添加openmmlab测试用例
Showing
Too many changes to show.
To preserve performance only 977 of 977+ files are displayed.
This source diff could not be displayed because it is too large. You can view the blob instead.
13.4 KB
69.4 KB
64 KB
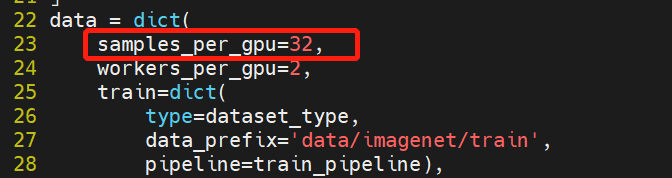
13.4 KB
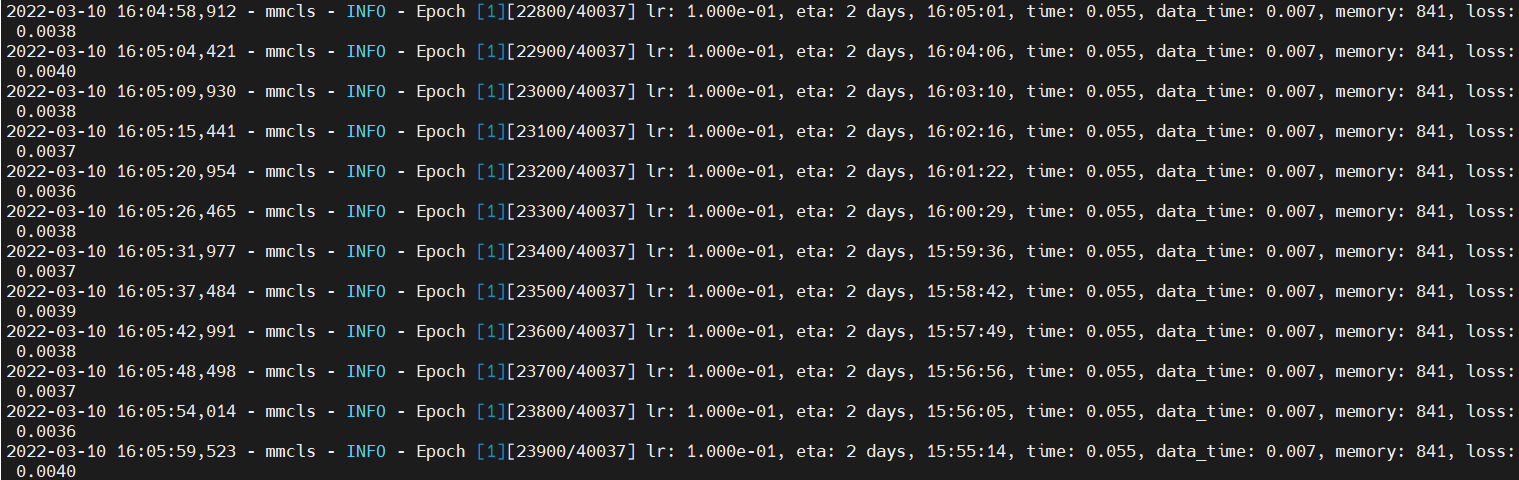
69.4 KB
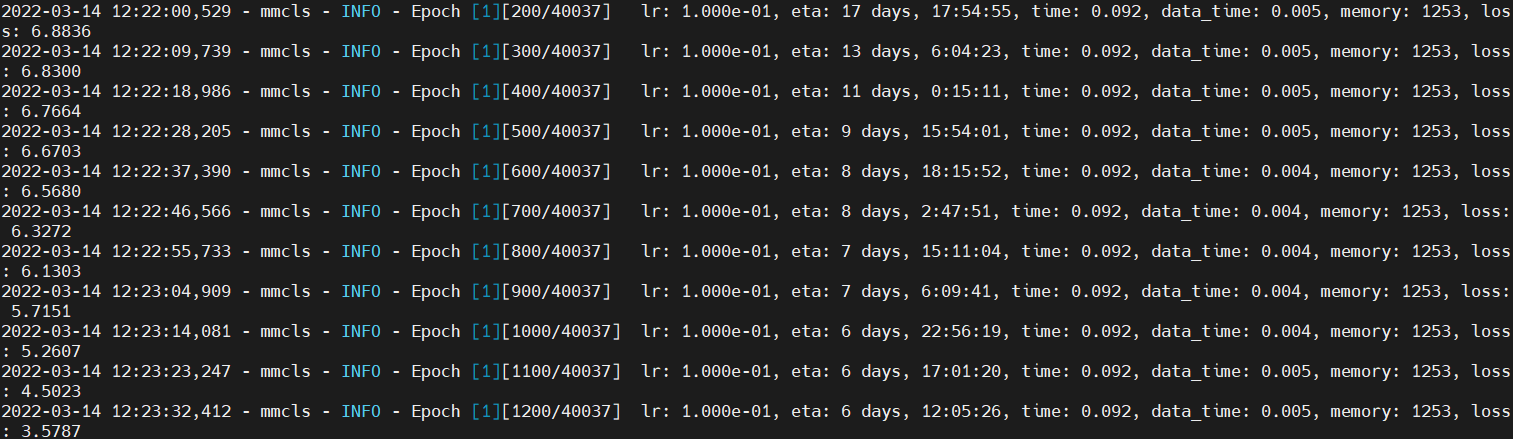
64 KB