---
title: "Forecasting Energy Demand"
description: "Energy demand forecasting tutorial using TimeGPT AI. Step-by-step Python guide for electricity consumption prediction with 90% faster predictions and superior accuracy."
icon: "bolt"
---
## Introduction
Energy demand forecasting is critical for grid operations, resource allocation, and infrastructure planning. Despite advances in methods, predicting consumption remains challenging due to weather, economic activity, and consumer behavior.
This tutorial demonstrates how TimeGPT simplifies in-zone electricity forecasting while delivering superior accuracy and speed. We will use the [PJM Hourly Energy Consumption dataset](https://www.pjm.com/) covering five regions from October 2023 to September 2024.
### What You'll Learn
- How to load and prepare energy consumption data
- How to generate 4-day ahead forecasts with TimeGPT
- How to evaluate forecast accuracy using MAE and sMAPE
- How TimeGPT compares to deep learning models like N-HiTS
The procedures in this tutorial apply to many time series forecasting scenarios beyond energy demand.
## How to Use TimeGPT to Forecast Energy Demand
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/Nixtla/nixtla/blob/main/nbs/docs/use-cases/3_electricity_demand.ipynb)
### Step 1: Initial Setup
Install and import required packages, then create a NixtlaClient instance to interact with TimeGPT.
```python
import time
import requests
import pandas as pd
from nixtla import NixtlaClient
from utilsforecast.losses import mae, smape
from utilsforecast.evaluation import evaluate
nixtla_client = NixtlaClient(
api_key='my_api_key_provided_by_nixtla' # Defaults to os.environ.get("NIXTLA_API_KEY")
)
```
### Step 2: Load Energy Consumption Data
Load the energy consumption dataset and convert datetime strings to timestamps.
```python
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Nixtla/transfer-learning-time-series/refs/heads/main/datasets/pjm_in_zone.csv')
df['ds'] = pd.to_datetime(df['ds'])
# Examine the dataset
df.groupby('unique_id').head(2)
```
| | unique_id | ds | y |
| ----- | ----------- | --------------------------- | ---------- |
| 0 | AP-AP | 2023-10-01 04:00:00+00:00 | 4042.513 |
| 1 | AP-AP | 2023-10-01 05:00:00+00:00 | 3850.067 |
Plot the data series to visualize seasonal patterns.
```python
nixtla_client.plot(
df,
max_insample_length=365
)
```
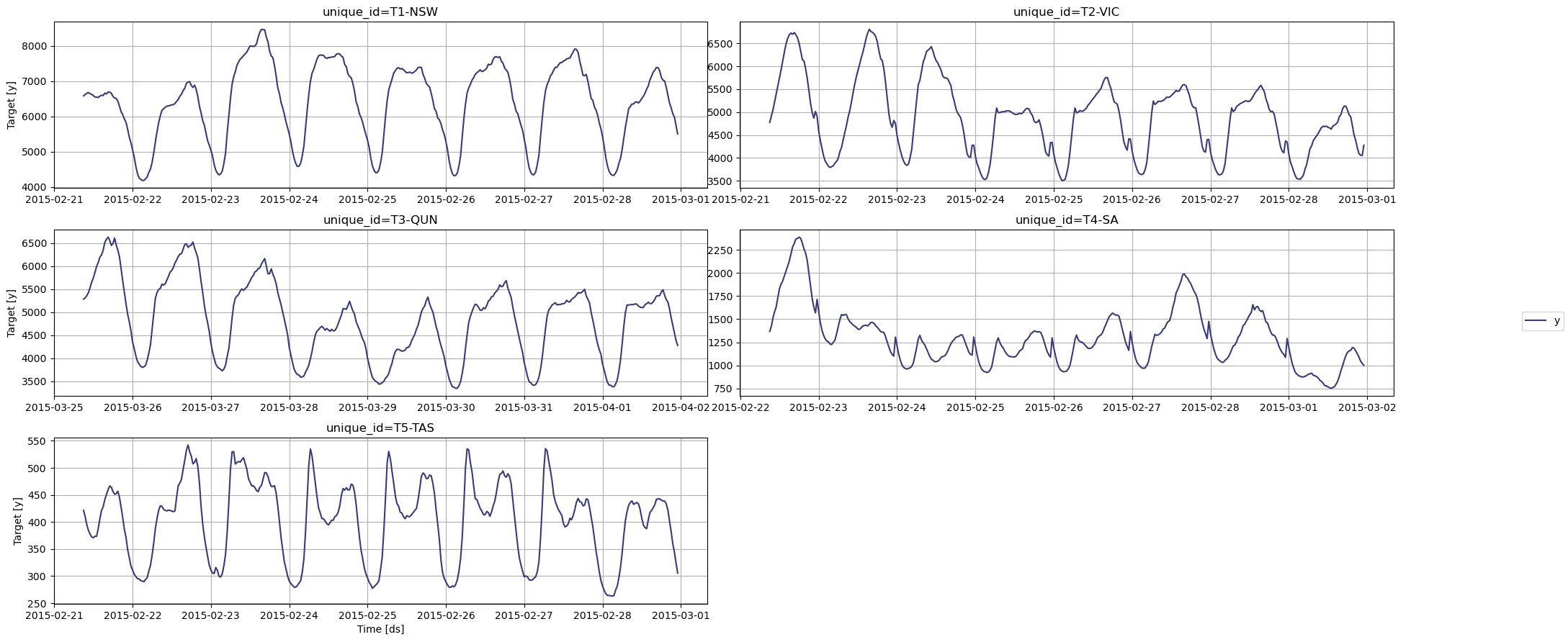
### Step 3: Generate Energy Demand Forecasts with TimeGPT
We'll split our dataset into:
- A training/input set for model calibration
- A testing set (last 4 days) to validate performance
```python
# Prepare test (last 4 days) and input data
test_df = df.groupby('unique_id').tail(96)
input_df = df.groupby('unique_id').apply(lambda group: group.iloc[-1104:-96]).reset_index(drop=True)
# Make forecasts
start = time.time()
fcst_df = nixtla_client.forecast(
df=input_df,
h=96,
level=[90],
finetune_steps=10,
finetune_loss='mae',
model='timegpt-1-long-horizon',
time_col='ds',
target_col='y',
id_col='unique_id'
)
end = time.time()
timegpt_duration = end - start
print(f"Time (TimeGPT): {timegpt_duration}")
# Visualize forecasts against actual values
nixtla_client.plot(
test_df,
fcst_df,
models=['TimeGPT'],
level=[90],
time_col='ds',
target_col='y'
)
```
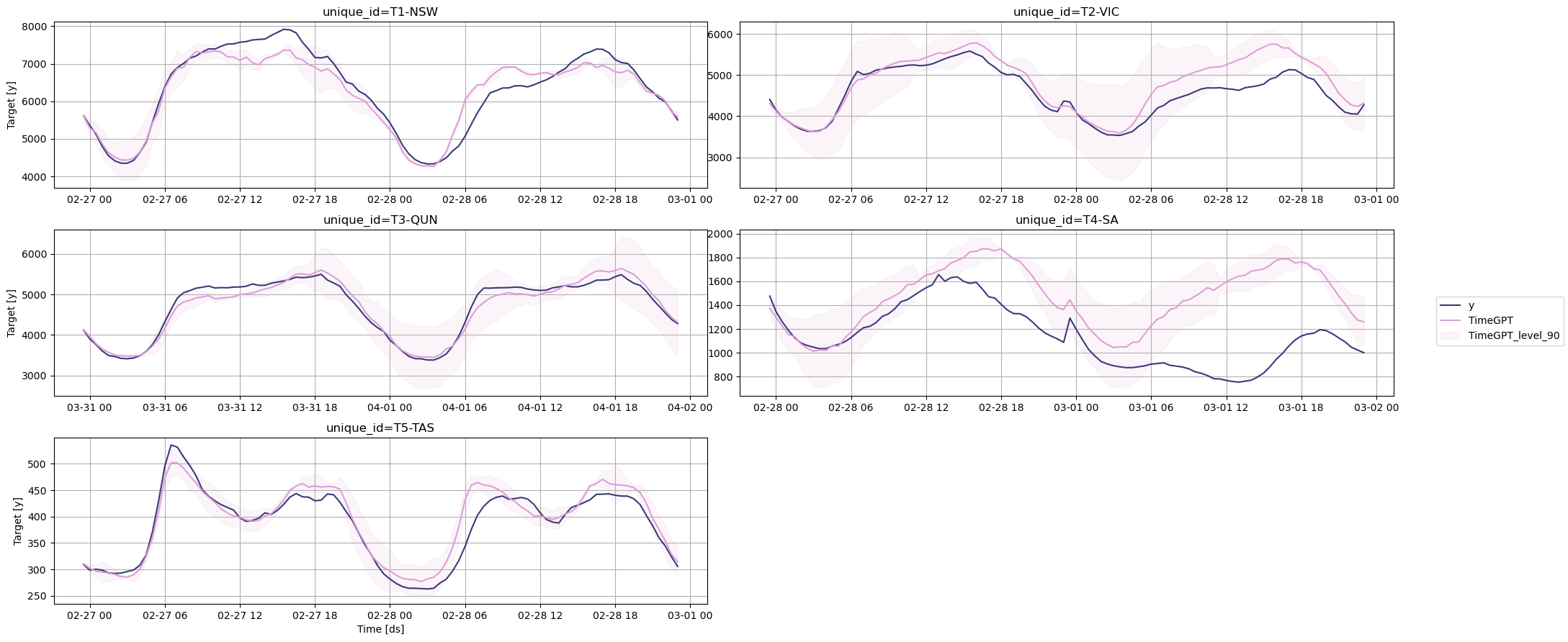
### Step 4: Evaluate Forecast Accuracy
Compute accuracy metrics (MAE and sMAPE) for TimeGPT.
```python
fcst_df['ds'] = pd.to_datetime(fcst_df['ds'])
test_df = pd.merge(test_df, fcst_df, 'left', ['unique_id', 'ds'])
evaluation = evaluate(test_df, [mae, smape], ["TimeGPT"], "y", "unique_id")
average_metrics = evaluation.groupby('metric')['TimeGPT'].mean()
average_metrics
```
### Step 5: Forecast with N-HiTS
For comparison, we train and forecast using the deep-learning model N-HiTS.
```python
from neuralforecast.core import NeuralForecast
from neuralforecast.models import NHITS
# Prepare training dataset by excluding the last 4 days
train_df = df.groupby('unique_id').apply(lambda group: group.iloc[:-96]).reset_index(drop=True)
models = [
NHITS(h=96, input_size=480, scaler_type='robust', batch_size=16, valid_batch_size=8)
]
nf = NeuralForecast(models=models, freq='H')
start = time.time()
nf.fit(df=train_df)
nhits_preds = nf.predict()
end = time.time()
print(f"Time (N-HiTS): {end - start}")
```
### Step 6: Evaluate N-HiTS
Compute accuracy metrics (MAE and sMAPE) for N-HiTS.
```python
preds_df = pd.merge(test_df, nhits_preds, 'left', ['unique_id', 'ds'])
evaluation = evaluate(preds_df, [mae, smape], ["NHITS"], "y", "unique_id")
average_metrics = evaluation.groupby('metric')['NHITS'].mean()
print(average_metrics)
```
## Conclusion
TimeGPT demonstrates substantial performance improvements over N-HiTS across key metrics:
- **Accuracy**: 18.6% lower MAE (882.6 vs 1084.7)
- **Error Rate**: 31.1% lower sMAPE
- **Speed**: 90% faster predictions (4.3 seconds vs 44 seconds)
These results make TimeGPT a powerful tool for forecasting energy consumption and other time-series tasks where both accuracy and speed are critical.
Experiment with the parameters to further optimize performance for your specific use case.
## Related Tutorials
Ready to explore more forecasting applications? Check out these guides:
- [Bitcoin Price Prediction with TimeGPT](/use_cases/bitcoin_price_prediction) - Financial time series forecasting
- [Exogenous Variables Guide](/forecasting/exogenous-variables/numeric_features) - Improve forecasts with external data
- [Long Horizon Forecasting](/forecasting/model-version/longhorizon_model) - Extended forecast periods
Learn more about [TimeGPT capabilities](/introduction/introduction) for time series prediction.