add new model resnet50v1.5
Showing
img/.gitkeep
0 → 100644
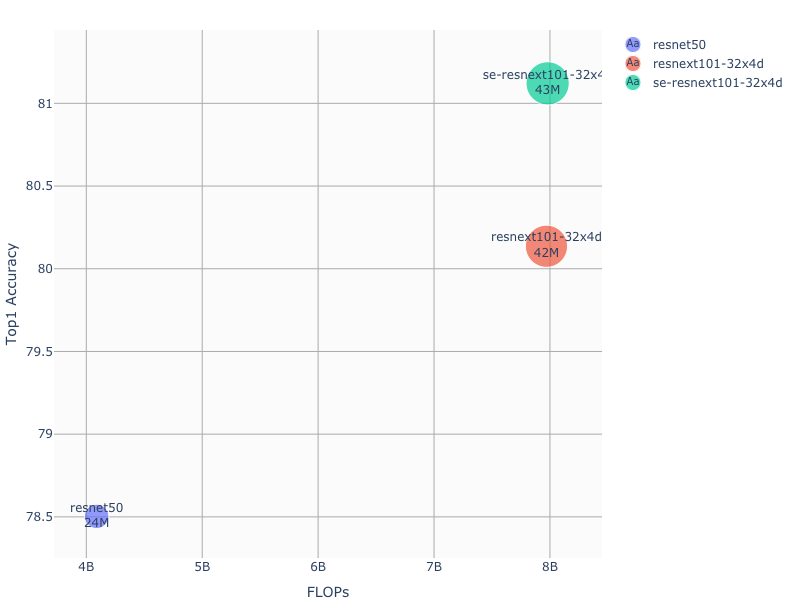
img/ACCvsFLOPS.png
0 → 100644
47.3 KB
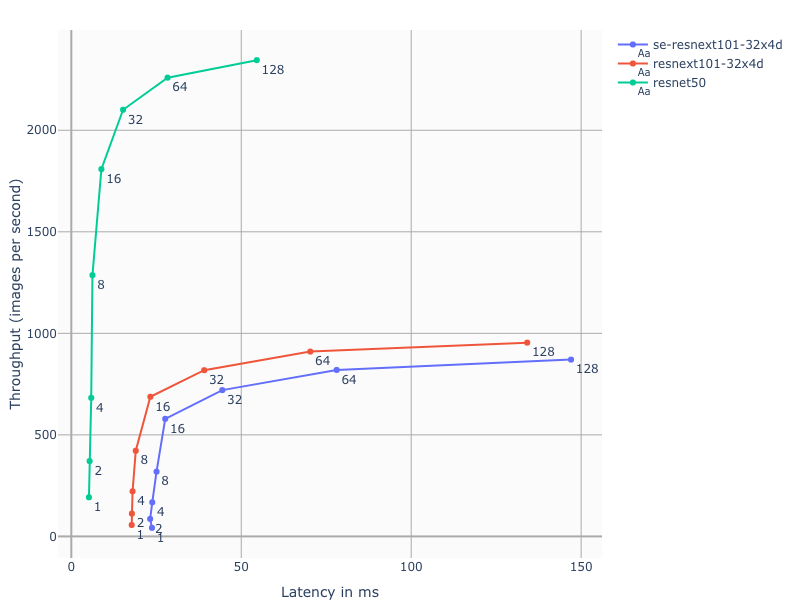
img/LATvsTHR.png
0 → 100644
61.1 KB
launch.py
0 → 100644
main.py
0 → 100644
model2onnx.py
0 → 100644
multiproc.py
0 → 100644
quant_main.py
0 → 100644
requirements.txt
0 → 100644
| git+https://github.com/NVIDIA/dllogger@v1.0.0#egg=dllogger | ||
| pynvml==11.0.0 |
resnet50v1.5/README.md
0 → 100644
30.3 KB
34.1 KB
31.2 KB