# Parameter Offload
## 📖 Overview
LightX2V implements an advanced parameter offload mechanism specifically designed for large model inference under limited hardware resources. The system provides an excellent speed-memory balance by intelligently managing model weights across different memory hierarchies.
**Core Features:**
- **Block/Phase-level Offload**: Efficiently manages model weights in block/phase units for optimal memory usage
- **Block**: The basic computational unit of Transformer models, containing complete Transformer layers (self-attention, cross-attention, feedforward networks, etc.), serving as a larger memory management unit
- **Phase**: Finer-grained computational stages within blocks, containing individual computational components (such as self-attention, cross-attention, feedforward networks, etc.), providing more precise memory control
- **Multi-tier Storage Support**: GPU → CPU → Disk hierarchy with intelligent caching
- **Asynchronous Operations**: Overlaps computation and data transfer using CUDA streams
- **Disk/NVMe Serialization**: Supports secondary storage when memory is insufficient
## 🎯 Offload Strategies
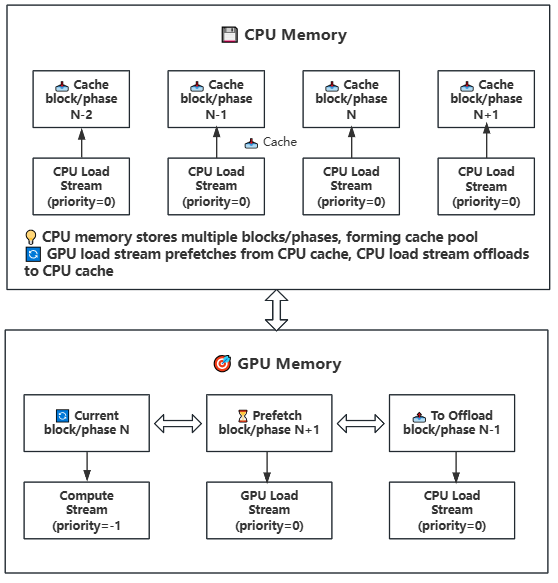
### Strategy 1: GPU-CPU Block/Phase Offload
**Use Case**: Insufficient GPU memory but sufficient system memory
**How It Works**: Manages model weights in block or phase units between GPU and CPU memory, utilizing CUDA streams to overlap computation and data transfer. Blocks contain complete Transformer layers, while Phases are individual computational components within blocks.
**Block vs Phase Explanation**:
- **Block Granularity**: Larger memory management unit containing complete Transformer layers (self-attention, cross-attention, feedforward networks, etc.), suitable for sufficient memory scenarios with reduced management overhead
- **Phase Granularity**: Finer-grained memory management containing individual computational components (such as self-attention, cross-attention, feedforward networks, etc.), suitable for memory-constrained scenarios with more flexible memory control
**Key Features:**
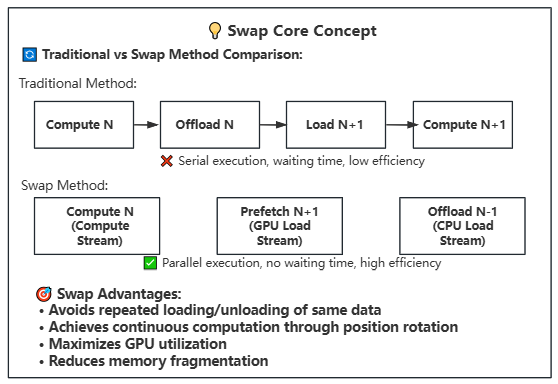
- **Asynchronous Transfer**: Uses three CUDA streams with different priorities for parallel computation and transfer
- Compute stream (priority=-1): High priority, handles current computation
- GPU load stream (priority=0): Medium priority, handles CPU to GPU prefetching
- CPU load stream (priority=0): Medium priority, handles GPU to CPU offloading
- **Prefetch Mechanism**: Preloads the next block/phase to GPU in advance
- **Intelligent Caching**: Maintains weight cache in CPU memory
- **Stream Synchronization**: Ensures correctness of data transfer and computation
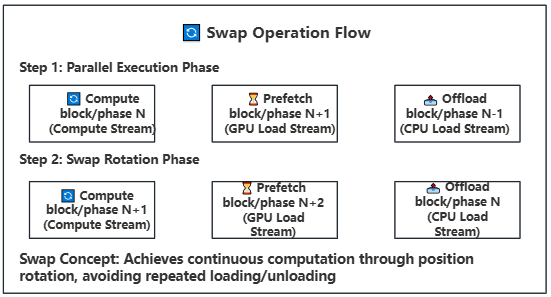
- **Swap Operation**: Rotates block/phase positions after computation for continuous execution
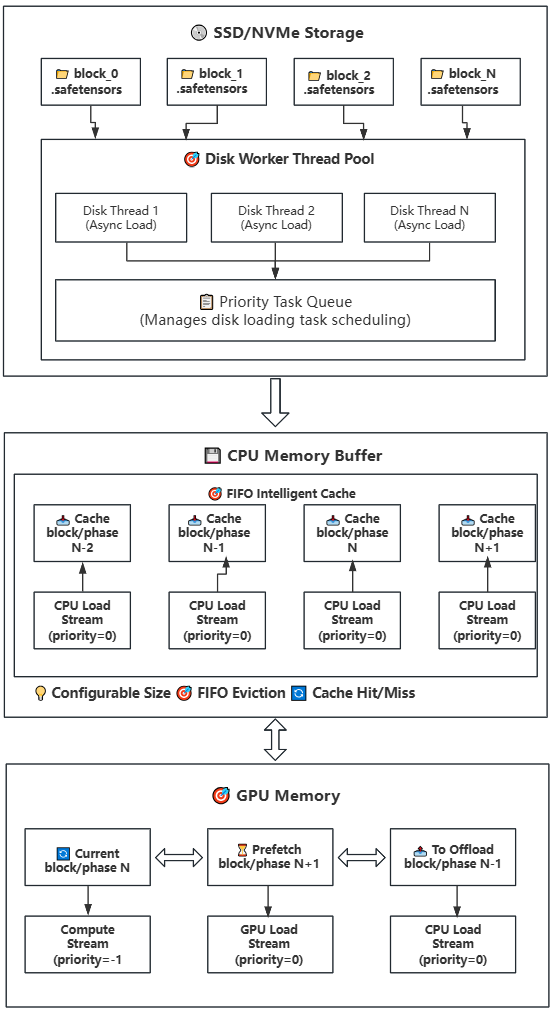
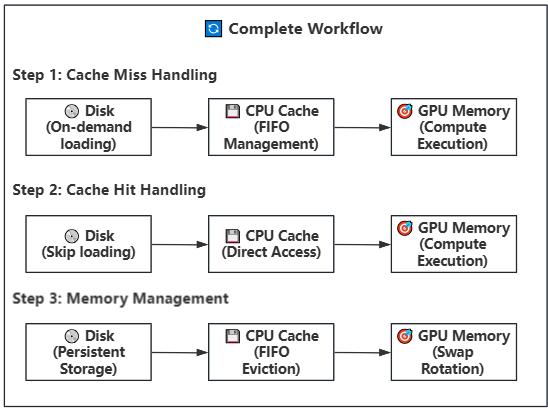
### Strategy 2: Disk-CPU-GPU Block/Phase Offload (Lazy Loading)
**Use Case**: Both GPU memory and system memory are insufficient
**How It Works**: Builds upon Strategy 1 by introducing disk storage, implementing a three-tier storage hierarchy (Disk → CPU → GPU). CPU continues to serve as a cache pool with configurable size, suitable for devices with limited CPU memory.
**Key Features:**
- **Lazy Loading**: Model weights are loaded from disk on-demand, avoiding loading the entire model at once
- **Intelligent Caching**: CPU memory buffer uses FIFO strategy with configurable size
- **Multi-threaded Prefetch**: Uses multiple disk worker threads for parallel loading
- **Asynchronous Transfer**: Uses CUDA streams to overlap computation and data transfer
- **Swap Rotation**: Achieves continuous computation through position rotation, avoiding repeated loading/offloading
**Working Steps**:
- **Disk Storage**: Model weights are stored on SSD/NVMe by block, one .safetensors file per block
- **Task Scheduling**: When a block/phase is needed, priority task queue assigns disk worker threads
- **Asynchronous Loading**: Multiple disk threads load weight files from disk to CPU memory buffer in parallel
- **Intelligent Caching**: CPU memory buffer manages cache using FIFO strategy with configurable size
- **Cache Hit**: If weights are already in cache, transfer directly to GPU without disk read
- **Prefetch Transfer**: Weights in cache are asynchronously transferred to GPU memory (using GPU load stream)
- **Compute Execution**: Weights on GPU perform computation (using compute stream) while background continues prefetching next block/phase
- **Swap Rotation**: After computation completes, rotate block/phase positions for continuous computation
- **Memory Management**: When CPU cache is full, automatically evict the least recently used weight block/phase
## ⚙️ Configuration Parameters
### GPU-CPU Offload Configuration
```python
config = {
"cpu_offload": True,
"offload_ratio": 1.0, # Offload ratio (0.0-1.0)
"offload_granularity": "block", # Offload granularity: "block" or "phase"
"lazy_load": False, # Disable lazy loading
}
```
### Disk-CPU-GPU Offload Configuration
```python
config = {
"cpu_offload": True,
"lazy_load": True, # Enable lazy loading
"offload_ratio": 1.0, # Offload ratio
"offload_granularity": "phase", # Recommended to use phase granularity
"num_disk_workers": 2, # Number of disk worker threads
"offload_to_disk": True, # Enable disk offload
}
```
**Intelligent Cache Key Parameters:**
- `max_memory`: Controls CPU cache size, affects cache hit rate and memory usage
- `num_disk_workers`: Controls number of disk loading threads, affects prefetch speed
- `offload_granularity`: Controls cache granularity (block or phase), affects cache efficiency
- `"block"`: Cache management in complete Transformer layer units
- `"phase"`: Cache management in individual computational component units
**Offload Configuration for Non-DIT Model Components (T5, CLIP, VAE):**
The offload behavior of these components follows these rules:
- **Default Behavior**: If not specified separately, T5, CLIP, VAE will follow the `cpu_offload` setting
- **Independent Configuration**: Can set offload strategy separately for each component for fine-grained control
**Configuration Example**:
```json
{
"cpu_offload": true, // DIT model offload switch
"t5_cpu_offload": false, // T5 encoder independent setting
"clip_cpu_offload": false, // CLIP encoder independent setting
"vae_cpu_offload": false // VAE encoder independent setting
}
```
For memory-constrained devices, a progressive offload strategy is recommended:
1. **Step 1**: Only enable `cpu_offload`, disable `t5_cpu_offload`, `clip_cpu_offload`, `vae_cpu_offload`
2. **Step 2**: If memory is still insufficient, gradually enable CPU offload for T5, CLIP, VAE
3. **Step 3**: If memory is still not enough, consider using quantization + CPU offload or enable `lazy_load`
**Practical Experience**:
- **RTX 4090 24GB + 14B Model**: Usually only need to enable `cpu_offload`, manually set other component offload to `false`, and use FP8 quantized version
- **Smaller Memory GPUs**: Need to combine quantization, CPU offload, and lazy loading
- **Quantization Schemes**: Refer to [Quantization Documentation](../method_tutorials/quantization.md) to select appropriate quantization strategy
**Configuration File Reference**:
- **Wan2.1 Series Models**: Refer to [offload config files](https://github.com/ModelTC/lightx2v/tree/main/configs/offload)
- **Wan2.2 Series Models**: Refer to [wan22 config files](https://github.com/ModelTC/lightx2v/tree/main/configs/wan22) with `4090` suffix
## 🎯 Usage Recommendations
- 🔄 GPU-CPU Block/Phase Offload: Suitable for insufficient GPU memory (RTX 3090/4090 24G) but sufficient system memory (>64/128G)
- 💾 Disk-CPU-GPU Block/Phase Offload: Suitable for both insufficient GPU memory (RTX 3060/4090 8G) and system memory (16/32G)
- 🚫 No Offload: Suitable for high-end hardware configurations pursuing best performance
## 🔍 Troubleshooting
### Common Issues and Solutions
1. **Disk I/O Bottleneck**
- Solution: Use NVMe SSD, increase num_disk_workers
2. **Memory Buffer Overflow**
- Solution: Increase max_memory or reduce num_disk_workers
3. **Loading Timeout**
- Solution: Check disk performance, optimize file system
**Note**: This offload mechanism is specifically designed for LightX2V, fully utilizing the asynchronous computing capabilities of modern hardware, significantly lowering the hardware threshold for large model inference.