add Chinese translation (#661)
Showing
zh_CN/docs/conf.py
0 → 100644
zh_CN/docs/gbdt_example.md
0 → 100644
zh_CN/docs/img/3_steps.jpg
0 → 100644
77.7 KB
zh_CN/docs/img/Assessor.png
0 → 100644
119 KB
162 KB
67.6 KB
92.2 KB
292 KB
71.5 KB
118 KB
36.7 KB
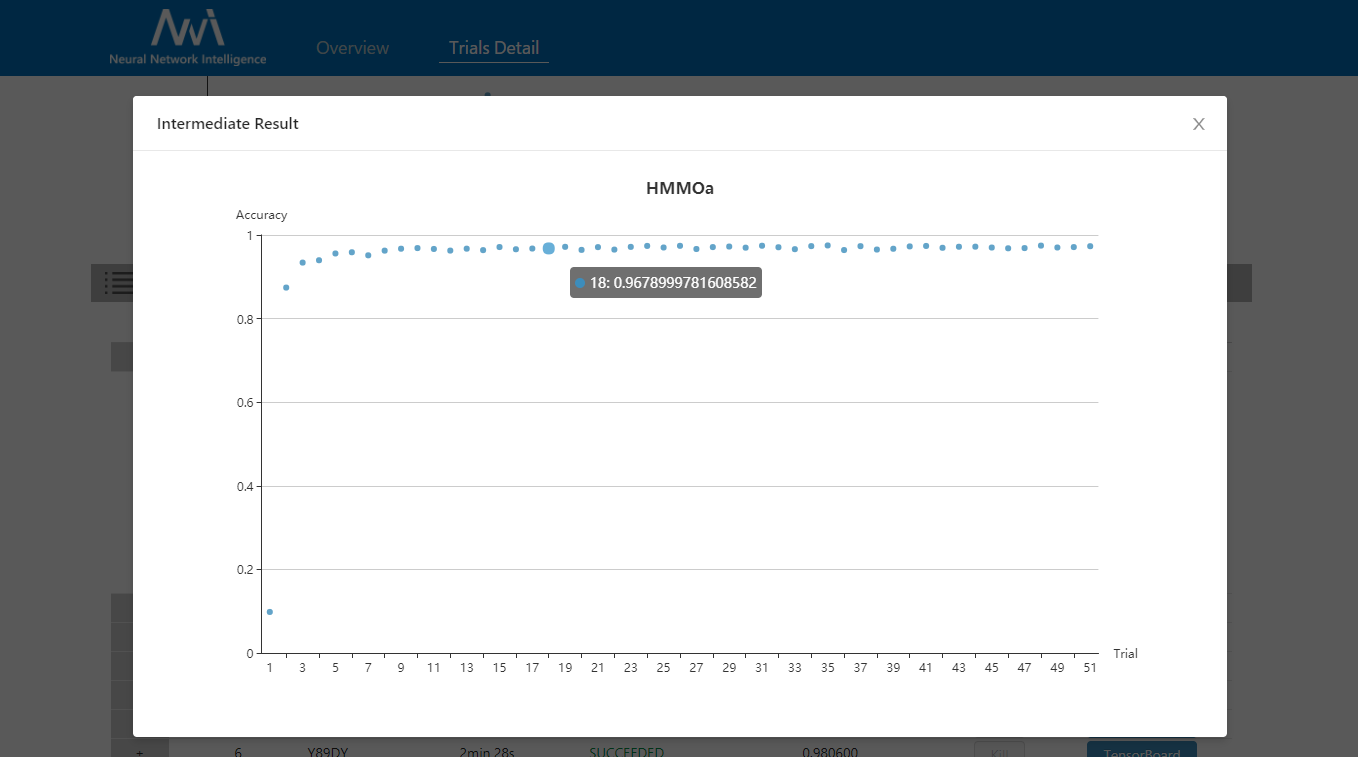
zh_CN/docs/img/accuracy.png
0 → 100644
28.8 KB
919 KB
33.2 KB
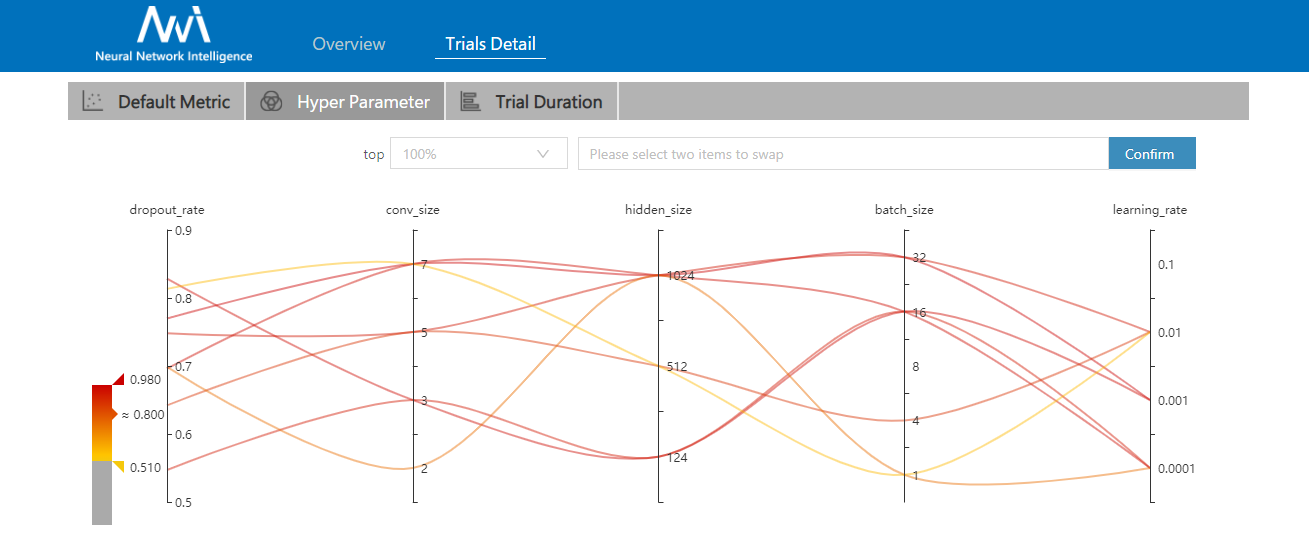
zh_CN/docs/img/hyperPara.png
0 → 100644
85.1 KB
35.9 KB
43.7 KB
123 KB
zh_CN/docs/img/nni_logo.png
0 → 100644
23.4 KB
22.2 KB