# Lightx2v Parameter Offloading Mechanism Technical Documentation
## 📖 Overview
Lightx2v implements a state-of-the-art parameter offloading mechanism specifically designed for efficient large model inference under limited hardware resources. This system provides excellent speed-memory balance through intelligent management of model weights across different memory hierarchies, enabling dynamic scheduling between GPU, CPU, and disk storage.
**Core Features:**
- **Intelligent Granularity Management**: Supports both Block and Phase offloading granularities for flexible memory control
- **Block Granularity**: Complete Transformer layers as management units, containing self-attention, cross-attention, feed-forward networks, etc., suitable for memory-sufficient environments
- **Phase Granularity**: Individual computational components as management units, providing finer-grained memory control for memory-constrained deployment scenarios
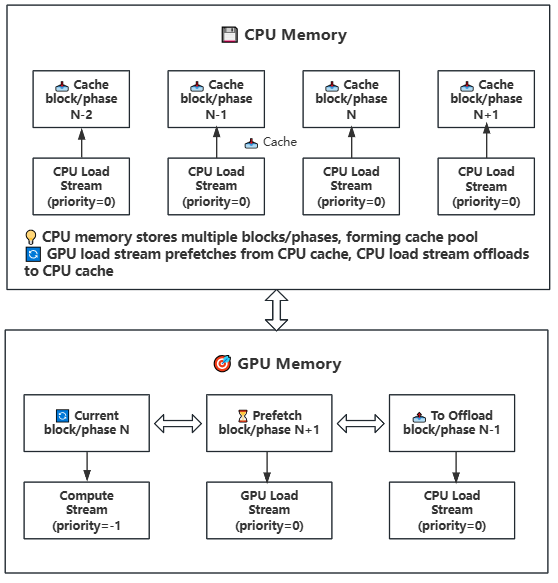
- **Multi-level Storage Architecture**: GPU → CPU → Disk three-tier storage hierarchy with intelligent caching strategies
- **Asynchronous Parallel Processing**: CUDA stream-based asynchronous computation and data transfer for maximum hardware utilization
- **Persistent Storage Support**: SSD/NVMe disk storage support for ultra-large model inference deployment
## 🎯 Offloading Strategy Details
### Strategy 1: GPU-CPU Granularity Offloading
**Applicable Scenarios**: GPU VRAM insufficient but system memory resources adequate
**Technical Principle**: Establishes efficient weight scheduling mechanism between GPU and CPU memory, managing model weights in Block or Phase units. Leverages CUDA stream asynchronous capabilities to achieve parallel execution of computation and data transfer. Blocks contain complete Transformer layer structures, while Phases correspond to individual computational components within layers.
**Granularity Selection Guide**:
- **Block Granularity**: Suitable for memory-sufficient environments, reduces management overhead and improves overall performance
- **Phase Granularity**: Suitable for memory-constrained environments, provides more flexible memory control and optimizes resource utilization
**Technical Features:**
- **Multi-stream Parallel Architecture**: Employs three CUDA streams with different priorities to parallelize computation and transfer
- Compute Stream (priority=-1): High priority, responsible for current computation tasks
- GPU Load Stream (priority=0): Medium priority, responsible for weight prefetching from CPU to GPU
- CPU Load Stream (priority=0): Medium priority, responsible for weight offloading from GPU to CPU
- **Intelligent Prefetching Mechanism**: Predictively loads next Block/Phase based on computation progress
- **Efficient Cache Management**: Maintains weight cache pool in CPU memory for improved access efficiency
- **Stream Synchronization Guarantee**: Ensures temporal correctness of data transfer and computation
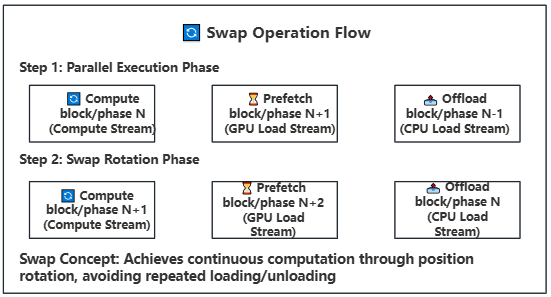
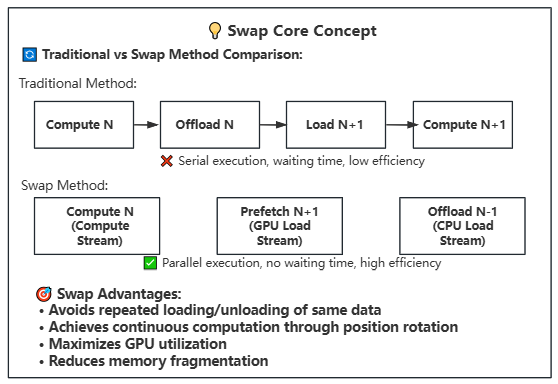
- **Position Rotation Optimization**: Achieves continuous computation through Swap operations, avoiding repeated loading/unloading
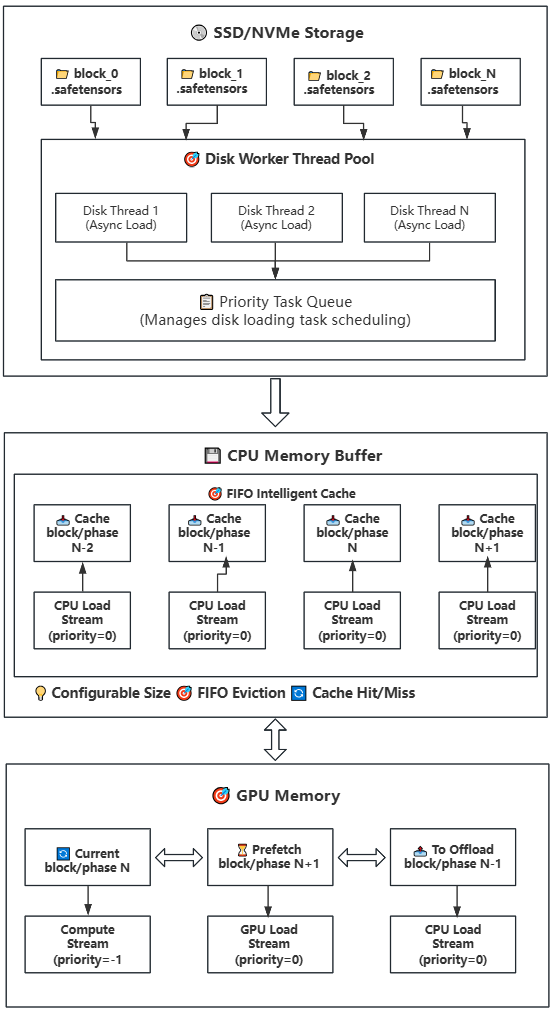
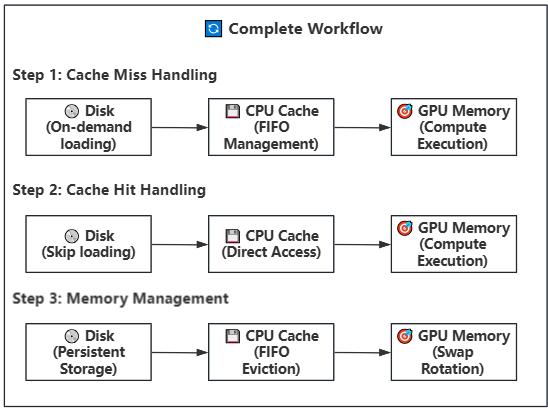
### Strategy 2: Disk-CPU-GPU Three-Level Offloading (Lazy Loading)
**Applicable Scenarios**: Both GPU VRAM and system memory resources insufficient in constrained environments
**Technical Principle**: Introduces disk storage layer on top of Strategy 1, constructing a Disk→CPU→GPU three-level storage architecture. CPU serves as a configurable intelligent cache pool, suitable for various memory-constrained deployment environments.
**Execution Steps Details:**
1. **Disk Storage Layer**: Model weights organized by Block on SSD/NVMe, each Block corresponding to one .safetensors file
2. **Task Scheduling Layer**: Priority queue-based intelligent scheduling system for disk loading task assignment
3. **Asynchronous Loading Layer**: Multi-threaded parallel reading of weight files from disk to CPU memory buffer
4. **Intelligent Cache Layer**: CPU memory buffer using FIFO strategy for cache management with dynamic size configuration
5. **Cache Hit Optimization**: Direct transfer to GPU when weights are already in cache, avoiding disk I/O overhead
6. **Prefetch Transfer Layer**: Weights in cache asynchronously transferred to GPU memory via GPU load stream
7. **Compute Execution Layer**: Weights on GPU perform computation (compute stream) while background continues prefetching next Block/Phase
8. **Position Rotation Layer**: Swap rotation after computation completion for continuous computation flow
9. **Memory Management Layer**: Automatic eviction of earliest used weight Blocks/Phases when CPU cache is full
**Technical Features:**
- **On-demand Loading Mechanism**: Model weights loaded from disk only when needed, avoiding loading entire model at once
- **Configurable Cache Strategy**: CPU memory buffer supports FIFO strategy with dynamically adjustable size
- **Multi-threaded Parallel Loading**: Leverages multiple disk worker threads for parallel data loading
- **Asynchronous Transfer Optimization**: CUDA stream-based asynchronous data transfer for maximum hardware utilization
- **Continuous Computation Guarantee**: Achieves continuous computation through position rotation mechanism, avoiding repeated loading/unloading operations
## ⚙️ Configuration Parameters Details
### GPU-CPU Offloading Configuration
```python
config = {
"cpu_offload": True, # Enable CPU offloading functionality
"offload_ratio": 1.0, # Offload ratio (0.0-1.0), 1.0 means complete offloading
"offload_granularity": "block", # Offload granularity selection: "block" or "phase"
"lazy_load": False, # Disable lazy loading mode
}
```
### Disk-CPU-GPU Offloading Configuration
```python
config = {
"cpu_offload": True, # Enable CPU offloading functionality
"lazy_load": True, # Enable lazy loading mode
"offload_ratio": 1.0, # Offload ratio setting
"offload_granularity": "phase", # Recommended to use phase granularity for better memory control
"num_disk_workers": 2, # Number of disk worker threads
"offload_to_disk": True, # Enable disk offloading functionality
"offload_path": ".", # Disk offload path configuration
}
```
**Intelligent Cache Key Parameter Descriptions:**
- `max_memory`: Controls CPU cache size upper limit, directly affects cache hit rate and memory usage
- `num_disk_workers`: Controls number of disk loading threads, affects data prefetch speed
- `offload_granularity`: Controls cache management granularity, affects cache efficiency and memory utilization
- `"block"`: Cache management in units of complete Transformer layers, suitable for memory-sufficient environments
- `"phase"`: Cache management in units of individual computational components, suitable for memory-constrained environments
Detailed configuration files can be referenced at [Official Configuration Repository](https://github.com/ModelTC/lightx2v/tree/main/configs/offload)
## 🎯 Deployment Strategy Recommendations
- 🔄 GPU-CPU Granularity Offloading: Suitable for insufficient GPU VRAM (RTX 3090/4090 24G) but adequate system memory (>64G)
- Advantages: Balances performance and memory usage, suitable for medium-scale model inference
- 💾 Disk-CPU-GPU Three-Level Offloading: Suitable for limited GPU VRAM (RTX 3060/4090 8G) and insufficient system memory (16-32G)
- Advantages: Supports ultra-large model inference with lowest hardware threshold
- 🚫 No Offload Mode: Suitable for high-end hardware configurations pursuing optimal inference performance
- Advantages: Maximizes computational efficiency, suitable for latency-sensitive application scenarios
## 🔍 Troubleshooting and Solutions
### Common Performance Issues and Optimization Strategies
1. **Disk I/O Performance Bottleneck**
- Problem Symptoms: Slow model loading speed, high inference latency
- Solutions:
- Upgrade to NVMe SSD storage devices
- Increase num_disk_workers parameter value
- Optimize file system configuration
2. **Memory Buffer Overflow**
- Problem Symptoms: Insufficient system memory, program abnormal exit
- Solutions:
- Increase max_memory parameter value
- Decrease num_disk_workers parameter value
- Adjust offload_granularity to "phase"
3. **Model Loading Timeout**
- Problem Symptoms: Timeout errors during model loading process
- Solutions:
- Check disk read/write performance
- Optimize file system parameters
- Verify storage device health status
## 📚 Technical Summary
Lightx2v's offloading mechanism is specifically designed for modern AI inference scenarios, fully leveraging GPU's asynchronous computing capabilities and multi-level storage architecture advantages. Through intelligent weight management and efficient parallel processing, this mechanism significantly reduces the hardware threshold for large model inference, providing developers with flexible and efficient deployment solutions.
**Technical Highlights:**
- 🚀 **Performance Optimization**: Asynchronous parallel processing maximizes hardware utilization
- 💾 **Intelligent Memory**: Multi-level caching strategies achieve optimal memory management
- 🔧 **Flexible Configuration**: Supports flexible configuration of multiple granularities and strategies
- 🛡️ **Stable and Reliable**: Comprehensive error handling and fault recovery mechanisms