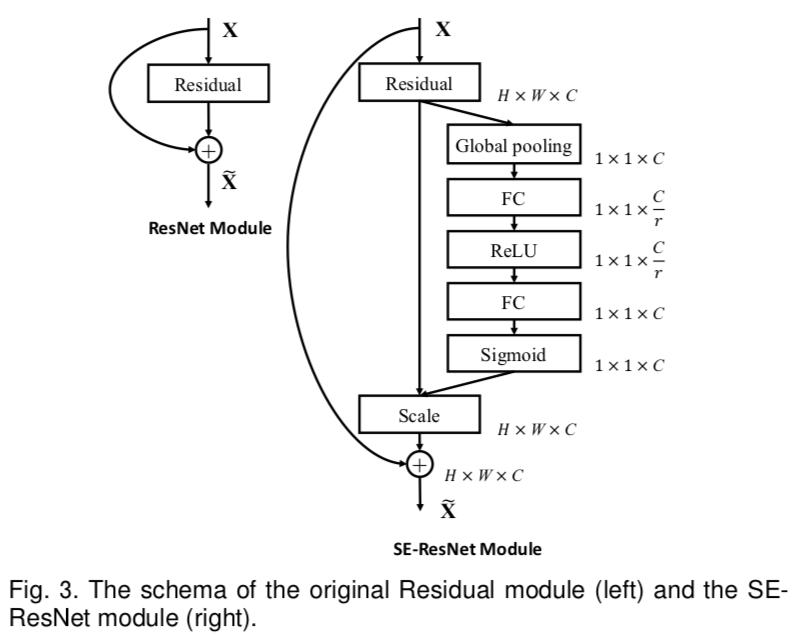
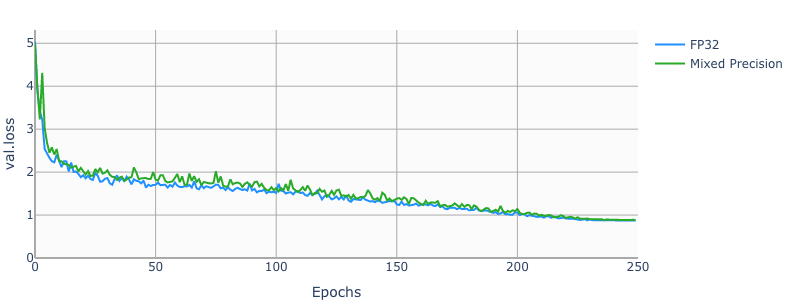
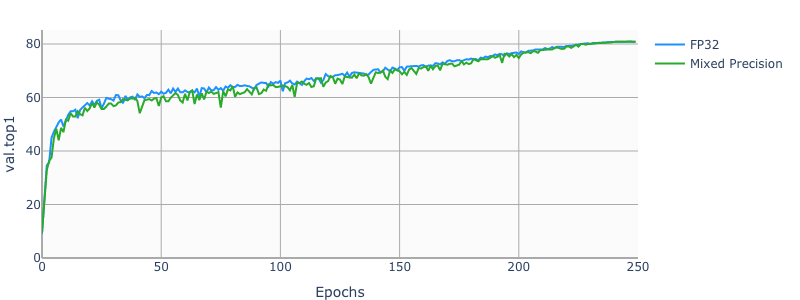
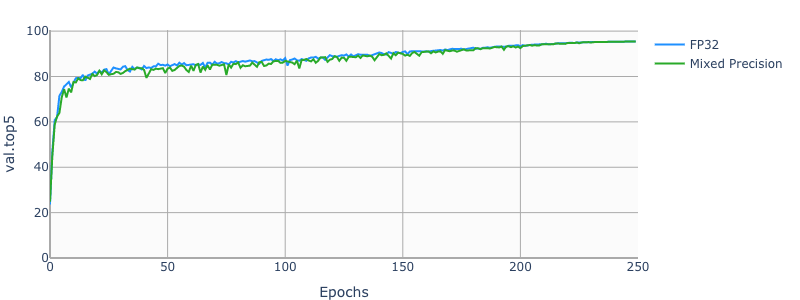
add new model resnet50v1.5
Showing
scripts/sernxt_partial.sh
0 → 100755
76.3 KB
30.7 KB
31.9 KB
28.9 KB
train_multi.sh
0 → 100755
triton/Dockerfile
0 → 100644
triton/calculate_metrics.py
0 → 100755
triton/client.py
0 → 100644
triton/convert_model.py
0 → 100755