Update tools_using_demo/cli_demo_tool.py, tools_using_demo/openai_api_demo.py,...
Update tools_using_demo/cli_demo_tool.py, tools_using_demo/openai_api_demo.py, tools_using_demo/README.md, tools_using_demo/README_en.md, tools_using_demo/tool_register.py, tensorrt_llm_demo/README.md, tensorrt_llm_demo/tensorrt_llm_cli_demo.py, resources/cli-demo.png, resources/web-demo2.png, resources/tool_en.png, resources/tool.png, resources/heart.png, resources/wechat.jpg, resources/web-demo.gif, resources/web-demo2.gif, resources/WECHAT.md, resources/code_en.gif, openai_api_demo/api_server.py, openai_api_demo/.env, openai_api_demo/openai_api_request.py, openai_api_demo/docker-compose.yml, openai_api_demo/utils.py, openai_api_demo/zhipu_api_request.py, openai_api_demo/langchain_openai_api.py, langchain_demo/ChatGLM3.py, langchain_demo/main.py, langchain_demo/tools/Calculator.py, langchain_demo/tools/DistanceConversion.py, langchain_demo/tools/Weather.py, Intel_device_demo/README.md, Intel_device_demo/ipex_llm_cpu_demo/api_server.py, Intel_device_demo/ipex_llm_cpu_demo/chatglm3_infer.py, Intel_device_demo/ipex_llm_cpu_demo/chatglm3_web_demo.py, Intel_device_demo/ipex_llm_cpu_demo/openai_api_request.py, Intel_device_demo/ipex_llm_cpu_demo/generate.py, Intel_device_demo/ipex_llm_cpu_demo/utils.py, Intel_device_demo/openvino_demo/openvino_cli_demo.py, Intel_device_demo/openvino_demo/README.md, finetune_demo/lora_finetune.ipynb, finetune_demo/finetune_hf.py, finetune_demo/inference_hf.py, finetune_demo/README.md, finetune_demo/README_en.md, finetune_demo/requirements.txt, finetune_demo/configs/ds_zero_3.json, finetune_demo/configs/ds_zero_2.json, finetune_demo/configs/ptuning_v2.yaml, finetune_demo/configs/lora.yaml, finetune_demo/configs/sft.yaml, composite_demo/assets/emojis.png, composite_demo/assets/demo.png, composite_demo/assets/heart.png, composite_demo/assets/tool.png, composite_demo/.streamlit/config.toml, composite_demo/client.py, composite_demo/conversation.py, composite_demo/README_en.md, composite_demo/main.py, composite_demo/demo_chat.py, composite_demo/README.md, composite_demo/requirements.txt, composite_demo/demo_tool.py, composite_demo/tool_registry.py, composite_demo/demo_ci.py, basic_demo/cli_demo_bad_word_ids.py, basic_demo/cli_demo.py, basic_demo/cli_batch_request_demo.py, basic_demo/web_demo_gradio.py, basic_demo/web_demo_streamlit.py, .github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug_report.yaml, .github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature-request.yaml, .github/PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE/pr_template.md, MODEL_LICENSE, .gitignore, DEPLOYMENT.md, DEPLOYMENT_en.md, LICENSE, PROMPT.md, README_en.md, requirements.txt, README.md, PROMPT_en.md, update_requirements.sh files
Showing
openai_api_demo/utils.py
0 → 100644
requirements.txt
0 → 100644
| # basic requirements | ||
| protobuf>=4.25.3 | ||
| transformers>=4.39.3 | ||
| tokenizers>=0.15.0 | ||
| cpm_kernels>=1.0.11 | ||
| torch>=2.1.0 | ||
| gradio>=4.26.0 | ||
| sentencepiece>=0.2.0 | ||
| sentence_transformers>=2.4.0 | ||
| accelerate>=0.29.2 | ||
| streamlit>=1.33.0 | ||
| fastapi>=0.110.0 | ||
| loguru~=0.7.2 | ||
| mdtex2html>=1.3.0 | ||
| latex2mathml>=3.77.0 | ||
| jupyter_client>=8.6.1 | ||
| nltk | ||
| # for openai demo | ||
| #openai>=1.17.1 | ||
| #zhipuai>=2.0.1 | ||
| #pydantic>=2.7.0 | ||
| #sse-starlette>=2.0.0 | ||
| #uvicorn>=0.29.0 | ||
| #timm>=0.9.16 | ||
| #tiktoken>=0.6.0 | ||
| # for langchain demo | ||
| #langchain>=0.1.16 | ||
| #langchainhub>=0.1.15 | ||
| #arxiv>=2.1.0 |
resources/WECHAT.md
0 → 100644
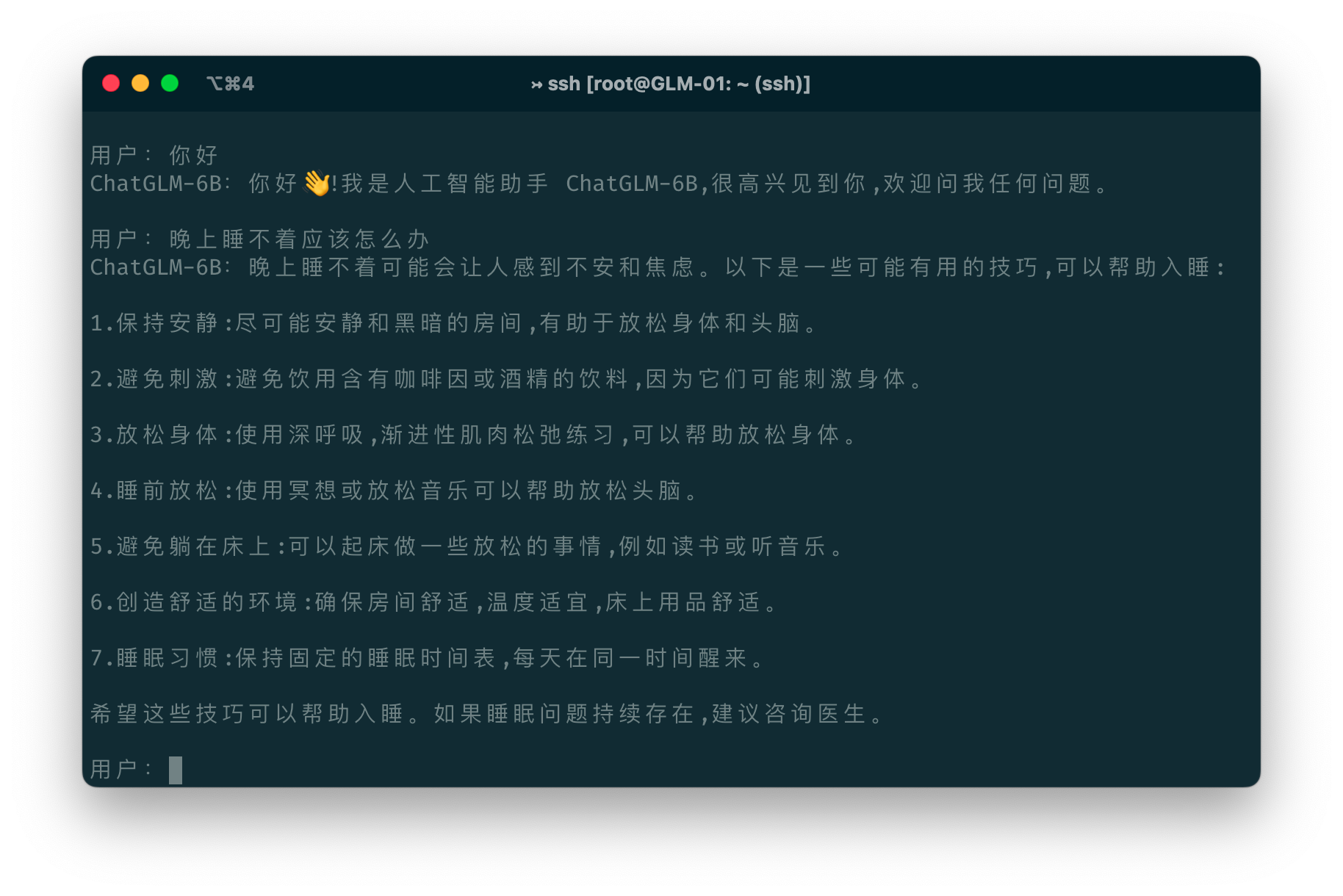
resources/cli-demo.png
0 → 100644
463 KB
resources/code_en.gif
0 → 100644
8.91 MB
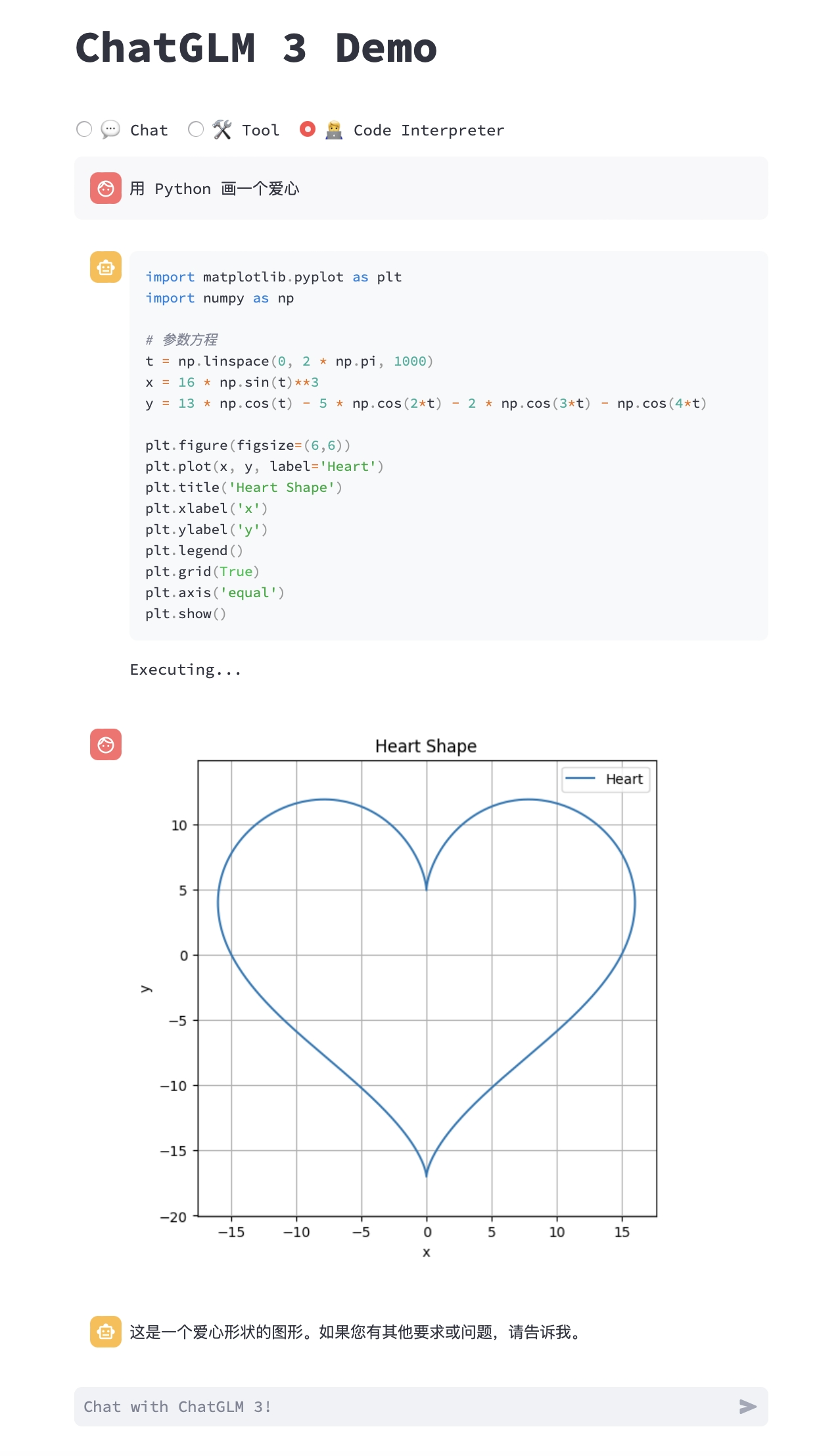
resources/heart.png
0 → 100644
377 KB
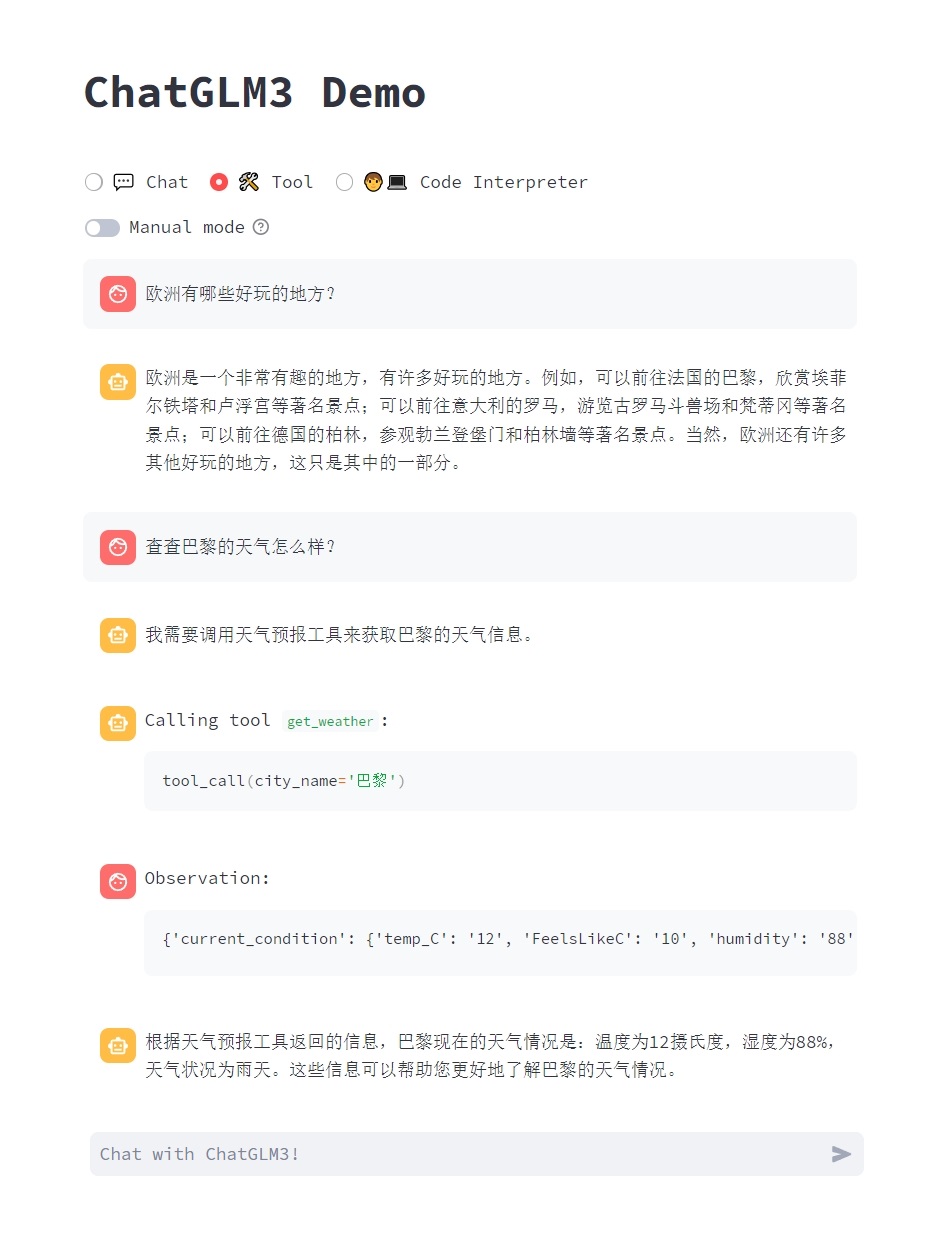
resources/tool.png
0 → 100644
148 KB
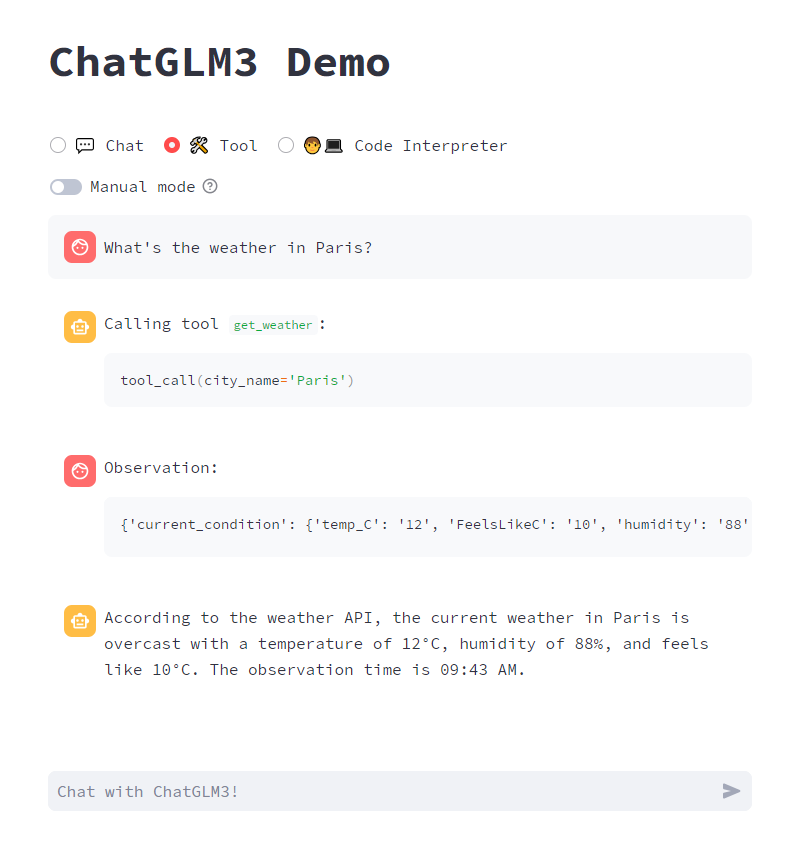
resources/tool_en.png
0 → 100644
44 KB
resources/web-demo.gif
0 → 100644
2.18 MB
resources/web-demo2.gif
0 → 100644
2.63 MB
resources/web-demo2.png
0 → 100644
481 KB
resources/wechat.jpg
0 → 100644
151 KB
tensorrt_llm_demo/README.md
0 → 100644
tools_using_demo/README.md
0 → 100644