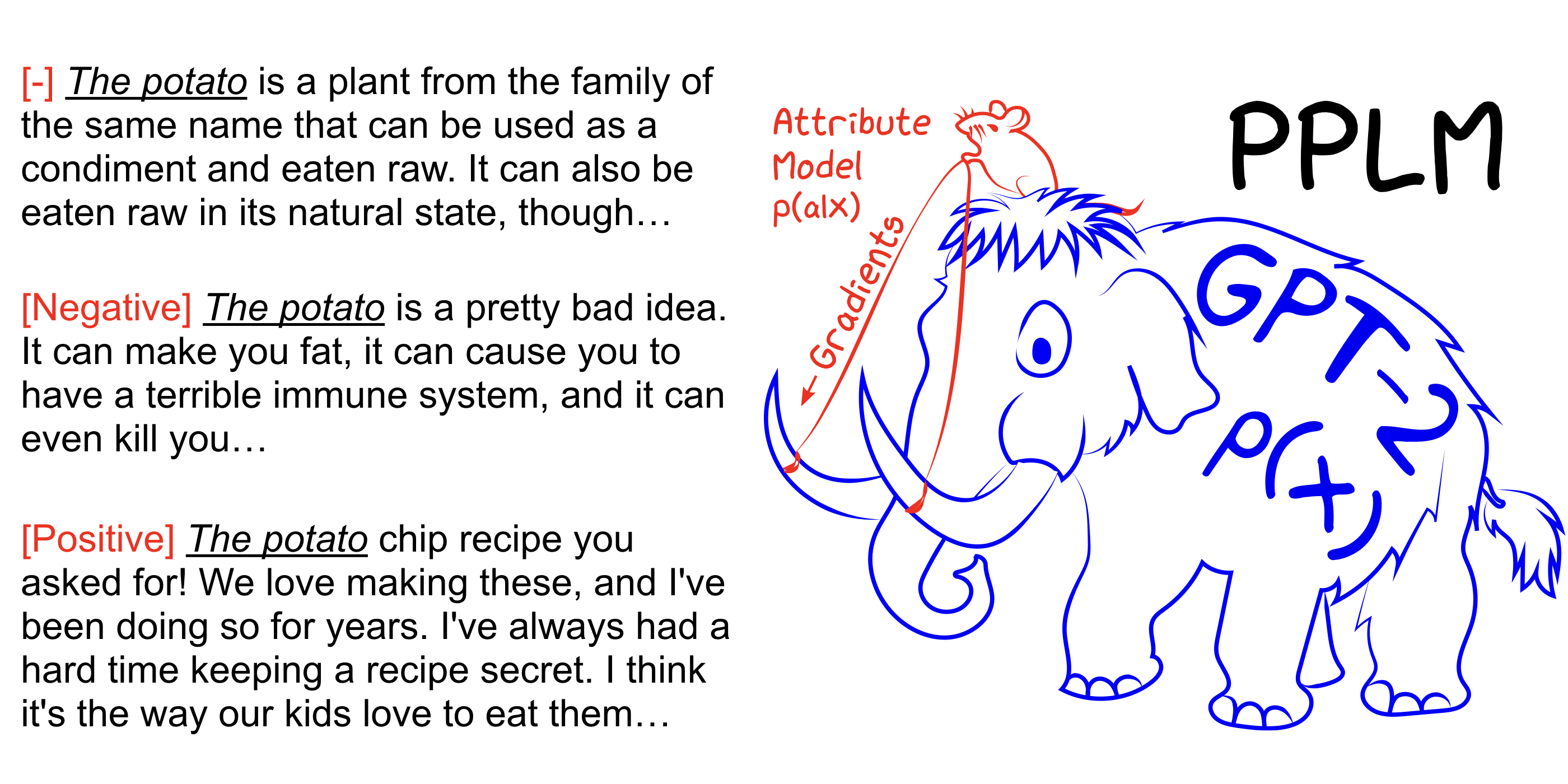
Merge remote-tracking branch 'refs/remotes/huggingface/master'
Showing
examples/pplm/README.md
0 → 100644
653 KB
examples/pplm/imgs/wooly.png
0 → 100644
664 KB
examples/pplm/run_pplm.py
0 → 100644
This diff is collapsed.
This diff is collapsed.