---
title: "Forecasting Bitcoin Prices"
description: "Master Bitcoin price forecasting with TimeGPT. Complete Python tutorial covering cryptocurrency prediction, anomaly detection, uncertainty quantification, and risk management strategies."
icon: "bitcoin"
---
## Introduction
[Time series forecasting](/forecasting/timegpt_quickstart) is essential in finance for trading, risk management, and strategic planning. However, predicting financial asset prices remains challenging due to market volatility.
Whether you believe financial forecasting is possible or your role requires it, [TimeGPT](/introduction/about_timegpt) simplifies the process.
This tutorial demonstrates how to use TimeGPT for Bitcoin price prediction and uncertainty quantification for risk management.
### Why Forecast Bitcoin Prices
Bitcoin (₿), the first decentralized cryptocurrency, records transactions on a blockchain. Bitcoins are mined by solving cryptographic tasks and can be used for payments, trading, or investment.
Bitcoin's volatility and popularity make price forecasting valuable for trading strategies and risk management.
### What You'll Learn
- How to load and prepare Bitcoin price data
- How to generate [short-term forecasts](/forecasting/timegpt_quickstart) with TimeGPT
- How to visualize and interpret forecast results
- How to [detect anomalies](/anomaly_detection/real-time/introduction) and add [exogenous variables](/forecasting/exogenous-variables/numeric_features)
The procedures in this tutorial apply to many [financial asset forecasting](/use_cases/forecasting_energy_demand) scenarios, not just Bitcoin.
## How to Forecast Bitcoin Prices with TimeGPT
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/Nixtla/nixtla/blob/main/nbs/docs/use-cases/2_bitcoin_price_prediction.ipynb)
### Step 1: Load Bitcoin Price Data
Start by loading the Bitcoin price data:
```python
import pandas as pd
# Load Bitcoin historical price data from 2020-2023
df = pd.read_csv(
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Nixtla/transfer-learning-time-series/main/datasets/bitcoin_price_usd.csv',
sep=','
)
df.head()
```
| | Date | Close |
|---|------------|--------------|
| 0 | 2020-01-01 | 7200.174316 |
| 1 | 2020-01-02 | 6985.470215 |
| 2 | 2020-01-03 | 7344.884277 |
| 3 | 2020-01-04 | 7410.656738 |
| 4 | 2020-01-05 | 7411.317383 |
This dataset includes daily Bitcoin closing prices (in USD) from 2020 to 2023. "Closing price" refers to the price at a specific daily time, not a traditional market close.
Next, rename the columns to match TimeGPT's expected `ds` (date) and `y` (target) format.
```python
# Rename columns to TimeGPT's expected format (ds=date, y=target value)
df.rename(columns={'Date': 'ds', 'Close': 'y'}, inplace=True)
```
### Step 2: Get Started with TimeGPT
Initialize the `NixtlaClient` with your Nixtla API key. To learn more about how to set up your API key, see [Setting up your API key](/setup/setting_up_your_api_key).
```python
from nixtla import NixtlaClient
# Initialize TimeGPT client with your API key
nixtla_client = NixtlaClient(
api_key='my_api_key_provided_by_nixtla'
)
```
### Step 3: Visualize the Data
Before attempting any forecasting, it is good practice to visualize the data we want to predict. The `NixtlaClient` class includes a `plot` method for this purpose.
The `plot` method has an `engine` argument that allows you to choose between different plotting libraries. Default is `matplotlib`, but you can also use `plotly` for interactive plots.
```python
# Visualize Bitcoin price history
nixtla_client.plot(df)
```

If you did not rename the columns, specify them explicitly:
```python
nixtla_client.plot(
df,
time_col='Date Column',
target_col='Close Column'
)
```
### Step 4: Forecast with TimeGPT
Now we are ready to generate predictions with TimeGPT. To do this, we will use the `forecast` method from the `NixtlaClient` class.
The `forecast` method requires the following arguments:
- `df`: The DataFrame containing the time series data
- `h`: (int) The forecast horizon. In this case, we will forecast the next 7 days.
- `level`: (list) The confidence level for the prediction intervals. Given the inherent volatility of Bitcoin, we will use multiple confidence levels.
```python
# Generate 7-day forecast with 50%, 80%, and 90% prediction intervals
level = [50, 80, 90]
fcst = nixtla_client.forecast(
df,
h=7, # Forecast horizon: 7 days
level=level # Confidence intervals for uncertainty quantification
)
fcst.head()
```
| | ds | TimeGPT | TimeGPT-lo-90 | TimeGPT-lo-80 | TimeGPT-lo-50 | TimeGPT-hi-50 | TimeGPT-hi-80 | TimeGPT-hi-90 |
|---|------------|--------------|---------------|---------------|---------------|---------------|---------------|---------------|
| 0 | 2024-01-01 | 42269.460938 | 39567.209020 | 40429.953636 | 41380.654646 | 43158.267229 | 44108.968239 | 44971.712855 |
| 1 | 2024-01-02 | 42469.917969 | 39697.941669 | 40578.197049 | 41466.511361 | 43473.324576 | 44361.638888 | 45241.894268 |
| 2 | 2024-01-03 | 42864.078125 | 40538.871243 | 41586.252507 | 42284.316674 | 43443.839576 | 44141.903743 | 45189.285007 |
| 3 | 2024-01-04 | 42881.621094 | 40603.117448 | 41216.106493 | 42058.539392 | 43704.702795 | 44547.135694 | 45160.124739 |
| 4 | 2024-01-05 | 42773.457031 | 40213.699760 | 40665.384780 | 41489.812431 | 44057.101632 | 44881.529282 | 45333.214302 |
We can pass the forecasts we just generated to the `plot` method to visualize the predictions with the historical data.
```python
# Plot historical data with forecast and confidence intervals
nixtla_client.plot(df, fcst, level=level)
```
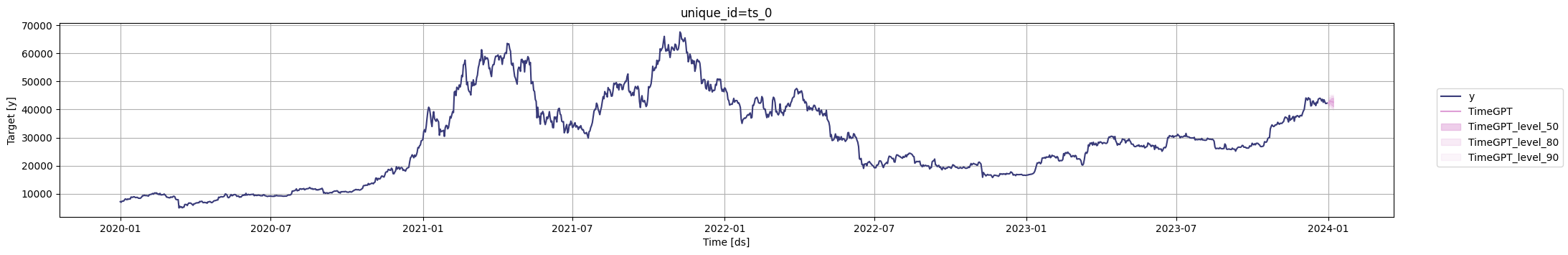
To get a closer look at the predictions, we can zoom in on the plot or specify the maximum number of in-sample observations to be plotted using the `max_insample_length` argument. Note that setting `max_insample_length=60`, for instance, will display the last 60 historical values along with the complete forecast.

### Step 5: Extend Bitcoin Price Analysis with TimeGPT
#### Anomaly Detection
Given Bitcoin's volatility, identifying anomalies can be valuable. Use TimeGPT's `detect_anomalies` method to evaluate each observation statistically within its series context. By default, it identifies anomalies using a 99% prediction interval, which you can adjust with the `level` argument.
```python
# Detect anomalies in Bitcoin price data
anomalies_df = nixtla_client.detect_anomalies(df)
# Visualize anomalies highlighted on the price chart
nixtla_client.plot(
df,
anomalies_df,
plot_anomalies=True
)
```
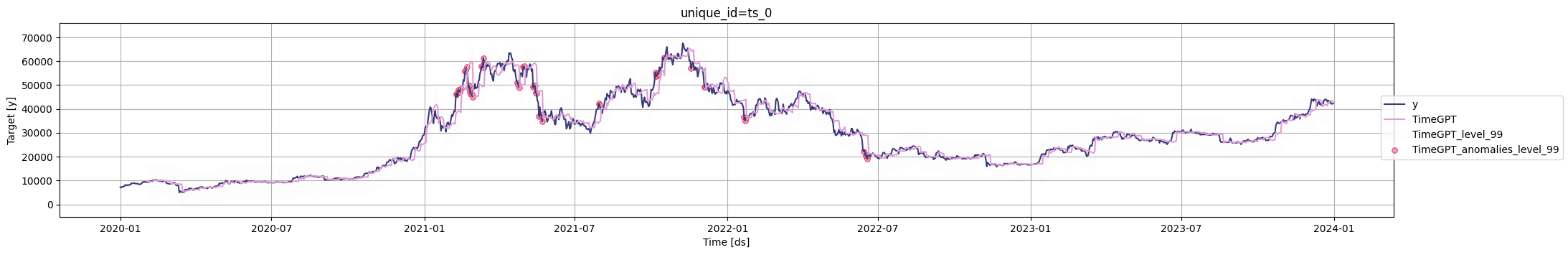
To learn how to incorporate exogenous variables to TimeGPT, see [Real-time Anomaly Detection](/anomaly_detection/real-time/introduction).
#### Add Exogenous Variables
To improve forecasts, include relevant data as exogenous variables, such as other cryptocurrency prices, stock market indices, or Bitcoin network transaction volumes.
To learn how to incorporate exogenous variables to TimeGPT, see [Numeric Features Guide](/forecasting/exogenous-variables/numeric_features).
## Understand the Model Limitations
As stated in the introduction, predicting Bitcoin prices is challenging. The predictions here may appear accurate because they use recent data and update frequently, but the real test is forecasting future prices, not historical performance.
For those who need or want to try to forecast these assets, `TimeGPT` can be an option that simplifies the forecasting process. With just a couple of lines of code, `TimeGPT` can help you:
- Produce point forecasts
- Quantify the uncertainty of your predictions
- Produce in-sample forecasts
- Detect anomalies
- Incorporate exogenous variables
To learn more about TimeGPT capabilities, see the [TimeGPT Introduction](/introduction/introduction).
## Conclusion
TimeGPT simplifies Bitcoin price forecasting by providing:
- Accurate short-term predictions with quantified uncertainty
- Automated anomaly detection for risk management
- Support for exogenous variables to improve forecast accuracy
This approach applies to various cryptocurrency and financial asset forecasting scenarios, helping traders and analysts make data-driven decisions despite market volatility.
### Next Steps
- Explore [energy demand forecasting](/use_cases/forecasting_energy_demand) with TimeGPT
- Learn about [cross-validation](/forecasting/evaluation/cross_validation) for model evaluation
- Understand [fine-tuning](/forecasting/fine-tuning/steps) for improved accuracy
- Scale forecasts with [distributed computing](/forecasting/forecasting-at-scale/computing_at_scale)
## References and Additional Material
- [Joaquín Amat Rodrigo and Javier Escobar Ortiz (2022), "Bitcoin price prediction with Python, when the past does not repeat itself"](https://www.cienciadedatos.net/documentos/py41-forecasting-cryptocurrency-bitcoin-machine-learning-python.html)