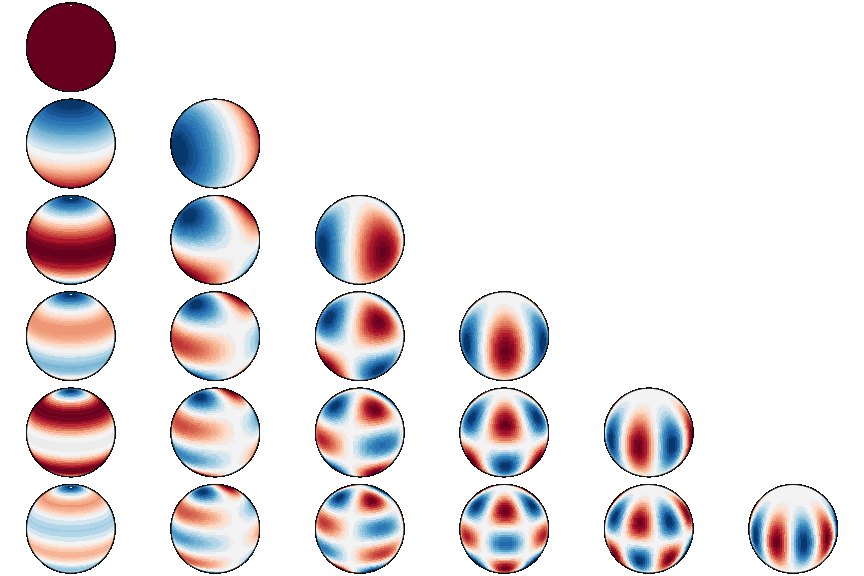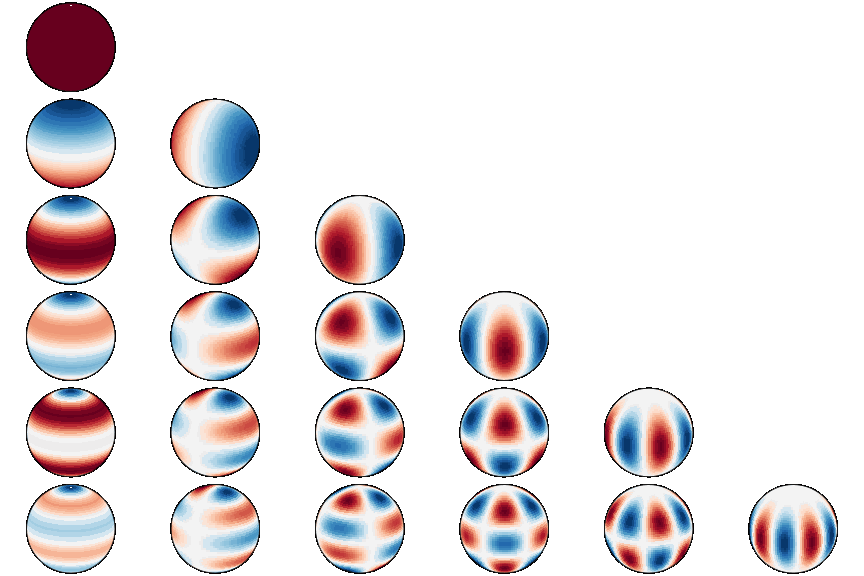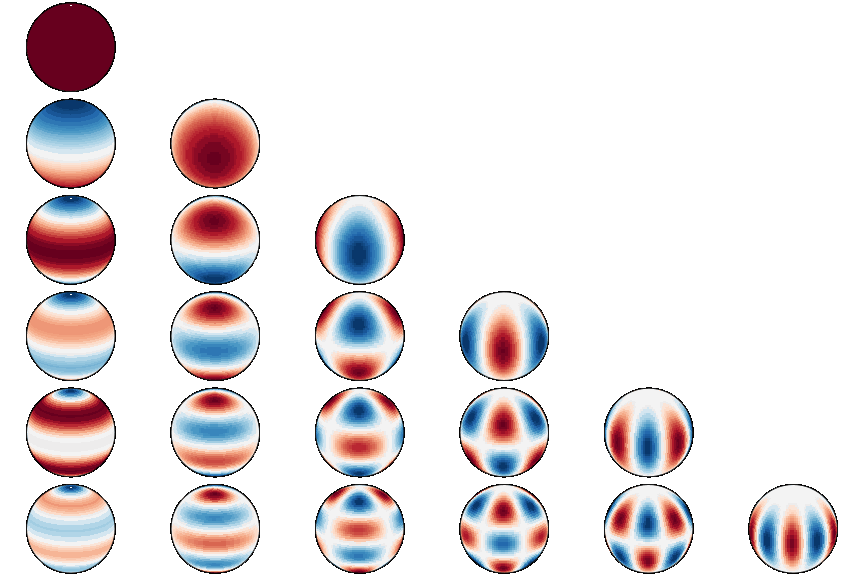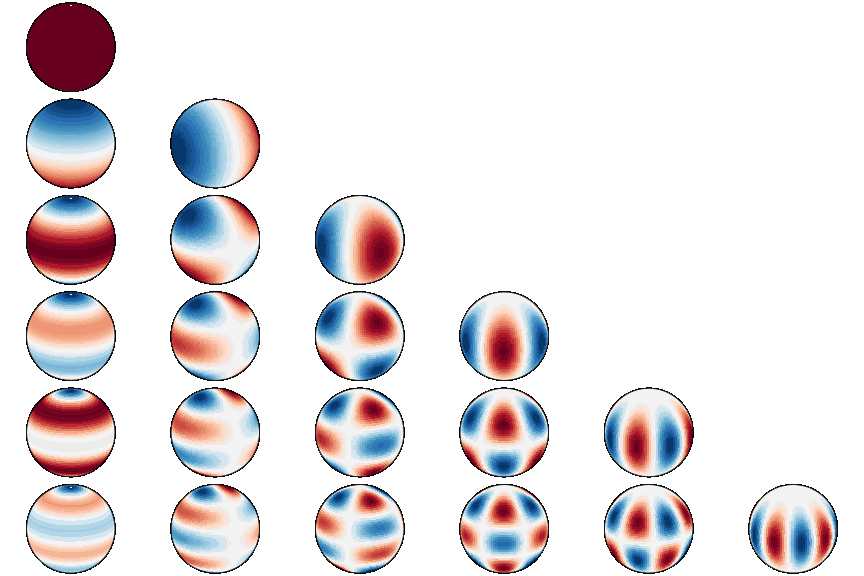Bbonev/documentation refactor (#14)
* Adding plotting routines and reworked Readme * Added illustration of spherical harmonics to Readme
Showing
132 Bytes
This source diff could not be displayed because it is too large. You can view the blob instead.
notebooks/plotting.py
0 → 100644