config.py:将cfg_mnet中的'pretrain': True,修改为'pretrain': False,
2. 执行如下命令就可以将weights目录下的mobilenet0.25_Final.pth模型转换为onnx文件了
```
# 进入Pytorch_Retinaface工程根目录
cd
# 转换模型
python convert_to_onnx.py
```
注意:如果需要修改模型的输入大小,可以修改args.long_side参数,默认为640x640。
模型转换成功后,会在当前目录生成FaceDetector.onnx文件,利用该模型就可以使用MIGraphX进行推理了,本示例在samples工程中的Python/RetinaFace目录中提供了已经修改好的代码,在该目录下执行python convert_to_onnx.py可以直接生成onnx文件。
### 推理
Pytorch_Retinaface工程提供了原始Pytorch版本的推理测试代码detect.py,我们只需要将其中使用Pytorch推理的部分转换为MIGraphX推理就可以了,samples工程中的Python/RetinaFace/detect.py文件为已经转换好的推理代码,下面我们看一下是如何转换的:
1. 将加载模型部分修改为migraphx的方式加载
```
# 加载模型
model = migraphx.parse_onnx("./FaceDetector.onnx")
```
2. 模型加载成功后,需要通过model.compile进行编译,可以通过device_id设置使用哪一块设备
```
model.compile(t=migraphx.get_target("gpu"),device_id=0)
```
3. 编译成功后,就可以输入图像进行推理了,由于本示例使用的onnx模型的输入大小是640x640,所以对于输入图像需要先resize到640x640
```
# resize到onnx模型输入大小
image_path = "./curve/test.jpg"
img_raw = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
img_raw = cv2.resize(img_raw, (640,640))
```
4. 预处理部分跟作者的代码保持一致即可,这部分不需要修改
5. 下面是最关键的一步,将pytorch推理net(img)转换为MIGraphX推理migraphx_run(model,args.cpu,img),其中migraphx_run实现如下:
```
def migraphx_run(model,cpu,data_tensor):
# 将输入的tensor数据转换为numpy
if cpu:
data_numpy=data_tensor.cpu().numpy()
device = torch.device("cpu")
else:
data_numpy=data_tensor.detach().cpu().numpy()
device = torch.device("cuda")
img_data = np.zeros(data_numpy.shape).astype("float32")
for i in range(data_numpy.shape[0]):
img_data[i, :, :, :] = data_numpy[i, :, :, :]
# 执行推理
result = model.run({model.get_parameter_names()[0]: migraphx.argument(img_data)})
# 将结果转换为tensor
result0=torch.from_numpy(np.array(result[0], copy=False)).to(device)
result1=torch.from_numpy(np.array(result[1], copy=False)).to(device)
result2=torch.from_numpy(np.array(result[2], copy=False)).to(device)
return (result0,result1,result2)
```
首先需要将tensor数据转换为numpy,转换好的数据保存在img_data中,然后通过{model.get_parameter_names()[0]: migraphx.argument(img_data)}创建MIGraphX的输入数据,并使用model.run执行推理,result为推理返回的结果,然后通过torch.from_numpy的方式转换为tensor类型并返回,为了保持与Pytorch推理结果的格式一致,转换的时候需要注意输出结果的顺序,MIGraphX的输出结果顺序与onnx中保持一致,可以通过netron (https://netron.app/) 查看:

所以第一个输出结果对应pytorch结果中的loc,第二个对应conf, 第三个对应landms,所以返回的结果是(result0,result1,result2)。
6. 推理执行成功后,需要执行后处理才能得到最终的检测结果,由于我们模型推理输出的格式与原始的Pytorch模型输出是一致的,所以后处理可以直接使用原来的,不需要修改。
### 运行示例
1. 参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2. 安装Pytorch
3. 安装依赖:
```
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
# 进入示例程序目录
cd Python/RetinaFace
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
4. 运行示例:
```
python detect.py
```
会在当前目录生成检测结果图像test.jpg

## YOLOV3检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV3是由Joseph Redmon和Ali Farhadi在《YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement》论文中提出的单阶段检测模型,算法基本思想首先通过特征提取网络对输入提取特征,backbone部分由YOLOV2时期的Darknet19进化至Darknet53加深了网络层数,引入了Resnet中的跨层加和操作;然后结合不同卷积层的特征实现多尺度训练,一共有13x13、26x26、52x52三种分辨率,分别用来预测大、中、小的物体;每种分辨率的特征图将输入图像分成不同数量的格子,每个格子预测B个bounding box,每个bounding box预测内容包括: Location(x, y, w, h)、Confidence Score和C个类别的概率,因此YOLOv3输出层的channel数为B*(5 + C)。YOLOv3的loss函数也有三部分组成:Location误差,Confidence误差和分类误差。
 本示例采用如下的开源实现:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3,作者在V9.6.0版本中提供多种不同的YOLOV3预训练模型,其中包括yolov3、yolov3-fixed、yolov3-spp、yolov3-tiny四个版本。本示例选择yolov3-tiny.pt预训练模型进行构建MIGraphX推理,下载YOLOV3的预训练模型yolov3-tiny.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV3工程的weights目录。
### 环境配置
运行YOLOV3模型的Python示例首先需要进行环境配置,包括安装torch、torchvision以及程序运行所需要的依赖。
1、安装torch、torchvision
2、安装程序运行的依赖
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV3工程根目录
cd
# 安装程序运行的依赖
pip install -r requirement.txt
```
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV3源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov3-tiny.pt预训练模型转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV3工程根目录
cd
# 转换模型
python export.py --weights ./weights/yolov3-tiny.pt --imgsz 416 416 --include onnx
```
注意:官方源码提供的模型转换的程序中包含更多的功能,例如动态shape模型的导出,可根据需要进行添加相关参数。
### 模型推理
#### 预处理
待检测图片输入模型进行检测之前需要进行预处理,主要包括调整输入的尺寸,归一化等操作。
1. 转换数据排布为NCHW
2. 归一化[0.0, 1.0]
3. 调整输入数据的尺寸为(1,3,416,416)
```
def prepare_input(self, image):
self.img_height, self.img_width = image.shape[:2]
input_img = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 调整图像的尺寸
input_img = cv2.resize(input_img, (self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight))
# 维度转换HWC->CHW
input_img = input_img.transpose(2, 0, 1)
# 维度拓展,增加batch维度
input_img = np.expand_dims(input_img, 0)
input_img = np.ascontiguousarray(input_img)
input_img = input_img.astype(np.float32)
# 归一化
input_img = input_img / 255
return input_img
```
其中模型输入的inputWidth、inputHeight通过migraphx对输入模型进行解析获取,代码位置见YOLOV3类初始化位置。
```
class YOLOv3:
def __init__(self, path, obj_thres=0.5, conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.5):
self.objectThreshold = obj_thres
self.confThreshold = conf_thres
self.nmsThreshold = iou_thres
# 获取模型检测的类别信息
self.classNames = list(map(lambda x: x.strip(), open('./weights/coco.names', 'r').readlines()))
# 解析推理模型
self.model = migraphx.parse_onnx(path)
# 获取模型的输入name
self.inputName = self.model.get_parameter_names()[0]
# 获取模型的输入尺寸
inputShape = self.model.get_parameter_shapes()[self.inputName].lens()
self.inputHeight = int(inputShape[2])
self.inputWidth = int(inputShape[3])
```
#### 推理
输入图片预处理完成之后开始进行推理,首先需要利用migraphx进行编译,然后对输入数据进行前向计算得到模型的输出result,在detect函数中调用定义的process_output函数对result进行后处理,得到图片中含有物体的anchor坐标信息、类别置信度、类别ID。
```
def detect(self, image):
# 输入图片预处理
input_img = self.prepare_input(image)
# 模型编译
self.model.compile(t=migraphx.get_target("gpu"), device_id=0) # device_id: 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备
print("Success to compile")
# 执行推理
print("Start to inference")
start = time.time()
result = self.model.run({self.model.get_parameter_names()[0]: migraphx.argument(input_img)})
print('net forward time: {:.4f}'.format(time.time() - start))
# 模型输出结果后处理
boxes, scores, class_ids = self.process_output(result)
return boxes, scores, class_ids
```
其中对migraphx推理输出result进行后处理,首先需要对生成的anchor根据是否有物体阈值objectThreshold、置信度阈值confThreshold进行筛选,相关过程定义在process_output函数中。获取筛选后的anchor的坐标信息之后,需要将坐标映射到原图中的位置,相关过程定义在rescale_boxes函数中。
```
def process_output(self, output):
predictions = np.squeeze(output[0])
# 筛选包含物体的anchor
obj_conf = predictions[:, 4]
predictions = predictions[obj_conf > self.objectThreshold]
obj_conf = obj_conf[obj_conf > self.objectThreshold]
# 筛选大于置信度阈值的anchor
predictions[:, 5:] *= obj_conf[:, np.newaxis]
scores = np.max(predictions[:, 5:], axis=1)
valid_scores = scores > self.confThreshold
predictions = predictions[valid_scores]
scores = scores[valid_scores]
# 获取最高置信度分数对应的类别ID
class_ids = np.argmax(predictions[:, 5:], axis=1)
# 获取每个物体对应的anchor
boxes = self.extract_boxes(predictions)
# 执行非极大值抑制消除冗余anchor
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes.tolist(), scores.tolist(), self.confThreshold, self.nmsThreshold).flatten()
return boxes[indices], scores[indices], class_ids[indices]
def rescale_boxes(self, boxes):
# 对anchor尺寸进行变换
input_shape = np.array([self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight, self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight])
boxes = np.divide(boxes, input_shape, dtype=np.float32)
boxes *= np.array([self.img_width, self.img_height, self.img_width, self.img_height])
return boxes
```
根据获取的detect函数输出的boxes、scores、class_ids信息在原图进行结果可视化,包括用绘制图片中检测到的物体位置、类别和置信度分数,得到最终的YOLOV3目标检测结果输出。
```
def draw_detections(self, image, boxes, scores, class_ids):
for box, score, class_id in zip(boxes, scores, class_ids):
cx, cy, w, h = box.astype(int)
# 绘制检测物体框
cv2.rectangle(image, (cx, cy), (cx + w, cy + h), (0, 255, 255), thickness=2)
label = self.classNames[class_id]
label = f'{label} {int(score * 100)}%'
labelSize, baseLine = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
cv2.putText(image, label, (cx, cy - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 255), thickness=2)
return image
```
### 运行示例
1.参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2.运行示例
```
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
#进入示例程序目录
cd Python/Detector/YOLOV3
# 运行示例
python detect_migraphx.py --imgpath ./data/images/dog.jpg --modelpath ./weights/yolov3-tiny.onnx --objectThreshold 0.4 --confThreshold 0.2 --nmsThreshold 0.4
```
输入参数中可根据需要进行修改,程序运行结束会在当前目录生成YOLOV3检测结果图片。

## YOLOV5检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV5是一种单阶段目标检测算法,该算法在YOLOV4的基础上添加了一些新的改进思路,使其速度与精度都得到了极大的性能提升。具体包括:输入端的Mosaic数据增强、自适应锚框计算、自适应图片缩放操作;主干网络的Focus结构与CSP结构;Neck端的FPN+PAN结构;输出端的损失函数GIOU_Loss以及预测框筛选的DIOU_nms。网络结构如图所示。
本示例采用如下的开源实现:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3,作者在V9.6.0版本中提供多种不同的YOLOV3预训练模型,其中包括yolov3、yolov3-fixed、yolov3-spp、yolov3-tiny四个版本。本示例选择yolov3-tiny.pt预训练模型进行构建MIGraphX推理,下载YOLOV3的预训练模型yolov3-tiny.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV3工程的weights目录。
### 环境配置
运行YOLOV3模型的Python示例首先需要进行环境配置,包括安装torch、torchvision以及程序运行所需要的依赖。
1、安装torch、torchvision
2、安装程序运行的依赖
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV3工程根目录
cd
# 安装程序运行的依赖
pip install -r requirement.txt
```
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV3源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov3-tiny.pt预训练模型转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV3工程根目录
cd
# 转换模型
python export.py --weights ./weights/yolov3-tiny.pt --imgsz 416 416 --include onnx
```
注意:官方源码提供的模型转换的程序中包含更多的功能,例如动态shape模型的导出,可根据需要进行添加相关参数。
### 模型推理
#### 预处理
待检测图片输入模型进行检测之前需要进行预处理,主要包括调整输入的尺寸,归一化等操作。
1. 转换数据排布为NCHW
2. 归一化[0.0, 1.0]
3. 调整输入数据的尺寸为(1,3,416,416)
```
def prepare_input(self, image):
self.img_height, self.img_width = image.shape[:2]
input_img = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 调整图像的尺寸
input_img = cv2.resize(input_img, (self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight))
# 维度转换HWC->CHW
input_img = input_img.transpose(2, 0, 1)
# 维度拓展,增加batch维度
input_img = np.expand_dims(input_img, 0)
input_img = np.ascontiguousarray(input_img)
input_img = input_img.astype(np.float32)
# 归一化
input_img = input_img / 255
return input_img
```
其中模型输入的inputWidth、inputHeight通过migraphx对输入模型进行解析获取,代码位置见YOLOV3类初始化位置。
```
class YOLOv3:
def __init__(self, path, obj_thres=0.5, conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.5):
self.objectThreshold = obj_thres
self.confThreshold = conf_thres
self.nmsThreshold = iou_thres
# 获取模型检测的类别信息
self.classNames = list(map(lambda x: x.strip(), open('./weights/coco.names', 'r').readlines()))
# 解析推理模型
self.model = migraphx.parse_onnx(path)
# 获取模型的输入name
self.inputName = self.model.get_parameter_names()[0]
# 获取模型的输入尺寸
inputShape = self.model.get_parameter_shapes()[self.inputName].lens()
self.inputHeight = int(inputShape[2])
self.inputWidth = int(inputShape[3])
```
#### 推理
输入图片预处理完成之后开始进行推理,首先需要利用migraphx进行编译,然后对输入数据进行前向计算得到模型的输出result,在detect函数中调用定义的process_output函数对result进行后处理,得到图片中含有物体的anchor坐标信息、类别置信度、类别ID。
```
def detect(self, image):
# 输入图片预处理
input_img = self.prepare_input(image)
# 模型编译
self.model.compile(t=migraphx.get_target("gpu"), device_id=0) # device_id: 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备
print("Success to compile")
# 执行推理
print("Start to inference")
start = time.time()
result = self.model.run({self.model.get_parameter_names()[0]: migraphx.argument(input_img)})
print('net forward time: {:.4f}'.format(time.time() - start))
# 模型输出结果后处理
boxes, scores, class_ids = self.process_output(result)
return boxes, scores, class_ids
```
其中对migraphx推理输出result进行后处理,首先需要对生成的anchor根据是否有物体阈值objectThreshold、置信度阈值confThreshold进行筛选,相关过程定义在process_output函数中。获取筛选后的anchor的坐标信息之后,需要将坐标映射到原图中的位置,相关过程定义在rescale_boxes函数中。
```
def process_output(self, output):
predictions = np.squeeze(output[0])
# 筛选包含物体的anchor
obj_conf = predictions[:, 4]
predictions = predictions[obj_conf > self.objectThreshold]
obj_conf = obj_conf[obj_conf > self.objectThreshold]
# 筛选大于置信度阈值的anchor
predictions[:, 5:] *= obj_conf[:, np.newaxis]
scores = np.max(predictions[:, 5:], axis=1)
valid_scores = scores > self.confThreshold
predictions = predictions[valid_scores]
scores = scores[valid_scores]
# 获取最高置信度分数对应的类别ID
class_ids = np.argmax(predictions[:, 5:], axis=1)
# 获取每个物体对应的anchor
boxes = self.extract_boxes(predictions)
# 执行非极大值抑制消除冗余anchor
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes.tolist(), scores.tolist(), self.confThreshold, self.nmsThreshold).flatten()
return boxes[indices], scores[indices], class_ids[indices]
def rescale_boxes(self, boxes):
# 对anchor尺寸进行变换
input_shape = np.array([self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight, self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight])
boxes = np.divide(boxes, input_shape, dtype=np.float32)
boxes *= np.array([self.img_width, self.img_height, self.img_width, self.img_height])
return boxes
```
根据获取的detect函数输出的boxes、scores、class_ids信息在原图进行结果可视化,包括用绘制图片中检测到的物体位置、类别和置信度分数,得到最终的YOLOV3目标检测结果输出。
```
def draw_detections(self, image, boxes, scores, class_ids):
for box, score, class_id in zip(boxes, scores, class_ids):
cx, cy, w, h = box.astype(int)
# 绘制检测物体框
cv2.rectangle(image, (cx, cy), (cx + w, cy + h), (0, 255, 255), thickness=2)
label = self.classNames[class_id]
label = f'{label} {int(score * 100)}%'
labelSize, baseLine = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
cv2.putText(image, label, (cx, cy - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 255), thickness=2)
return image
```
### 运行示例
1.参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2.运行示例
```
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
#进入示例程序目录
cd Python/Detector/YOLOV3
# 运行示例
python detect_migraphx.py --imgpath ./data/images/dog.jpg --modelpath ./weights/yolov3-tiny.onnx --objectThreshold 0.4 --confThreshold 0.2 --nmsThreshold 0.4
```
输入参数中可根据需要进行修改,程序运行结束会在当前目录生成YOLOV3检测结果图片。

## YOLOV5检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV5是一种单阶段目标检测算法,该算法在YOLOV4的基础上添加了一些新的改进思路,使其速度与精度都得到了极大的性能提升。具体包括:输入端的Mosaic数据增强、自适应锚框计算、自适应图片缩放操作;主干网络的Focus结构与CSP结构;Neck端的FPN+PAN结构;输出端的损失函数GIOU_Loss以及预测框筛选的DIOU_nms。网络结构如图所示。
 YOLOV5的官方源码地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5,官方源码中具有YOLOV5n、YOLOV5s、YOLOV5m、YOLOV5l等不同的版本。本示例采用YOLOV5s版本进行MIGraphX推理示例构建,下载YOLOV5s的预训练模型yolov5s.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV5工程的weights目录。
### 环境配置
运行YOLOV5模型的Python示例首先需要进行环境配置,包括安装torch、torchvision以及程序运行所需要的依赖。
1、安装torch、torchvision
2、安装程序运行的依赖
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV5工程根目录
cd
# 安装程序运行的依赖
pip install -r requirement.txt
```
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV5源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov5s.pt预训练模型转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV5工程根目录
cd
# 转换模型
python export.py --weights ./weights/yolov5s.pt --imgsz 608 608 --include onnx
```
注意:官方源码提供的模型转换的程序中包含更多的功能,例如动态shape模型的导出,可根据需要进行添加相关参数。
### 模型推理
#### 预处理
待检测图片输入模型进行检测之前需要进行预处理,主要包括调整输入的尺寸,归一化等操作。
1. 转换数据排布为NCHW
2. 归一化[0.0, 1.0]
3. 调整输入数据的尺寸为(1,3,608,608)
```
def prepare_input(self, image):
self.img_height, self.img_width = image.shape[:2]
input_img = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 调整图像的尺寸
input_img = cv2.resize(input_img, (self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight))
# 维度转换HWC->CHW
input_img = input_img.transpose(2, 0, 1)
# 维度拓展,增加batch维度
input_img = np.expand_dims(input_img, 0)
input_img = np.ascontiguousarray(input_img)
input_img = input_img.astype(np.float32)
# 归一化
input_img = input_img / 255
return input_img
```
其中模型输入的inputWidth、inputHeight通过migraphx对输入模型进行解析获取,代码位置见YOLOV5类初始化位置。
```
class YOLOv5:
def __init__(self, path, obj_thres=0.5, conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.5):
self.objectThreshold = obj_thres
self.confThreshold = conf_thres
self.nmsThreshold = iou_thres
# 获取模型检测的类别信息
self.classNames = list(map(lambda x: x.strip(), open('./weights/coco.names', 'r').readlines()))
# 解析推理模型
self.model = migraphx.parse_onnx(path)
# 获取模型的输入name
self.inputName = self.model.get_parameter_names()[0]
# 获取模型的输入尺寸
inputShape = self.model.get_parameter_shapes()[self.inputName].lens()
self.inputHeight = int(inputShape[2])
self.inputWidth = int(inputShape[3])
```
#### 推理
输入图片预处理完成之后开始进行推理,首先需要利用migraphx进行编译,然后对输入数据进行前向计算得到模型的输出result,在detect函数中调用定义的process_output函数对result进行后处理,得到图片中含有物体的anchor坐标信息、类别置信度、类别ID。
```
def detect(self, image):
# 输入图片预处理
input_img = self.prepare_input(image)
# 模型编译
self.model.compile(t=migraphx.get_target("gpu"), device_id=0) # device_id: 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备
print("Success to compile")
# 执行推理
print("Start to inference")
start = time.time()
result = self.model.run({self.model.get_parameter_names()[0]: migraphx.argument(input_img)})
print('net forward time: {:.4f}'.format(time.time() - start))
# 模型输出结果后处理
boxes, scores, class_ids = self.process_output(result)
return boxes, scores, class_ids
```
其中对migraphx推理输出result进行后处理,首先需要对生成的anchor根据是否有物体阈值objectThreshold、置信度阈值confThreshold进行筛选,相关过程定义在process_output函数中。获取筛选后的anchor的坐标信息之后,需要将坐标映射到原图中的位置,相关过程定义在rescale_boxes函数中。
```
def process_output(self, output):
predictions = np.squeeze(output[0])
# 筛选包含物体的anchor
obj_conf = predictions[:, 4]
predictions = predictions[obj_conf > self.objectThreshold]
obj_conf = obj_conf[obj_conf > self.objectThreshold]
# 筛选大于置信度阈值的anchor
predictions[:, 5:] *= obj_conf[:, np.newaxis]
scores = np.max(predictions[:, 5:], axis=1)
valid_scores = scores > self.confThreshold
predictions = predictions[valid_scores]
scores = scores[valid_scores]
# 获取最高置信度分数对应的类别ID
class_ids = np.argmax(predictions[:, 5:], axis=1)
# 获取每个物体对应的anchor
boxes = self.extract_boxes(predictions)
# 执行非极大值抑制消除冗余anchor
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes.tolist(), scores.tolist(), self.confThreshold, self.nmsThreshold).flatten()
return boxes[indices], scores[indices], class_ids[indices]
def rescale_boxes(self, boxes):
# 对anchor尺寸进行变换
input_shape = np.array([self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight, self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight])
boxes = np.divide(boxes, input_shape, dtype=np.float32)
boxes *= np.array([self.img_width, self.img_height, self.img_width, self.img_height])
return boxes
```
根据获取的detect函数输出的boxes、scores、class_ids信息在原图进行结果可视化,包括用绘制图片中检测到的物体位置、类别和置信度分数,得到最终的YOLOV5目标检测结果输出。
```
def draw_detections(self, image, boxes, scores, class_ids):
for box, score, class_id in zip(boxes, scores, class_ids):
cx, cy, w, h = box.astype(int)
# 绘制检测物体框
cv2.rectangle(image, (cx, cy), (cx + w, cy + h), (0, 255, 255), thickness=2)
label = self.classNames[class_id]
label = f'{label} {int(score * 100)}%'
labelSize, baseLine = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
cv2.putText(image, label, (cx, cy - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 255), thickness=2)
return image
```
### 运行示例
1.参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2.运行示例
```
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
#进入示例程序目录
cd Python/Detector/YOLOV5
# 运行示例
python detect_migraphx.py --imgpath ./data/images/bus.jpg --modelpath ./weights/yolov5s.onnx --objectThreshold 0.5 --confThreshold 0.25 --nmsThreshold 0.5
```
输入参数中可根据需要进行修改,程序运行结束会在当前目录生成YOLOV5检测结果图片。
YOLOV5的官方源码地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5,官方源码中具有YOLOV5n、YOLOV5s、YOLOV5m、YOLOV5l等不同的版本。本示例采用YOLOV5s版本进行MIGraphX推理示例构建,下载YOLOV5s的预训练模型yolov5s.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV5工程的weights目录。
### 环境配置
运行YOLOV5模型的Python示例首先需要进行环境配置,包括安装torch、torchvision以及程序运行所需要的依赖。
1、安装torch、torchvision
2、安装程序运行的依赖
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV5工程根目录
cd
# 安装程序运行的依赖
pip install -r requirement.txt
```
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV5源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov5s.pt预训练模型转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV5工程根目录
cd
# 转换模型
python export.py --weights ./weights/yolov5s.pt --imgsz 608 608 --include onnx
```
注意:官方源码提供的模型转换的程序中包含更多的功能,例如动态shape模型的导出,可根据需要进行添加相关参数。
### 模型推理
#### 预处理
待检测图片输入模型进行检测之前需要进行预处理,主要包括调整输入的尺寸,归一化等操作。
1. 转换数据排布为NCHW
2. 归一化[0.0, 1.0]
3. 调整输入数据的尺寸为(1,3,608,608)
```
def prepare_input(self, image):
self.img_height, self.img_width = image.shape[:2]
input_img = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 调整图像的尺寸
input_img = cv2.resize(input_img, (self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight))
# 维度转换HWC->CHW
input_img = input_img.transpose(2, 0, 1)
# 维度拓展,增加batch维度
input_img = np.expand_dims(input_img, 0)
input_img = np.ascontiguousarray(input_img)
input_img = input_img.astype(np.float32)
# 归一化
input_img = input_img / 255
return input_img
```
其中模型输入的inputWidth、inputHeight通过migraphx对输入模型进行解析获取,代码位置见YOLOV5类初始化位置。
```
class YOLOv5:
def __init__(self, path, obj_thres=0.5, conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.5):
self.objectThreshold = obj_thres
self.confThreshold = conf_thres
self.nmsThreshold = iou_thres
# 获取模型检测的类别信息
self.classNames = list(map(lambda x: x.strip(), open('./weights/coco.names', 'r').readlines()))
# 解析推理模型
self.model = migraphx.parse_onnx(path)
# 获取模型的输入name
self.inputName = self.model.get_parameter_names()[0]
# 获取模型的输入尺寸
inputShape = self.model.get_parameter_shapes()[self.inputName].lens()
self.inputHeight = int(inputShape[2])
self.inputWidth = int(inputShape[3])
```
#### 推理
输入图片预处理完成之后开始进行推理,首先需要利用migraphx进行编译,然后对输入数据进行前向计算得到模型的输出result,在detect函数中调用定义的process_output函数对result进行后处理,得到图片中含有物体的anchor坐标信息、类别置信度、类别ID。
```
def detect(self, image):
# 输入图片预处理
input_img = self.prepare_input(image)
# 模型编译
self.model.compile(t=migraphx.get_target("gpu"), device_id=0) # device_id: 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备
print("Success to compile")
# 执行推理
print("Start to inference")
start = time.time()
result = self.model.run({self.model.get_parameter_names()[0]: migraphx.argument(input_img)})
print('net forward time: {:.4f}'.format(time.time() - start))
# 模型输出结果后处理
boxes, scores, class_ids = self.process_output(result)
return boxes, scores, class_ids
```
其中对migraphx推理输出result进行后处理,首先需要对生成的anchor根据是否有物体阈值objectThreshold、置信度阈值confThreshold进行筛选,相关过程定义在process_output函数中。获取筛选后的anchor的坐标信息之后,需要将坐标映射到原图中的位置,相关过程定义在rescale_boxes函数中。
```
def process_output(self, output):
predictions = np.squeeze(output[0])
# 筛选包含物体的anchor
obj_conf = predictions[:, 4]
predictions = predictions[obj_conf > self.objectThreshold]
obj_conf = obj_conf[obj_conf > self.objectThreshold]
# 筛选大于置信度阈值的anchor
predictions[:, 5:] *= obj_conf[:, np.newaxis]
scores = np.max(predictions[:, 5:], axis=1)
valid_scores = scores > self.confThreshold
predictions = predictions[valid_scores]
scores = scores[valid_scores]
# 获取最高置信度分数对应的类别ID
class_ids = np.argmax(predictions[:, 5:], axis=1)
# 获取每个物体对应的anchor
boxes = self.extract_boxes(predictions)
# 执行非极大值抑制消除冗余anchor
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes.tolist(), scores.tolist(), self.confThreshold, self.nmsThreshold).flatten()
return boxes[indices], scores[indices], class_ids[indices]
def rescale_boxes(self, boxes):
# 对anchor尺寸进行变换
input_shape = np.array([self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight, self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight])
boxes = np.divide(boxes, input_shape, dtype=np.float32)
boxes *= np.array([self.img_width, self.img_height, self.img_width, self.img_height])
return boxes
```
根据获取的detect函数输出的boxes、scores、class_ids信息在原图进行结果可视化,包括用绘制图片中检测到的物体位置、类别和置信度分数,得到最终的YOLOV5目标检测结果输出。
```
def draw_detections(self, image, boxes, scores, class_ids):
for box, score, class_id in zip(boxes, scores, class_ids):
cx, cy, w, h = box.astype(int)
# 绘制检测物体框
cv2.rectangle(image, (cx, cy), (cx + w, cy + h), (0, 255, 255), thickness=2)
label = self.classNames[class_id]
label = f'{label} {int(score * 100)}%'
labelSize, baseLine = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
cv2.putText(image, label, (cx, cy - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 255), thickness=2)
return image
```
### 运行示例
1.参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2.运行示例
```
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
#进入示例程序目录
cd Python/Detector/YOLOV5
# 运行示例
python detect_migraphx.py --imgpath ./data/images/bus.jpg --modelpath ./weights/yolov5s.onnx --objectThreshold 0.5 --confThreshold 0.25 --nmsThreshold 0.5
```
输入参数中可根据需要进行修改,程序运行结束会在当前目录生成YOLOV5检测结果图片。
 ## YOLOV7检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV7是2022年最新出现的一种YOLO系列目标检测模型,在论文 [YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.02696)中提出。
## YOLOV7检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV7是2022年最新出现的一种YOLO系列目标检测模型,在论文 [YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.02696)中提出。
 本示例采用YOLOv7的官方源码:https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7,作者提供了多个预训练模型,本示例使用yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型,将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型下载下来后,保存到Pytorch_YOLOV7工程的weights目录。
### 环境配置
运行YOLOV7模型的Python示例首先需要进行环境配置,包括安装torch、torchvision以及程序运行所需要的依赖。
1、安装torch、torchvision
2、安装程序运行的依赖
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV7工程根目录
cd
# 安装程序运行的依赖
pip install -r requirement.txt
```
### 模型转换
通过下面的步骤可以将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV7工程根目录
cd
#转换模型
python export.py --weights ./weight/yolov7-tiny.pt --img-size 640 640
```
注意:如果需要修改onnx模型的输入大小,可以调整--img-size参数,同时模型输入batch默认为1,若想修改可以通过添加--batch-size设置,程序运行结束后,在当前目录下会生成onnx格式的YOLOV7模型,并将该模型保存到了samples工程中的Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV7目录中,可以用来MIGraphX加载推理。
### 模型推理
#### 预处理
待检测图片输入模型进行检测之前需要进行预处理,主要包括调整输入的尺寸,归一化等操作。
1. 转换数据排布为NCHW
2. 调整输入数据的尺寸为(1,3,640,640)
```python
def prepare_input(self, image):
self.img_height, self.img_width = image.shape[:2]
input_img = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 调整图像的尺寸为YOLOV7的输入尺寸
input_img = cv2.resize(input_img, (self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight))
# 调整输入数据的维度
input_img = input_img.transpose(2, 0, 1)
# 拓展维度,增加batch维度
input_img = np.expand_dims(input_img, 0)
input_img = np.ascontiguousarray(input_img)
input_img = input_img.astype(np.float32)
# 归一化[0.0, 1.0]
input_img = input_img / 255
return input_img
```
其中模型输入的inputWidth、inputHeight通过migraphx对输入模型进行解析获取,代码位置见YOLOV7类初始化位置。
```
class YOLOv7:
def __init__(self, path, obj_thres=0.5, conf_thres=0.7, iou_thres=0.5):
self.objectThreshold = obj_thres
self.confThreshold = conf_thres
self.nmsThreshold = iou_thres
# 获取模型检测的类别信息
self.classNames = list(map(lambda x: x.strip(), open('./weights/coco.names', 'r').readlines()))
# 解析推理模型
self.model = migraphx.parse_onnx(path)
# 获取模型的输入name
self.inputName = self.model.get_parameter_names()[0]
# 获取模型的输入尺寸
inputShape = self.model.get_parameter_shapes()[self.inputName].lens()
self.inputHeight = int(inputShape[2])
self.inputWidth = int(inputShape[3])
```
#### 推理
输入图片预处理完成之后开始进行推理,首先需要利用migraphx进行编译,然后对输入数据进行前向计算得到模型的输出result,在detect函数中调用定义的process_output函数对result进行后处理,得到图片中含有物体的anchor坐标信息、类别置信度、类别ID。
```
def detect(self, image):
# 输入图片预处理
input_img = self.prepare_input(image)
# 模型编译
self.model.compile(t=migraphx.get_target("gpu"), device_id=0) # device_id: 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备
print("Success to compile")
# 执行推理
print("Start to inference")
start = time.time()
result = self.model.run({self.model.get_parameter_names()[0]: migraphx.argument(input_img)})
print('net forward time: {:.4f}'.format(time.time() - start))
# 模型输出结果后处理
boxes, scores, class_ids = self.process_output(result)
return boxes, scores, class_ids
```
其中对migraphx推理输出result进行后处理,首先需要对生成的anchor根据是否有物体阈值objectThreshold、置信度阈值confThreshold进行筛选,相关过程定义在process_output函数中。获取筛选后的anchor的坐标信息之后,需要将坐标映射到原图中的位置,相关过程定义在rescale_boxes函数中。
```
def process_output(self, output):
predictions = np.squeeze(output[0])
# 筛选包含物体的anchor
obj_conf = predictions[:, 4]
predictions = predictions[obj_conf > self.objectThreshold]
obj_conf = obj_conf[obj_conf > self.objectThreshold]
# 筛选大于置信度阈值的anchor
predictions[:, 5:] *= obj_conf[:, np.newaxis]
scores = np.max(predictions[:, 5:], axis=1)
valid_scores = scores > self.confThreshold
predictions = predictions[valid_scores]
scores = scores[valid_scores]
# 获取最高置信度分数对应的类别ID
class_ids = np.argmax(predictions[:, 5:], axis=1)
# 获取每个物体对应的anchor
boxes = self.extract_boxes(predictions)
# 执行非极大值抑制消除冗余anchor
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes.tolist(), scores.tolist(), self.confThreshold, self.nmsThreshold).flatten()
return boxes[indices], scores[indices], class_ids[indices]
def rescale_boxes(self, boxes):
# 对anchor尺寸进行变换
input_shape = np.array([self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight, self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight])
boxes = np.divide(boxes, input_shape, dtype=np.float32)
boxes *= np.array([self.img_width, self.img_height, self.img_width, self.img_height])
return boxes
```
根据获取的detect函数输出的boxes、scores、class_ids信息在原图进行结果可视化,包括用绘制图片中检测到的物体位置、类别和置信度分数,得到最终的YOLOV7目标检测结果输出。
```
def draw_detections(self, image, boxes, scores, class_ids):
for box, score, class_id in zip(boxes, scores, class_ids):
cx, cy, w, h = box.astype(int)
# 绘制检测物体框
cv2.rectangle(image, (cx, cy), (cx + w, cy + h), (0, 255, 255), thickness=2)
label = self.classNames[class_id]
label = f'{label} {int(score * 100)}%'
labelSize, baseLine = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
cv2.putText(image, label, (cx, cy - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 255), thickness=2)
return image
```
### 运行示例
1.参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2.运行示例
```
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
#进入示例程序目录
cd Python/Detector/YOLOV7
# 运行示例
python detect_migraphx.py --imgpath ./inference/images/bus.jpg --modelpath ./weights/yolov7-tiny.onnx --objectThreshold 0.5 --confThreshold 0.25 --nmsThreshold 0.5
```
输入参数中可根据需要进行修改,程序运行结束会在当前目录生成YOLOV7检测结果图片。
本示例采用YOLOv7的官方源码:https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7,作者提供了多个预训练模型,本示例使用yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型,将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型下载下来后,保存到Pytorch_YOLOV7工程的weights目录。
### 环境配置
运行YOLOV7模型的Python示例首先需要进行环境配置,包括安装torch、torchvision以及程序运行所需要的依赖。
1、安装torch、torchvision
2、安装程序运行的依赖
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV7工程根目录
cd
# 安装程序运行的依赖
pip install -r requirement.txt
```
### 模型转换
通过下面的步骤可以将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV7工程根目录
cd
#转换模型
python export.py --weights ./weight/yolov7-tiny.pt --img-size 640 640
```
注意:如果需要修改onnx模型的输入大小,可以调整--img-size参数,同时模型输入batch默认为1,若想修改可以通过添加--batch-size设置,程序运行结束后,在当前目录下会生成onnx格式的YOLOV7模型,并将该模型保存到了samples工程中的Resource/Models/Detector/YOLOV7目录中,可以用来MIGraphX加载推理。
### 模型推理
#### 预处理
待检测图片输入模型进行检测之前需要进行预处理,主要包括调整输入的尺寸,归一化等操作。
1. 转换数据排布为NCHW
2. 调整输入数据的尺寸为(1,3,640,640)
```python
def prepare_input(self, image):
self.img_height, self.img_width = image.shape[:2]
input_img = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 调整图像的尺寸为YOLOV7的输入尺寸
input_img = cv2.resize(input_img, (self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight))
# 调整输入数据的维度
input_img = input_img.transpose(2, 0, 1)
# 拓展维度,增加batch维度
input_img = np.expand_dims(input_img, 0)
input_img = np.ascontiguousarray(input_img)
input_img = input_img.astype(np.float32)
# 归一化[0.0, 1.0]
input_img = input_img / 255
return input_img
```
其中模型输入的inputWidth、inputHeight通过migraphx对输入模型进行解析获取,代码位置见YOLOV7类初始化位置。
```
class YOLOv7:
def __init__(self, path, obj_thres=0.5, conf_thres=0.7, iou_thres=0.5):
self.objectThreshold = obj_thres
self.confThreshold = conf_thres
self.nmsThreshold = iou_thres
# 获取模型检测的类别信息
self.classNames = list(map(lambda x: x.strip(), open('./weights/coco.names', 'r').readlines()))
# 解析推理模型
self.model = migraphx.parse_onnx(path)
# 获取模型的输入name
self.inputName = self.model.get_parameter_names()[0]
# 获取模型的输入尺寸
inputShape = self.model.get_parameter_shapes()[self.inputName].lens()
self.inputHeight = int(inputShape[2])
self.inputWidth = int(inputShape[3])
```
#### 推理
输入图片预处理完成之后开始进行推理,首先需要利用migraphx进行编译,然后对输入数据进行前向计算得到模型的输出result,在detect函数中调用定义的process_output函数对result进行后处理,得到图片中含有物体的anchor坐标信息、类别置信度、类别ID。
```
def detect(self, image):
# 输入图片预处理
input_img = self.prepare_input(image)
# 模型编译
self.model.compile(t=migraphx.get_target("gpu"), device_id=0) # device_id: 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备
print("Success to compile")
# 执行推理
print("Start to inference")
start = time.time()
result = self.model.run({self.model.get_parameter_names()[0]: migraphx.argument(input_img)})
print('net forward time: {:.4f}'.format(time.time() - start))
# 模型输出结果后处理
boxes, scores, class_ids = self.process_output(result)
return boxes, scores, class_ids
```
其中对migraphx推理输出result进行后处理,首先需要对生成的anchor根据是否有物体阈值objectThreshold、置信度阈值confThreshold进行筛选,相关过程定义在process_output函数中。获取筛选后的anchor的坐标信息之后,需要将坐标映射到原图中的位置,相关过程定义在rescale_boxes函数中。
```
def process_output(self, output):
predictions = np.squeeze(output[0])
# 筛选包含物体的anchor
obj_conf = predictions[:, 4]
predictions = predictions[obj_conf > self.objectThreshold]
obj_conf = obj_conf[obj_conf > self.objectThreshold]
# 筛选大于置信度阈值的anchor
predictions[:, 5:] *= obj_conf[:, np.newaxis]
scores = np.max(predictions[:, 5:], axis=1)
valid_scores = scores > self.confThreshold
predictions = predictions[valid_scores]
scores = scores[valid_scores]
# 获取最高置信度分数对应的类别ID
class_ids = np.argmax(predictions[:, 5:], axis=1)
# 获取每个物体对应的anchor
boxes = self.extract_boxes(predictions)
# 执行非极大值抑制消除冗余anchor
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes.tolist(), scores.tolist(), self.confThreshold, self.nmsThreshold).flatten()
return boxes[indices], scores[indices], class_ids[indices]
def rescale_boxes(self, boxes):
# 对anchor尺寸进行变换
input_shape = np.array([self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight, self.inputWidth, self.inputHeight])
boxes = np.divide(boxes, input_shape, dtype=np.float32)
boxes *= np.array([self.img_width, self.img_height, self.img_width, self.img_height])
return boxes
```
根据获取的detect函数输出的boxes、scores、class_ids信息在原图进行结果可视化,包括用绘制图片中检测到的物体位置、类别和置信度分数,得到最终的YOLOV7目标检测结果输出。
```
def draw_detections(self, image, boxes, scores, class_ids):
for box, score, class_id in zip(boxes, scores, class_ids):
cx, cy, w, h = box.astype(int)
# 绘制检测物体框
cv2.rectangle(image, (cx, cy), (cx + w, cy + h), (0, 255, 255), thickness=2)
label = self.classNames[class_id]
label = f'{label} {int(score * 100)}%'
labelSize, baseLine = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
cv2.putText(image, label, (cx, cy - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 255), thickness=2)
return image
```
### 运行示例
1.参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2.运行示例
```
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
#进入示例程序目录
cd Python/Detector/YOLOV7
# 运行示例
python detect_migraphx.py --imgpath ./inference/images/bus.jpg --modelpath ./weights/yolov7-tiny.onnx --objectThreshold 0.5 --confThreshold 0.25 --nmsThreshold 0.5
```
输入参数中可根据需要进行修改,程序运行结束会在当前目录生成YOLOV7检测结果图片。
 ## 图像分割
本示例采用了经典的Unet模型进行图像分割,模型下载地址:https://www.dropbox.com/s/3ntkhyk30x05uuv/unet_13_256.onnx,将unet_13_256.onnx文件保存在Resource\Models\Segmentation文件夹下。模型结构如下图所示(可以通过netron工具(https://netron.app/)查看模型结构),该模型的输入shape为[batch_size,3,256,256],输出shape为[batch_size,1,256,256],数据排布为NCHW。

### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
1.尺度变换,将图像resize到256x256大小
2.归一化,将数据归一化到[0.0, 1.0]之间
3.数据排布,将数据从HWC转换为CHW,再将维度转换为NCHW
本示例代码通过如下方式实现预处理操作:
```python
def Preprocessing(pil_img, newW, newH):
assert newW > 0 and newH > 0, 'Scale is too small' # 判断规定的尺寸是否为空
img_nd = cv2.resize(pil_img, (newW, newH)) # 将图像尺寸修改为256x256
img_nd = cv2.cvtColor(img_nd, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # BGR转换为RGB
img_trans = img_nd.transpose((2, 0, 1)) # HWC转换为CHW
if img_trans.max() > 1: # 保证数据处于0-1之间的浮点数
img_trans = img_trans / 255.0
img_trans = np.expand_dims(img_trans, 0) # CHW转换为NCHW
img = img_trans.astype(np.float32) # 转换成浮点型数据
return img
```
### 推理
完成图像预处理后,就可以执行推理,得到推理结果。
```python
# 加载模型
model = migraphx.parse_onnx("../../Resource/Models/Segmentation/unet_13_256.onnx")
# 编译模型
model.compile(migraphx.get_target("gpu"), device_id=0) #device_id: 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备
# 图像预处理
img = cv2.imread("../../Resource/Images/car1.jpeg")
input_img = Preprocessing(img, 256, 256)
# 模型推理
mask = model.run({'inputs':input_img})
output_mask = np.array(mask[0])[0] # 获取推理结果,shape为(1,256,256)
probs = Sigmoid(output_mask) # 计算sigmoid值
# 0/1像素值,当概率值大于0.996时,值为255,小于等于0.996时,值为0
output_mask[probs > 0.996] = 255
output_mask[probs <= 0.996] = 0
output = output_mask.astype(np.uint8)[0] # 将浮点数类型转换为无符号整型,shape为(256,256)
cv2.imwrite("output.jpg", output) # 保存图像分割结果
```
1.Preprocessing函数返回预处理后的数据(numpy类型),然后通过model.run({'inputs':input_img})得到推理结果,因为只有输入一张图片,所以通过mask[0]获取第一个输出节点的数据即可。
2.模型得到的推理结果并不能直接作为分割结果。首先,需要计算sigmoid值,当概率值大于0.996时值为255,小于等于0.996时值为0。其次,将数据类型转换为无符号整形。最终,保存结果得到分割图像。
注:本次采用的模型权重onnx文件是通过使用具有普通背景的汽车图像来训练的。因此,“现实世界“图像的分割结果不完美是意料之中的。为了获得更好的结果,建议对现实世界示例数据集上的模型进行微调。
### 运行示例
1.参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2.安装依赖:
```Python
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
# 进入示例程序目录
cd Python/Segmentation
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
3.在Python/Segmentation目录下执行如下命令运行该示例程序:
```
python Unet.py
```
输出结果为:

## 超分辨率重建
### 模型简介
图像超分辨率重建技术是指设计并采用某种算法,使得可以通过观测到的低分辨率(Low Resolution, LR)图像重建出近似真实高分辨率(High Resolution , HR)图像的方法。本次部署的超分模型是2016提出的ESPCN网络,主要通过一系列卷积层不断提取图像特征,最后通过sub-pixel亚像素卷积层提高图像分辨率,从而实现图像超分辨率的方法。ESPCN网络结构如下图所示:

本示例采用onnx官方提供的ESPCN模型示例:https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/main/vision/super_resolution/sub_pixel_cnn_2016,将super.onnx文件保存在Resource\Models\Super_Resolution文件夹下。
### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对输入图像做如下预处理操作:
1.图像尺寸resize到224x224
2.分离图像通道,变为B、G、R三个通道图像;
3.BGR格式通过公式转换为YCrCb格式,得到Y、Cb、Cr三通道图像;
4.只处理Y通道图像,转换数据排布为NCHW;
本示例代码采用了OpenCV实现预处理操作:
```python
def bgr_to_ycbcr(B, G, R):
Y = 0.299 * R + 0.587 * G + 0.114 * B
Cr = (R - Y) * 0.713 + 128
Cb = (B - Y) * 0.564 + 128
return Y, Cr, Cb
def Preprocessing(pathOfImage):
orig_img = cv2.imread(pathOfImage, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # cv2.IMREAD_COLOR:彩色图,cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE:灰度图
img = cv2.resize(orig_img, (224,224)) # 调整图像为固定尺寸224x224
bImg, gImg, rImg = cv2.split(img) # 分离图片
img_y_0, img_cr, img_cb = bgr_to_ycbcr(bImg, gImg, rImg) # bgr转换为YCbCr
img_ndarray = np.asarray(img_y_0) # 复制img_y_0对象,转换为array([224,224])
img_y = np.reshape(img_ndarray, (1,1,224,224)) # 改变数组形状,满足模型输入,变为(1,1,224,224) 转换为(N,C,H,W)格式
img_y = img_y.astype(np.float32) / 255.0 # unit8转换成float32
return img_y, img_cr, img_cb
```
### 推理
完成图像预处理后,就开始执行推理,得到推理结果。
```python
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 加载模型
model = migraphx.parse_onnx("../../Resource/Models/Super/super.onnx")
inputName = model.get_parameter_names()
inputShape = model.get_parameter_shapes()
print("inputName:{0} \ninputShape:{1}".format(inputName, inputShape))
# 编译模型
model.compile(t=migraphx.get_target("gpu"), device_id=0) # device_id: 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备
# 图像预处理
pathOfImage = "../../Resource/Images/cat.jpg"
img_Y, img_cr, img_cb = Preprocessing(pathOfImage)
# 模型推理结果
results = model.run({"input": img_Y})
# 获取输出节点属性
result = results[0] # 获取第一个输出节点的数据,migraphx.argument类型
outputShape = result.get_shape() # 输出节点的shape,migraphx.shape类型
outputSize = outputShape.lens() # 每一维大小,维度顺序为(N,C,H,W)
numberOfOutput = outputShape.elements() # 输出节点元素的个数
data = np.array(results[0])[0]
img_out_y = np.uint8((data * 255.0).clip(0, 255)[0]) # 将浮点型数据转换为0-255之间整型数据
# 将YCbCr格式转换为BGR格式,再将三通道合并到一起,得到重建图像
img_cr = cv2.resize(img_cr, (672, 672))
img_cb = cv2.resize(img_cb, (672, 672))
final_img = ycbcr_to_bgr(img_out_y, img_cr, img_cb)
cv2.imwrite("output.jpg", final_img) # 保存超分辨率重建图像的结果
```
1.Preprocessing函数返回Y、Cr、Cb三通道图像,只将Y通道图像作为输入数据,通过执行model.run({"input": img_Y})得到推理结果,因为只有输入一张图片,所以只通过results[0]获取第一个输出节点的数据即可。
2.该模型只处理Y通道图像,得到推理结果之后,再通过ycrcb_to_bgr()函数将YCrCb格式转换为BGR格式,转换公式采用的是opencv官方提供的公式,链接:https://docs.opencv.org/3.4.11/de/d25/imgproc_color_conversions.html,最后再将三通道合并到一起,得到最终的重建图像。
### 运行示例
1.参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2.安装依赖:
```
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
# 进入示例程序目录
cd Python/Super_Resolution
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
3.在Python/Super_Resolution目录下执行如下命令运行该示例程序:
```python
# 运行示例
python Espcn.py
```
输出结果如下,左图为原图,右图为重建过后的图像,分辨率提高了三倍。

## 图像分割
本示例采用了经典的Unet模型进行图像分割,模型下载地址:https://www.dropbox.com/s/3ntkhyk30x05uuv/unet_13_256.onnx,将unet_13_256.onnx文件保存在Resource\Models\Segmentation文件夹下。模型结构如下图所示(可以通过netron工具(https://netron.app/)查看模型结构),该模型的输入shape为[batch_size,3,256,256],输出shape为[batch_size,1,256,256],数据排布为NCHW。

### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
1.尺度变换,将图像resize到256x256大小
2.归一化,将数据归一化到[0.0, 1.0]之间
3.数据排布,将数据从HWC转换为CHW,再将维度转换为NCHW
本示例代码通过如下方式实现预处理操作:
```python
def Preprocessing(pil_img, newW, newH):
assert newW > 0 and newH > 0, 'Scale is too small' # 判断规定的尺寸是否为空
img_nd = cv2.resize(pil_img, (newW, newH)) # 将图像尺寸修改为256x256
img_nd = cv2.cvtColor(img_nd, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # BGR转换为RGB
img_trans = img_nd.transpose((2, 0, 1)) # HWC转换为CHW
if img_trans.max() > 1: # 保证数据处于0-1之间的浮点数
img_trans = img_trans / 255.0
img_trans = np.expand_dims(img_trans, 0) # CHW转换为NCHW
img = img_trans.astype(np.float32) # 转换成浮点型数据
return img
```
### 推理
完成图像预处理后,就可以执行推理,得到推理结果。
```python
# 加载模型
model = migraphx.parse_onnx("../../Resource/Models/Segmentation/unet_13_256.onnx")
# 编译模型
model.compile(migraphx.get_target("gpu"), device_id=0) #device_id: 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备
# 图像预处理
img = cv2.imread("../../Resource/Images/car1.jpeg")
input_img = Preprocessing(img, 256, 256)
# 模型推理
mask = model.run({'inputs':input_img})
output_mask = np.array(mask[0])[0] # 获取推理结果,shape为(1,256,256)
probs = Sigmoid(output_mask) # 计算sigmoid值
# 0/1像素值,当概率值大于0.996时,值为255,小于等于0.996时,值为0
output_mask[probs > 0.996] = 255
output_mask[probs <= 0.996] = 0
output = output_mask.astype(np.uint8)[0] # 将浮点数类型转换为无符号整型,shape为(256,256)
cv2.imwrite("output.jpg", output) # 保存图像分割结果
```
1.Preprocessing函数返回预处理后的数据(numpy类型),然后通过model.run({'inputs':input_img})得到推理结果,因为只有输入一张图片,所以通过mask[0]获取第一个输出节点的数据即可。
2.模型得到的推理结果并不能直接作为分割结果。首先,需要计算sigmoid值,当概率值大于0.996时值为255,小于等于0.996时值为0。其次,将数据类型转换为无符号整形。最终,保存结果得到分割图像。
注:本次采用的模型权重onnx文件是通过使用具有普通背景的汽车图像来训练的。因此,“现实世界“图像的分割结果不完美是意料之中的。为了获得更好的结果,建议对现实世界示例数据集上的模型进行微调。
### 运行示例
1.参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2.安装依赖:
```Python
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
# 进入示例程序目录
cd Python/Segmentation
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
3.在Python/Segmentation目录下执行如下命令运行该示例程序:
```
python Unet.py
```
输出结果为:

## 超分辨率重建
### 模型简介
图像超分辨率重建技术是指设计并采用某种算法,使得可以通过观测到的低分辨率(Low Resolution, LR)图像重建出近似真实高分辨率(High Resolution , HR)图像的方法。本次部署的超分模型是2016提出的ESPCN网络,主要通过一系列卷积层不断提取图像特征,最后通过sub-pixel亚像素卷积层提高图像分辨率,从而实现图像超分辨率的方法。ESPCN网络结构如下图所示:

本示例采用onnx官方提供的ESPCN模型示例:https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/main/vision/super_resolution/sub_pixel_cnn_2016,将super.onnx文件保存在Resource\Models\Super_Resolution文件夹下。
### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对输入图像做如下预处理操作:
1.图像尺寸resize到224x224
2.分离图像通道,变为B、G、R三个通道图像;
3.BGR格式通过公式转换为YCrCb格式,得到Y、Cb、Cr三通道图像;
4.只处理Y通道图像,转换数据排布为NCHW;
本示例代码采用了OpenCV实现预处理操作:
```python
def bgr_to_ycbcr(B, G, R):
Y = 0.299 * R + 0.587 * G + 0.114 * B
Cr = (R - Y) * 0.713 + 128
Cb = (B - Y) * 0.564 + 128
return Y, Cr, Cb
def Preprocessing(pathOfImage):
orig_img = cv2.imread(pathOfImage, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # cv2.IMREAD_COLOR:彩色图,cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE:灰度图
img = cv2.resize(orig_img, (224,224)) # 调整图像为固定尺寸224x224
bImg, gImg, rImg = cv2.split(img) # 分离图片
img_y_0, img_cr, img_cb = bgr_to_ycbcr(bImg, gImg, rImg) # bgr转换为YCbCr
img_ndarray = np.asarray(img_y_0) # 复制img_y_0对象,转换为array([224,224])
img_y = np.reshape(img_ndarray, (1,1,224,224)) # 改变数组形状,满足模型输入,变为(1,1,224,224) 转换为(N,C,H,W)格式
img_y = img_y.astype(np.float32) / 255.0 # unit8转换成float32
return img_y, img_cr, img_cb
```
### 推理
完成图像预处理后,就开始执行推理,得到推理结果。
```python
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 加载模型
model = migraphx.parse_onnx("../../Resource/Models/Super/super.onnx")
inputName = model.get_parameter_names()
inputShape = model.get_parameter_shapes()
print("inputName:{0} \ninputShape:{1}".format(inputName, inputShape))
# 编译模型
model.compile(t=migraphx.get_target("gpu"), device_id=0) # device_id: 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备
# 图像预处理
pathOfImage = "../../Resource/Images/cat.jpg"
img_Y, img_cr, img_cb = Preprocessing(pathOfImage)
# 模型推理结果
results = model.run({"input": img_Y})
# 获取输出节点属性
result = results[0] # 获取第一个输出节点的数据,migraphx.argument类型
outputShape = result.get_shape() # 输出节点的shape,migraphx.shape类型
outputSize = outputShape.lens() # 每一维大小,维度顺序为(N,C,H,W)
numberOfOutput = outputShape.elements() # 输出节点元素的个数
data = np.array(results[0])[0]
img_out_y = np.uint8((data * 255.0).clip(0, 255)[0]) # 将浮点型数据转换为0-255之间整型数据
# 将YCbCr格式转换为BGR格式,再将三通道合并到一起,得到重建图像
img_cr = cv2.resize(img_cr, (672, 672))
img_cb = cv2.resize(img_cb, (672, 672))
final_img = ycbcr_to_bgr(img_out_y, img_cr, img_cb)
cv2.imwrite("output.jpg", final_img) # 保存超分辨率重建图像的结果
```
1.Preprocessing函数返回Y、Cr、Cb三通道图像,只将Y通道图像作为输入数据,通过执行model.run({"input": img_Y})得到推理结果,因为只有输入一张图片,所以只通过results[0]获取第一个输出节点的数据即可。
2.该模型只处理Y通道图像,得到推理结果之后,再通过ycrcb_to_bgr()函数将YCrCb格式转换为BGR格式,转换公式采用的是opencv官方提供的公式,链接:https://docs.opencv.org/3.4.11/de/d25/imgproc_color_conversions.html,最后再将三通道合并到一起,得到最终的重建图像。
### 运行示例
1.参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2.安装依赖:
```
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
# 进入示例程序目录
cd Python/Super_Resolution
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
3.在Python/Super_Resolution目录下执行如下命令运行该示例程序:
```python
# 运行示例
python Espcn.py
```
输出结果如下,左图为原图,右图为重建过后的图像,分辨率提高了三倍。

 本示例采用如下的开源实现:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3, 作者在V9.6.0版本中提供多种不同的YOLOV3预训练模型,其中包括yolov3、yolov3-fixed、yolov3-spp、yolov3-tiny四个版本。本示例选择yolov3-tiny.pt预训练模型进行构建MIGraphX推理,下载YOLOV3的预训练模型yolov3-tiny.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV3工程的weights目录。
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV3源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov3-tiny.pt转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV3工程根目录
cd
本示例采用如下的开源实现:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3, 作者在V9.6.0版本中提供多种不同的YOLOV3预训练模型,其中包括yolov3、yolov3-fixed、yolov3-spp、yolov3-tiny四个版本。本示例选择yolov3-tiny.pt预训练模型进行构建MIGraphX推理,下载YOLOV3的预训练模型yolov3-tiny.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV3工程的weights目录。
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV3源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov3-tiny.pt转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV3工程根目录
cd  ## YOLOV7检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV7是2022年最新出现的一种YOLO系列目标检测模型,在论文 [YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.02696)中提出。
## YOLOV7检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV7是2022年最新出现的一种YOLO系列目标检测模型,在论文 [YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.02696)中提出。
 本示例采用YOLOv7的官方源码:https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7, 作者提供了多个预训练模型,本示例使用yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型,将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型下载下来后,保存到Pytorch_YOLOV7工程的weights目录。
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV7源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV7工程根目录
cd
本示例采用YOLOv7的官方源码:https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7, 作者提供了多个预训练模型,本示例使用yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型,将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型下载下来后,保存到Pytorch_YOLOV7工程的weights目录。
### 模型转换
官方提供的YOLOV7源码中包含导出onnx模型的程序,通过下面的步骤可以将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型转换成onnx格式:
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV7工程根目录
cd  ## 图像分割
本示例采用了经典的Unet模型进行图像分割,模型下载地址:https://www.dropbox.com/s/3ntkhyk30x05uuv/unet_13_256.onnx,将unet_13_256.onnx文件保存在Resource\Models\Segmentation文件夹下。模型结构如下图所示(可以通过netron工具(https://netron.app/)查看具体的模型结构),该模型的输入shape为[batch_size,3,256,256],输出shape为[batch_size,1,256,256],数据排布为NCHW。

### 参数设置
samples工程中的Resource/Configuration.xml文件的Unet节点表示图像分割模型Unet的参数,主要包括模型存放路径。
```xml
## 图像分割
本示例采用了经典的Unet模型进行图像分割,模型下载地址:https://www.dropbox.com/s/3ntkhyk30x05uuv/unet_13_256.onnx,将unet_13_256.onnx文件保存在Resource\Models\Segmentation文件夹下。模型结构如下图所示(可以通过netron工具(https://netron.app/)查看具体的模型结构),该模型的输入shape为[batch_size,3,256,256],输出shape为[batch_size,1,256,256],数据排布为NCHW。

### 参数设置
samples工程中的Resource/Configuration.xml文件的Unet节点表示图像分割模型Unet的参数,主要包括模型存放路径。
```xml
 本示例采用如下的开源实现:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3,作者在V9.6.0版本中提供多种不同的YOLOV3预训练模型,其中包括yolov3、yolov3-fixed、yolov3-spp、yolov3-tiny四个版本。本示例选择yolov3-tiny.pt预训练模型进行构建MIGraphX推理,下载YOLOV3的预训练模型yolov3-tiny.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV3工程的weights目录。
### 环境配置
运行YOLOV3模型的Python示例首先需要进行环境配置,包括安装torch、torchvision以及程序运行所需要的依赖。
1、安装torch、torchvision
2、安装程序运行的依赖
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV3工程根目录
cd
本示例采用如下的开源实现:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3,作者在V9.6.0版本中提供多种不同的YOLOV3预训练模型,其中包括yolov3、yolov3-fixed、yolov3-spp、yolov3-tiny四个版本。本示例选择yolov3-tiny.pt预训练模型进行构建MIGraphX推理,下载YOLOV3的预训练模型yolov3-tiny.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV3工程的weights目录。
### 环境配置
运行YOLOV3模型的Python示例首先需要进行环境配置,包括安装torch、torchvision以及程序运行所需要的依赖。
1、安装torch、torchvision
2、安装程序运行的依赖
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV3工程根目录
cd  YOLOV5的官方源码地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5,官方源码中具有YOLOV5n、YOLOV5s、YOLOV5m、YOLOV5l等不同的版本。本示例采用YOLOV5s版本进行MIGraphX推理示例构建,下载YOLOV5s的预训练模型yolov5s.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV5工程的weights目录。
### 环境配置
运行YOLOV5模型的Python示例首先需要进行环境配置,包括安装torch、torchvision以及程序运行所需要的依赖。
1、安装torch、torchvision
2、安装程序运行的依赖
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV5工程根目录
cd
YOLOV5的官方源码地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5,官方源码中具有YOLOV5n、YOLOV5s、YOLOV5m、YOLOV5l等不同的版本。本示例采用YOLOV5s版本进行MIGraphX推理示例构建,下载YOLOV5s的预训练模型yolov5s.pt保存在Pytorch_YOLOV5工程的weights目录。
### 环境配置
运行YOLOV5模型的Python示例首先需要进行环境配置,包括安装torch、torchvision以及程序运行所需要的依赖。
1、安装torch、torchvision
2、安装程序运行的依赖
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV5工程根目录
cd  ## YOLOV7检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV7是2022年最新出现的一种YOLO系列目标检测模型,在论文 [YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.02696)中提出。
## YOLOV7检测器
### 模型简介
YOLOV7是2022年最新出现的一种YOLO系列目标检测模型,在论文 [YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.02696)中提出。
 本示例采用YOLOv7的官方源码:https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7,作者提供了多个预训练模型,本示例使用yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型,将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型下载下来后,保存到Pytorch_YOLOV7工程的weights目录。
### 环境配置
运行YOLOV7模型的Python示例首先需要进行环境配置,包括安装torch、torchvision以及程序运行所需要的依赖。
1、安装torch、torchvision
2、安装程序运行的依赖
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV7工程根目录
cd
本示例采用YOLOv7的官方源码:https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7,作者提供了多个预训练模型,本示例使用yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型,将yolov7-tiny.pt预训练模型下载下来后,保存到Pytorch_YOLOV7工程的weights目录。
### 环境配置
运行YOLOV7模型的Python示例首先需要进行环境配置,包括安装torch、torchvision以及程序运行所需要的依赖。
1、安装torch、torchvision
2、安装程序运行的依赖
```
# 进入Pytorch_YOLOV7工程根目录
cd  ## 图像分割
本示例采用了经典的Unet模型进行图像分割,模型下载地址:https://www.dropbox.com/s/3ntkhyk30x05uuv/unet_13_256.onnx,将unet_13_256.onnx文件保存在Resource\Models\Segmentation文件夹下。模型结构如下图所示(可以通过netron工具(https://netron.app/)查看模型结构),该模型的输入shape为[batch_size,3,256,256],输出shape为[batch_size,1,256,256],数据排布为NCHW。

### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
1.尺度变换,将图像resize到256x256大小
2.归一化,将数据归一化到[0.0, 1.0]之间
3.数据排布,将数据从HWC转换为CHW,再将维度转换为NCHW
本示例代码通过如下方式实现预处理操作:
```python
def Preprocessing(pil_img, newW, newH):
assert newW > 0 and newH > 0, 'Scale is too small' # 判断规定的尺寸是否为空
img_nd = cv2.resize(pil_img, (newW, newH)) # 将图像尺寸修改为256x256
img_nd = cv2.cvtColor(img_nd, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # BGR转换为RGB
img_trans = img_nd.transpose((2, 0, 1)) # HWC转换为CHW
if img_trans.max() > 1: # 保证数据处于0-1之间的浮点数
img_trans = img_trans / 255.0
img_trans = np.expand_dims(img_trans, 0) # CHW转换为NCHW
img = img_trans.astype(np.float32) # 转换成浮点型数据
return img
```
### 推理
完成图像预处理后,就可以执行推理,得到推理结果。
```python
# 加载模型
model = migraphx.parse_onnx("../../Resource/Models/Segmentation/unet_13_256.onnx")
# 编译模型
model.compile(migraphx.get_target("gpu"), device_id=0) #device_id: 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备
# 图像预处理
img = cv2.imread("../../Resource/Images/car1.jpeg")
input_img = Preprocessing(img, 256, 256)
# 模型推理
mask = model.run({'inputs':input_img})
output_mask = np.array(mask[0])[0] # 获取推理结果,shape为(1,256,256)
probs = Sigmoid(output_mask) # 计算sigmoid值
# 0/1像素值,当概率值大于0.996时,值为255,小于等于0.996时,值为0
output_mask[probs > 0.996] = 255
output_mask[probs <= 0.996] = 0
output = output_mask.astype(np.uint8)[0] # 将浮点数类型转换为无符号整型,shape为(256,256)
cv2.imwrite("output.jpg", output) # 保存图像分割结果
```
1.Preprocessing函数返回预处理后的数据(numpy类型),然后通过model.run({'inputs':input_img})得到推理结果,因为只有输入一张图片,所以通过mask[0]获取第一个输出节点的数据即可。
2.模型得到的推理结果并不能直接作为分割结果。首先,需要计算sigmoid值,当概率值大于0.996时值为255,小于等于0.996时值为0。其次,将数据类型转换为无符号整形。最终,保存结果得到分割图像。
注:本次采用的模型权重onnx文件是通过使用具有普通背景的汽车图像来训练的。因此,“现实世界“图像的分割结果不完美是意料之中的。为了获得更好的结果,建议对现实世界示例数据集上的模型进行微调。
### 运行示例
1.参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2.安装依赖:
```Python
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd
## 图像分割
本示例采用了经典的Unet模型进行图像分割,模型下载地址:https://www.dropbox.com/s/3ntkhyk30x05uuv/unet_13_256.onnx,将unet_13_256.onnx文件保存在Resource\Models\Segmentation文件夹下。模型结构如下图所示(可以通过netron工具(https://netron.app/)查看模型结构),该模型的输入shape为[batch_size,3,256,256],输出shape为[batch_size,1,256,256],数据排布为NCHW。

### 预处理
在将数据输入到模型之前,需要对图像做如下预处理操作:
1.尺度变换,将图像resize到256x256大小
2.归一化,将数据归一化到[0.0, 1.0]之间
3.数据排布,将数据从HWC转换为CHW,再将维度转换为NCHW
本示例代码通过如下方式实现预处理操作:
```python
def Preprocessing(pil_img, newW, newH):
assert newW > 0 and newH > 0, 'Scale is too small' # 判断规定的尺寸是否为空
img_nd = cv2.resize(pil_img, (newW, newH)) # 将图像尺寸修改为256x256
img_nd = cv2.cvtColor(img_nd, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # BGR转换为RGB
img_trans = img_nd.transpose((2, 0, 1)) # HWC转换为CHW
if img_trans.max() > 1: # 保证数据处于0-1之间的浮点数
img_trans = img_trans / 255.0
img_trans = np.expand_dims(img_trans, 0) # CHW转换为NCHW
img = img_trans.astype(np.float32) # 转换成浮点型数据
return img
```
### 推理
完成图像预处理后,就可以执行推理,得到推理结果。
```python
# 加载模型
model = migraphx.parse_onnx("../../Resource/Models/Segmentation/unet_13_256.onnx")
# 编译模型
model.compile(migraphx.get_target("gpu"), device_id=0) #device_id: 设置GPU设备,默认为0号设备
# 图像预处理
img = cv2.imread("../../Resource/Images/car1.jpeg")
input_img = Preprocessing(img, 256, 256)
# 模型推理
mask = model.run({'inputs':input_img})
output_mask = np.array(mask[0])[0] # 获取推理结果,shape为(1,256,256)
probs = Sigmoid(output_mask) # 计算sigmoid值
# 0/1像素值,当概率值大于0.996时,值为255,小于等于0.996时,值为0
output_mask[probs > 0.996] = 255
output_mask[probs <= 0.996] = 0
output = output_mask.astype(np.uint8)[0] # 将浮点数类型转换为无符号整型,shape为(256,256)
cv2.imwrite("output.jpg", output) # 保存图像分割结果
```
1.Preprocessing函数返回预处理后的数据(numpy类型),然后通过model.run({'inputs':input_img})得到推理结果,因为只有输入一张图片,所以通过mask[0]获取第一个输出节点的数据即可。
2.模型得到的推理结果并不能直接作为分割结果。首先,需要计算sigmoid值,当概率值大于0.996时值为255,小于等于0.996时值为0。其次,将数据类型转换为无符号整形。最终,保存结果得到分割图像。
注:本次采用的模型权重onnx文件是通过使用具有普通背景的汽车图像来训练的。因此,“现实世界“图像的分割结果不完美是意料之中的。为了获得更好的结果,建议对现实世界示例数据集上的模型进行微调。
### 运行示例
1.参考《MIGraphX教程》中的安装方法安装MIGraphX并设置好PYTHONPATH
2.安装依赖:
```Python
# 进入migraphx samples工程根目录
cd 