# Qwen3
参数量仅为DeepSeek-R1的1/3,成本大幅下降,性能全面超越R1、OpenAI-o1等全球顶尖模型,将快思考与慢思考集成进同一个模型。
## 论文
`无`
## 模型结构
Qwen3采用通用的Decoder-Only结构,引入了MoE提升性能,首个「混合推理模型」,将「快思考」与「慢思考」集成进同一个模型。
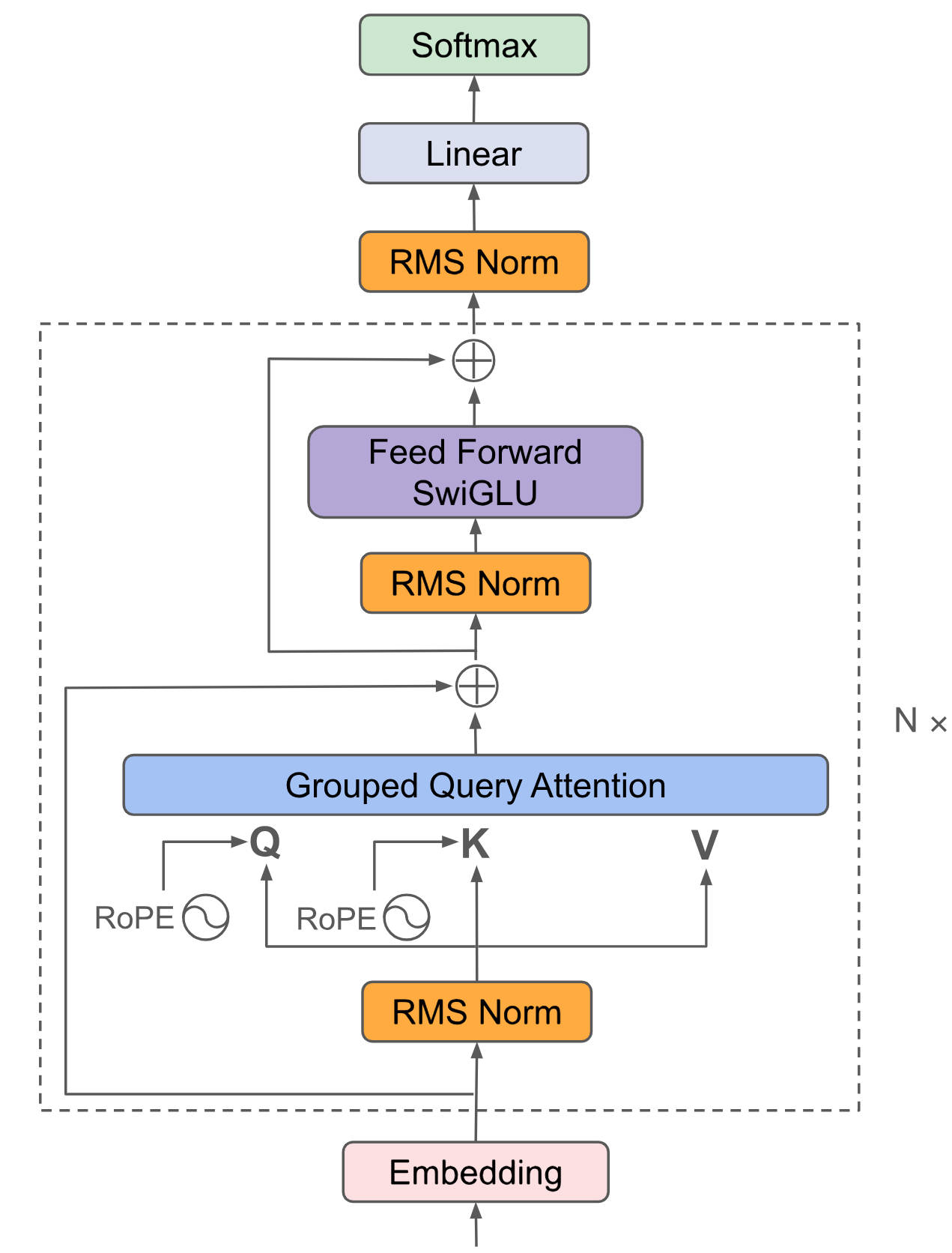
## 算法原理
将输入embedding后放入attention、ffn等提取特征,最后利用Softmax将解码器最后一层产生的未经归一化的分数向量(logits)转换为概率分布,其中每个元素表示生成对应词汇的概率,这使得模型可以生成一个分布,并从中选择最可能的词作为预测结果。
## 环境配置
```
mv Qwen3_pytorch Qwen3 # 去框架名后缀
```
### Docker(方法一)
```
docker pull image.sourcefind.cn:5000/dcu/admin/base/custom:vllm0.8.4-ubuntu22.04-dtk25.04-rc7-das1.5-py3.10-20250429-dev-qwen3-only
# docker pull image.sourcefind.cn:5000/dcu/admin/base/pytorch:2.4.1-ubuntu22.04-dtk25.04-py3.10-fixpy
# 为以上拉取的docker的镜像ID替换,本镜像为:6e12a1c4ae4d
docker run -it --shm-size=64G -v $PWD/Qwen3:/home/Qwen3 -v /opt/hyhal:/opt/hyhal:ro --privileged=true --device=/dev/kfd --device=/dev/dri/ --group-add video --name qwen3 bash
cd /home/Qwen3
pip install -r requirements.txt -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
```
### Dockerfile(方法二)
```
cd /home/Qwen3/docker
docker build --no-cache -t qwen3:latest .
docker run --shm-size=64G --name qwen3 -v /opt/hyhal:/opt/hyhal:ro --privileged=true --device=/dev/kfd --device=/dev/dri/ --group-add video -v $PWD/../../Qwen3:/home/Qwen3 -it qwen3 bash
# 若遇到Dockerfile启动的方式安装环境需要长时间等待,可注释掉里面的pip安装,启动容器后再安装python库:pip install -r requirements.txt。
```
### Anaconda(方法三)
1、关于本项目DCU显卡所需的特殊深度学习库可从光合开发者社区下载安装:
- https://developer.sourcefind.cn/tool/
```
DTK驱动:dtk2504
python:python3.10
torch:2.4.1
torchvision:0.19.1
triton:3.0.0
vllm:0.8.4
flash-attn:2.6.1
deepspeed:0.14.2
apex:1.4.0
transformers:4.51.0
```
`Tips:以上dtk驱动、python、torch等DCU相关工具版本需要严格一一对应。`
2、其它非特殊库参照requirements.txt安装
```
cd /home/Qwen3
pip install -r requirements.txt -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
```
## 数据集
`无`
## 训练
无
## 推理
预训练权重目录结构:
```
/home/Qwen3/
└── Qwen/Qwen3-8B
```
### 单机多卡
```
cd /home/Qwen3
# 方法一:pytorch推理
# 本项目以Qwen3-8B示例,其它Qwen3模型以此类推。
python infer_transformers.py
方法二:vllm推理
python infer_vllm.py # vllm=0.8.4
```
更多资料可参考源项目中的[`README_orgin`](./README_orgin.md)。
## result
vllm推理效果示例:
`输入: `
```
prompt: "Give me a short introduction to large language models."
```
`输出:`
```
Generated text: "\nOkay, the user wants a short introduction to large language models. Let me start by defining what they are. They're AI systems trained on massive text data, right? I should mention their ability to understand and generate human-like text. Maybe include examples like GPT or BERT.\n\nWait, the user might not know the difference between different models. Should I explain the training process? Like using unsupervised learning on vast datasets. Also, highlight their applications: answering questions, writing stories, coding. But keep it concise since it's supposed to be short.\n\nOh, and maybe touch on their significance in NLP. Emphasize that they can handle multiple languages and tasks. Need to make sure it's clear without too much jargon. Let me check if I'm missing any key points. Oh, scalability and adaptability could be important. Alright, structure it with a definition, how they work, applications, and impact. Keep each part brief.\n\n\nLarge language models (LLMs) are advanced artificial intelligence systems trained on vast amounts of text data to understand and generate human-like language. They use deep learning techniques to process and produce coherent responses across multiple languages and tasks, such as answering questions, writing stories, coding, and more. By analyzing patterns in text, LLMs can adapt to diverse contexts, making them powerful tools for natural language processing (NLP) and a wide range of applications, from customer service to creative writing. Their ability to scale and learn from extensive datasets has revolutionized how machines interact with and understand human communication."
```
### 精度
DCU与GPU精度一致,推理框架:pytorch。
## 应用场景
### 算法类别
`对话问答`
### 热点应用行业
`制造,广媒,金融,能源,医疗,家居,教育`
## 预训练权重
魔搭社区下载地址为:[Qwen/Qwen3-8B](https://www.modelscope.cn/Qwen/Qwen3-8B.git)
## 源码仓库及问题反馈
- http://developer.sourcefind.cn/codes/modelzoo/Qwen3_pytorch.git
## 参考资料
- https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3.git

