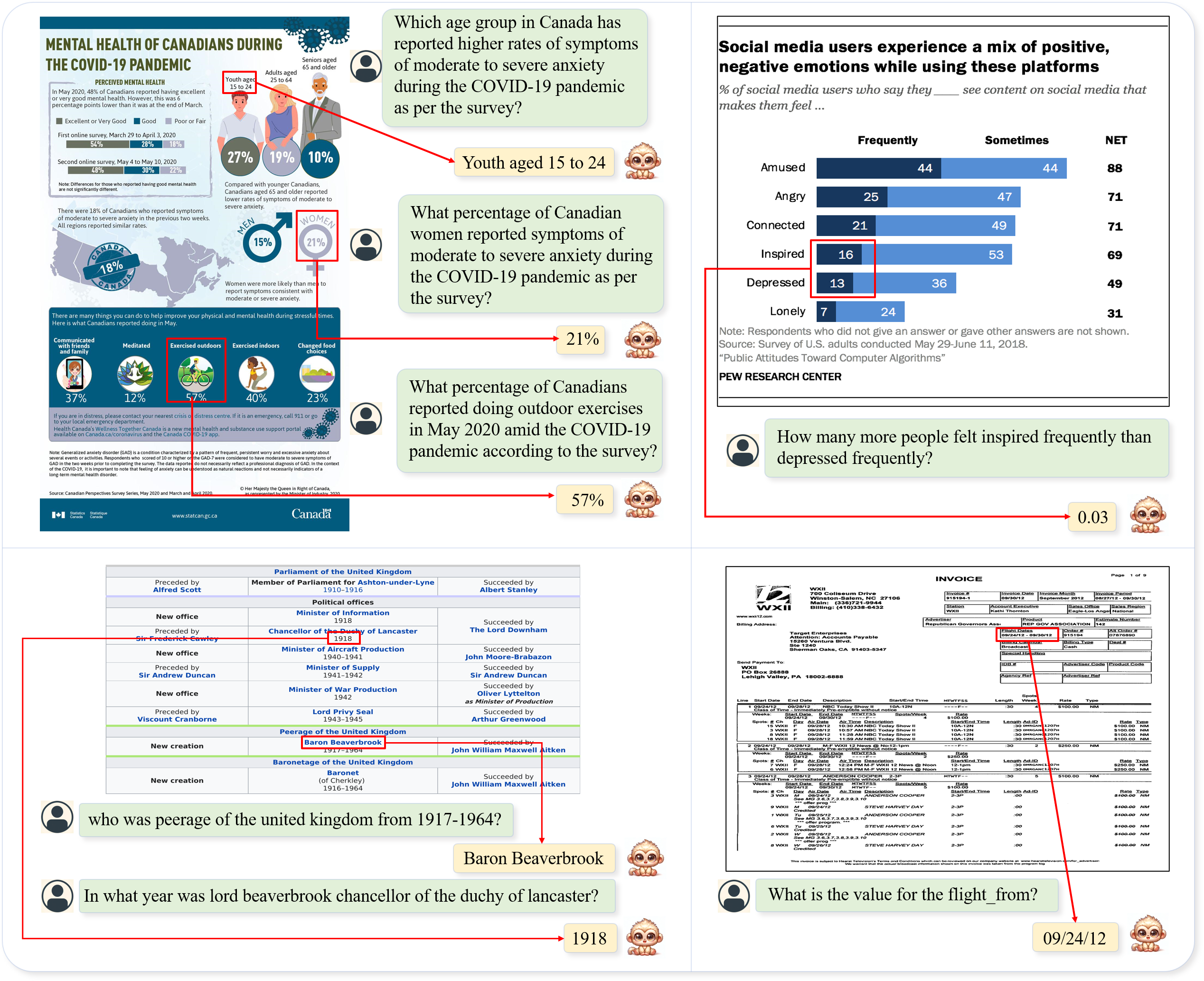
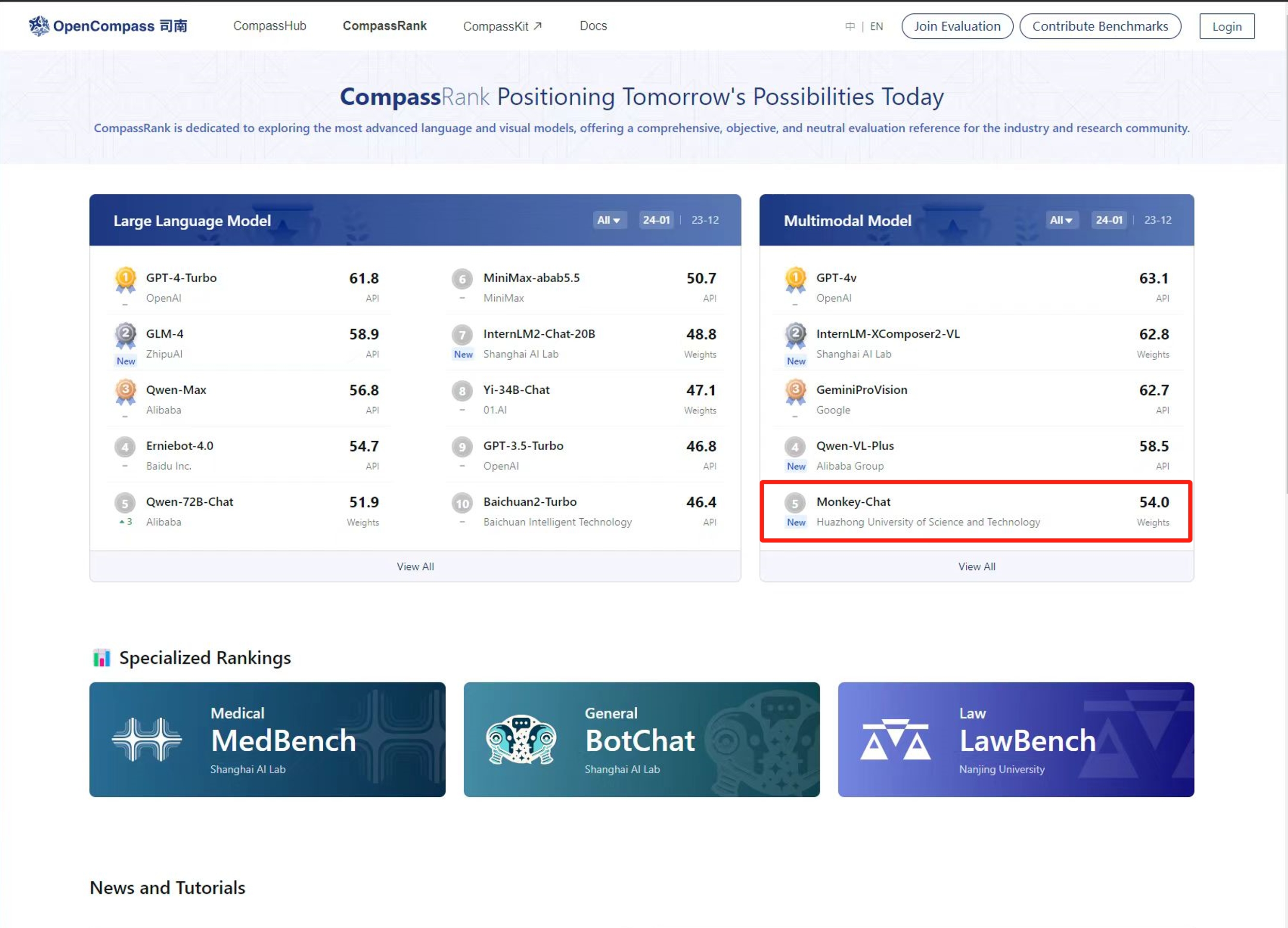
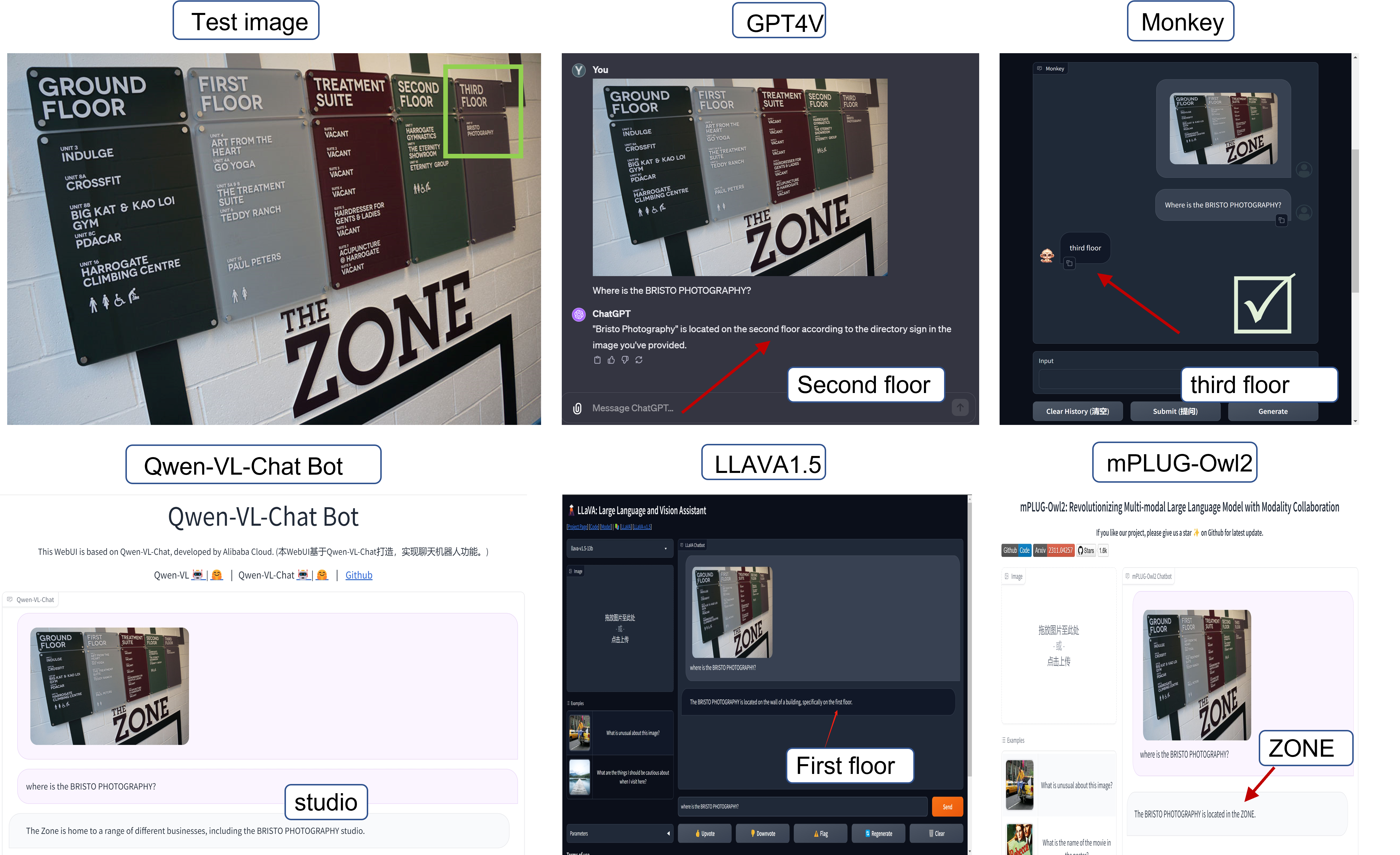
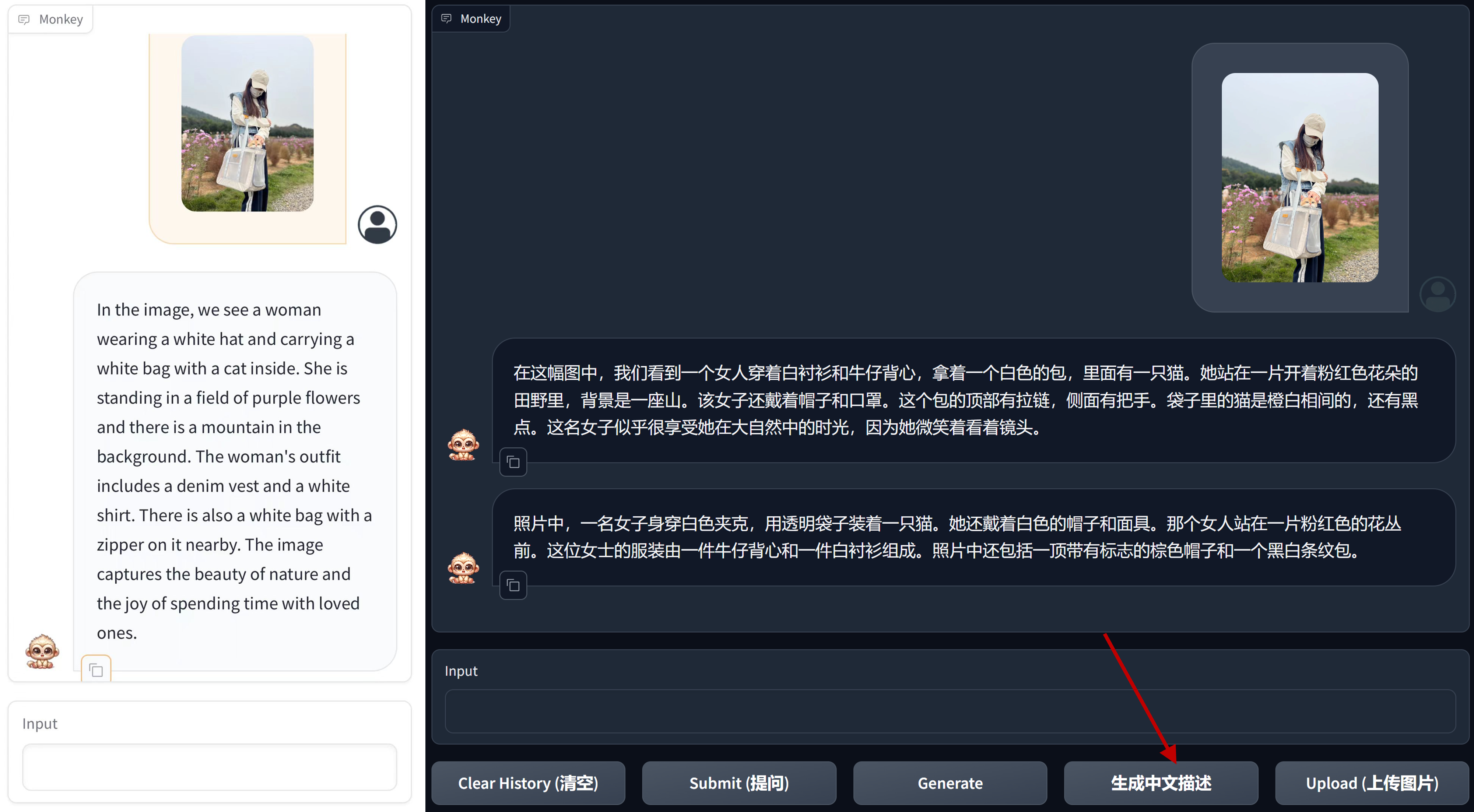
TextMonkey (#75)
* textmonkey
* textmonkey code
* Delete README_cn.md
---------
Co-authored-by:  Yuliang Liu <34134635+Yuliang-Liu@users.noreply.github.com>
Yuliang Liu <34134635+Yuliang-Liu@users.noreply.github.com>
Showing
README_cn.md
deleted
100644 → 0
eval/eval_doc.sh
0 → 100644
eval/evaluate_vqa_doc.py
0 → 100644
images/Doc_Chart.png
deleted
100644 → 0
1.94 MB
2.41 MB
963 KB
images/caption_1.png
deleted
100644 → 0
900 KB
images/compare.png
deleted
100644 → 0
1.93 MB
This image diff could not be displayed because it is too large. You can view the blob instead.
7.33 MB
3.61 MB
5.27 MB
This image diff could not be displayed because it is too large. You can view the blob instead.
2.53 MB
images/logo_hust.png
deleted
100644 → 0
140 KB
images/logo_king.png
deleted
100644 → 0
6.5 KB