 -
-
- OpenMMLab website
-
-
- HOT
-
-
-
- OpenMMLab platform
-
-
- TRY IT OUT
-
-
-
- 
 -
-Then, you can clone the repositories to local:
-
-```shell
-git clone git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git
+```{note}
+If you plan to add some new features that involve large changes, it is encouraged to open an issue for discussion first.
```
+### Code style
-After that, you should ddd official repository as the upstream repository
+#### Python
-```bash
-git remote add upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv
-```
+We adopt [PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) as the preferred code style.
-Check whether remote repository has been added successfully by `git remote -v`
+We use the following tools for linting and formatting:
-```bash
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (fetch)
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (push)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (fetch)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (push)
-```
+- [flake8](http://flake8.pycqa.org/en/latest/): A wrapper around some linter tools.
+- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): A formatter for Python files.
+- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): A Python utility to sort imports.
+- [markdownlint](https://github.com/markdownlint/markdownlint): A linter to check markdown files and flag style issues.
+- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): A formatter to format docstring.
-> Here's a brief introduction to origin and upstream. When we use "git clone", we create an "origin" remote by default, which points to the repository cloned from. As for "upstream", we add it ourselves to point to the target repository. Of course, if you don't like the name "upstream", you could name it as you wish. Usually, we'll push the code to "origin". If the pushed code conflicts with the latest code in official("upstream"), we should pull the latest code from upstream to resolve the conflicts, and then push to "origin" again. The posted Pull Request will be updated automatically.
+Style configurations of yapf and isort can be found in [setup.cfg](./setup.cfg).
-#### 2. Configure pre-commit
+We use [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) that checks and formats for `flake8`, `yapf`, `isort`, `trailing whitespaces`, `markdown files`,
+fixes `end-of-files`, `double-quoted-strings`, `python-encoding-pragma`, `mixed-line-ending`, sorts `requirments.txt` automatically on every commit.
+The config for a pre-commit hook is stored in [.pre-commit-config](./.pre-commit-config.yaml).
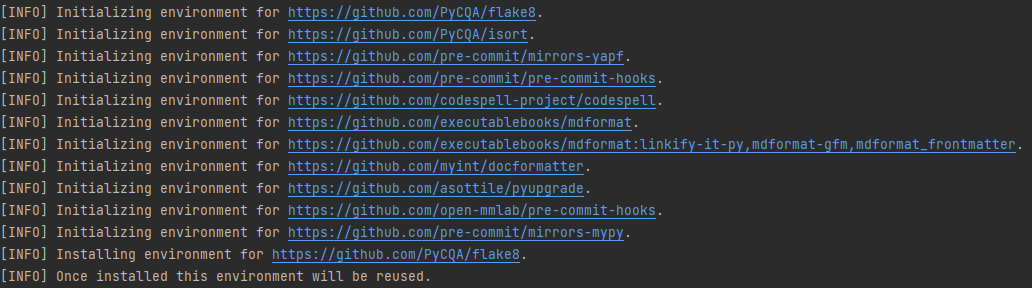
-You should configure [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/#intro) in the local development environment to make sure the code style matches that of OpenMMLab. **Note**: The following code should be executed under the MMCV directory.
+After you clone the repository, you will need to install initialize pre-commit hook.
```shell
pip install -U pre-commit
-pre-commit install
-```
-
-Check that pre-commit is configured successfully, and install the hooks defined in `.pre-commit-config.yaml`.
-
-```shell
-pre-commit run --all-files
-```
-
-
-
-Then, you can clone the repositories to local:
-
-```shell
-git clone git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git
+```{note}
+If you plan to add some new features that involve large changes, it is encouraged to open an issue for discussion first.
```
+### Code style
-After that, you should ddd official repository as the upstream repository
+#### Python
-```bash
-git remote add upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv
-```
+We adopt [PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) as the preferred code style.
-Check whether remote repository has been added successfully by `git remote -v`
+We use the following tools for linting and formatting:
-```bash
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (fetch)
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (push)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (fetch)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (push)
-```
+- [flake8](http://flake8.pycqa.org/en/latest/): A wrapper around some linter tools.
+- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): A formatter for Python files.
+- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): A Python utility to sort imports.
+- [markdownlint](https://github.com/markdownlint/markdownlint): A linter to check markdown files and flag style issues.
+- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): A formatter to format docstring.
-> Here's a brief introduction to origin and upstream. When we use "git clone", we create an "origin" remote by default, which points to the repository cloned from. As for "upstream", we add it ourselves to point to the target repository. Of course, if you don't like the name "upstream", you could name it as you wish. Usually, we'll push the code to "origin". If the pushed code conflicts with the latest code in official("upstream"), we should pull the latest code from upstream to resolve the conflicts, and then push to "origin" again. The posted Pull Request will be updated automatically.
+Style configurations of yapf and isort can be found in [setup.cfg](./setup.cfg).
-#### 2. Configure pre-commit
+We use [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) that checks and formats for `flake8`, `yapf`, `isort`, `trailing whitespaces`, `markdown files`,
+fixes `end-of-files`, `double-quoted-strings`, `python-encoding-pragma`, `mixed-line-ending`, sorts `requirments.txt` automatically on every commit.
+The config for a pre-commit hook is stored in [.pre-commit-config](./.pre-commit-config.yaml).
-You should configure [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/#intro) in the local development environment to make sure the code style matches that of OpenMMLab. **Note**: The following code should be executed under the MMCV directory.
+After you clone the repository, you will need to install initialize pre-commit hook.
```shell
pip install -U pre-commit
-pre-commit install
-```
-
-Check that pre-commit is configured successfully, and install the hooks defined in `.pre-commit-config.yaml`.
-
-```shell
-pre-commit run --all-files
-```
-
- -
-
-
-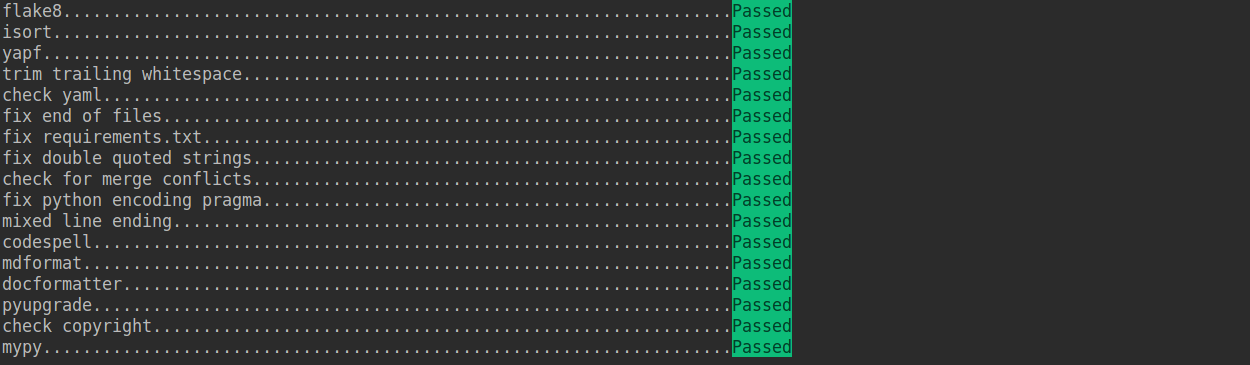 -
-If the installation process is interrupted, you can repeatedly run `pre-commit run ... ` to continue the installation.
-
-If the code does not conform to the code style specification, pre-commit will raise a warning and fixes some of the errors automatically.
-
-
-
-If the installation process is interrupted, you can repeatedly run `pre-commit run ... ` to continue the installation.
-
-If the code does not conform to the code style specification, pre-commit will raise a warning and fixes some of the errors automatically.
-
-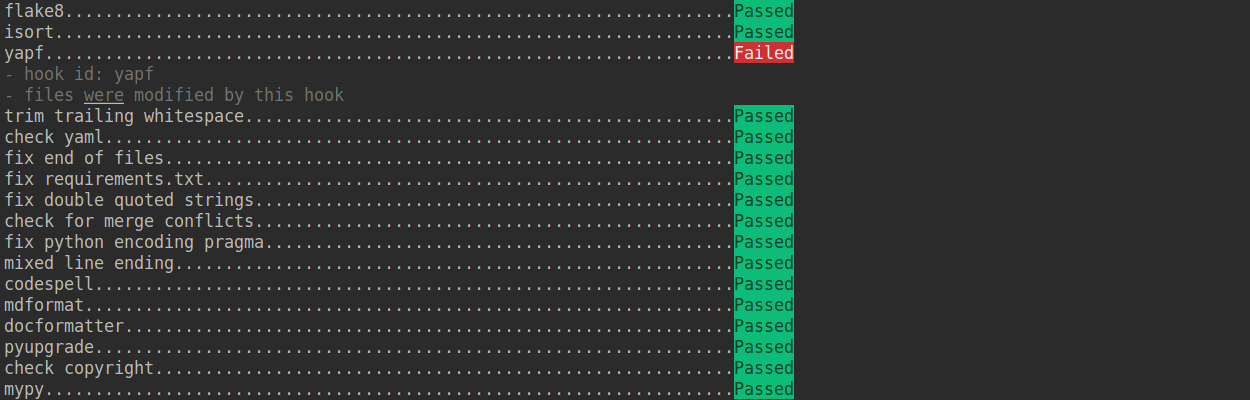 -
-If we want to commit our code bypassing the pre-commit hook, we can use the `--no-verify` option(**only for temporarily commit**).
-
-```shell
-git commit -m "xxx" --no-verify
-```
-
-#### 3. Create a development branch
-
-After configuring the pre-commit, we should create a branch based on the master branch to develop the new feature or fix the bug. The proposed branch name is `username/pr_name`
-
-```shell
-git checkout -b yhc/refactor_contributing_doc
-```
-
-In subsequent development, if the master branch of the local repository is behind the master branch of "upstream", we need to pull the upstream for synchronization, and then execute the above command:
-
-```shell
-git pull upstream master
-```
-
-#### 4. Commit the code and pass the unit test
-
-- MMCV introduces mypy to do static type checking to increase the robustness of the code. Therefore, we need to add Type Hints to our code and pass the mypy check. If you are not familiar with Type Hints, you can refer to [this tutorial](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
-
-- The committed code should pass through the unit test
-
- ```shell
- # Pass all unit tests
- pytest tests
-
- # Pass the unit test of runner
- pytest tests/test_runner/test_runner.py
- ```
-
- If the unit test fails for lack of dependencies, you can install the dependencies referring to the [guidance](#unit-test)
-
-- If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result referring to [guidance](#document-rendering)
-
-#### 5. Push the code to remote
-
-We could push the local commits to remote after passing through the check of unit test and pre-commit. You can associate the local branch with remote branch by adding `-u` option.
-
-```shell
-git push -u origin {branch_name}
-```
-
-This will allow you to use the `git push` command to push code directly next time, without having to specify a branch or the remote repository.
-
-#### 6. Create a Pull Request
-
-(1) Create a pull request in GitHub's Pull request interface
-
-
-
-If we want to commit our code bypassing the pre-commit hook, we can use the `--no-verify` option(**only for temporarily commit**).
-
-```shell
-git commit -m "xxx" --no-verify
-```
-
-#### 3. Create a development branch
-
-After configuring the pre-commit, we should create a branch based on the master branch to develop the new feature or fix the bug. The proposed branch name is `username/pr_name`
-
-```shell
-git checkout -b yhc/refactor_contributing_doc
-```
-
-In subsequent development, if the master branch of the local repository is behind the master branch of "upstream", we need to pull the upstream for synchronization, and then execute the above command:
-
-```shell
-git pull upstream master
-```
-
-#### 4. Commit the code and pass the unit test
-
-- MMCV introduces mypy to do static type checking to increase the robustness of the code. Therefore, we need to add Type Hints to our code and pass the mypy check. If you are not familiar with Type Hints, you can refer to [this tutorial](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
-
-- The committed code should pass through the unit test
-
- ```shell
- # Pass all unit tests
- pytest tests
-
- # Pass the unit test of runner
- pytest tests/test_runner/test_runner.py
- ```
-
- If the unit test fails for lack of dependencies, you can install the dependencies referring to the [guidance](#unit-test)
-
-- If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result referring to [guidance](#document-rendering)
-
-#### 5. Push the code to remote
-
-We could push the local commits to remote after passing through the check of unit test and pre-commit. You can associate the local branch with remote branch by adding `-u` option.
-
-```shell
-git push -u origin {branch_name}
-```
-
-This will allow you to use the `git push` command to push code directly next time, without having to specify a branch or the remote repository.
-
-#### 6. Create a Pull Request
-
-(1) Create a pull request in GitHub's Pull request interface
-
- -
-(2) Modify the PR description according to the guidelines so that other developers can better understand your changes
-
-
-
-(2) Modify the PR description according to the guidelines so that other developers can better understand your changes
-
- -
-Find more details about Pull Request description in [pull request guidelines](#pr-specs).
-
-**note**
-
-(a) The Pull Request description should contain the reason for the change, the content of the change, and the impact of the change, and be associated with the relevant Issue (see [documentation](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue)
-
-(b) If it is your first contribution, please sign the CLA
-
-
-
-Find more details about Pull Request description in [pull request guidelines](#pr-specs).
-
-**note**
-
-(a) The Pull Request description should contain the reason for the change, the content of the change, and the impact of the change, and be associated with the relevant Issue (see [documentation](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue)
-
-(b) If it is your first contribution, please sign the CLA
-
-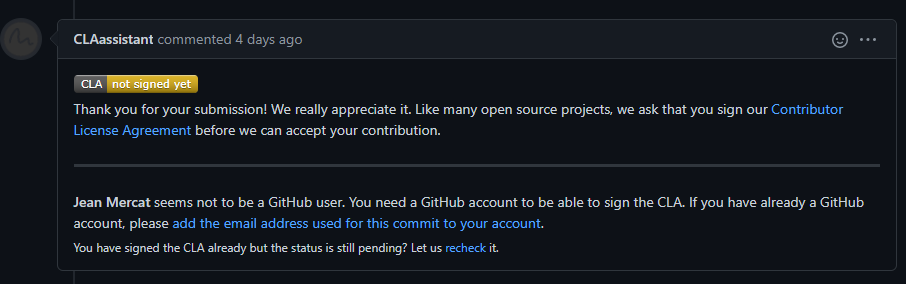 -
-(c) Check whether the Pull Request pass through the CI
-
-
-
-(c) Check whether the Pull Request pass through the CI
-
- -
-MMCV will run unit test for the posted Pull Request on different platforms (Linux, Window, Mac), based on different versions of Python, PyTorch, CUDA to make sure the code is correct. We can see the specific test information by clicking `Details` in the above image so that we can modify the code.
-
-(3) If the Pull Request passes the CI, then you can wait for the review from other developers. You'll modify the code based on the reviewer's comments, and repeat the steps [4](#4-commit-the-code-and-pass-the-unit-test)-[5](#5-push-the-code-to-remote) until all reviewers approve it. Then, we will merge it ASAP.
-
-
-
-MMCV will run unit test for the posted Pull Request on different platforms (Linux, Window, Mac), based on different versions of Python, PyTorch, CUDA to make sure the code is correct. We can see the specific test information by clicking `Details` in the above image so that we can modify the code.
-
-(3) If the Pull Request passes the CI, then you can wait for the review from other developers. You'll modify the code based on the reviewer's comments, and repeat the steps [4](#4-commit-the-code-and-pass-the-unit-test)-[5](#5-push-the-code-to-remote) until all reviewers approve it. Then, we will merge it ASAP.
-
- -
-#### 7. Resolve conflicts
-
-If your local branch conflicts with the latest master branch of "upstream", you'll need to resolove them. There are two ways to do this:
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git rebase upstream/master
```
-or
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git merge upstream/master
-```
-
-If you are very good at handling conflicts, then you can use rebase to resolve conflicts, as this will keep your commit logs tidy. If you are not familiar with `rebase`, then you can use `merge` to resolve conflicts.
-
-### Guidance
-
-#### Unit test
-
-If you cannot run the unit test of some modules for lacking of some dependencies, such as [video](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/master/mmcv/video) module, you can try to install the following dependencies:
+From the repository folder
```shell
-# Linux
-sudo apt-get update -y
-sudo apt-get install -y libturbojpeg
-sudo apt-get install -y ffmpeg
-
-# Windows
-conda install ffmpeg
+pre-commit install
```
-We should also make sure the committed code will not decrease the coverage of unit test, we could run the following command to check the coverage of unit test:
+Try the following steps to install ruby when you encounter an issue on installing markdownlint
```shell
-python -m coverage run -m pytest /path/to/test_file
-python -m coverage html
-# check file in htmlcov/index.html
-```
-
-#### Document rendering
+# install rvm
+curl -L https://get.rvm.io | bash -s -- --autolibs=read-fail
+[[ -s "$HOME/.rvm/scripts/rvm" ]] && source "$HOME/.rvm/scripts/rvm"
+rvm autolibs disable
-If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result. We could install the dependencies and run the following command to render the documents and check the results:
-
-```shell
-pip install -r requirements/docs.txt
-cd docs/zh_cn/
-# or docs/en
-make html
-# check file in ./docs/zh_cn/_build/html/index.html
+# install ruby
+rvm install 2.7.1
```
-### Code style
+Or refer to [this repo](https://github.com/innerlee/setup) and take [`zzruby.sh`](https://github.com/innerlee/setup/blob/master/zzruby.sh) according its instruction.
-#### Python
+After this on every commit check code linters and formatter will be enforced.
-We adopt [PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) as the preferred code style.
-
-We use the following tools for linting and formatting:
-
-- [flake8](https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8): A wrapper around some linter tools.
-- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): A Python utility to sort imports.
-- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): A formatter for Python files.
-- [codespell](https://github.com/codespell-project/codespell): A Python utility to fix common misspellings in text files.
-- [mdformat](https://github.com/executablebooks/mdformat): Mdformat is an opinionated Markdown formatter that can be used to enforce a consistent style in Markdown files.
-- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): A formatter to format docstring.
-
-Style configurations of yapf and isort can be found in [setup.cfg](./setup.cfg).
-
-We use [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) that checks and formats for `flake8`, `yapf`, `isort`, `trailing whitespaces`, `markdown files`,
-fixes `end-of-files`, `double-quoted-strings`, `python-encoding-pragma`, `mixed-line-ending`, sorts `requirments.txt` automatically on every commit.
-The config for a pre-commit hook is stored in [.pre-commit-config](./.pre-commit-config.yaml).
+>Before you create a PR, make sure that your code lints and is formatted by yapf.
#### C++ and CUDA
We follow the [Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html).
-
-### PR Specs
-
-1. Use [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com) hook to avoid issues of code style
-
-2. One short-time branch should be matched with only one PR
-
-3. Accomplish a detailed change in one PR. Avoid large PR
-
- - Bad: Support Faster R-CNN
- - Acceptable: Add a box head to Faster R-CNN
- - Good: Add a parameter to box head to support custom conv-layer number
-
-4. Provide clear and significant commit message
-
-5. Provide clear and meaningful PR description
-
- - Task name should be clarified in title. The general format is: \[Prefix\] Short description of the PR (Suffix)
- - Prefix: add new feature \[Feature\], fix bug \[Fix\], related to documents \[Docs\], in developing \[WIP\] (which will not be reviewed temporarily)
- - Introduce main changes, results and influences on other modules in short description
- - Associate related issues and pull requests with a milestone
diff --git a/CONTRIBUTING_zh-CN.md b/CONTRIBUTING_zh-CN.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 00622031dd567957829f38d0425d3d23741c8f2f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/CONTRIBUTING_zh-CN.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,274 +0,0 @@
-## 贡献代码
-
-欢迎加入 MMCV 社区,我们致力于打造最前沿的计算机视觉基础库,我们欢迎任何类型的贡献,包括但不限于
-
-**修复错误**
-
-修复代码实现错误的步骤如下:
-
-1. 如果提交的代码改动较大,建议先提交 issue,并正确描述 issue 的现象、原因和复现方式,讨论后确认修复方案。
-2. 修复错误并补充相应的单元测试,提交拉取请求。
-
-**新增功能或组件**
-
-1. 如果新功能或模块涉及较大的代码改动,建议先提交 issue,确认功能的必要性。
-2. 实现新增功能并添单元测试,提交拉取请求。
-
-**文档补充**
-
-修复文档可以直接提交拉取请求
-
-添加文档或将文档翻译成其他语言步骤如下
-
-1. 提交 issue,确认添加文档的必要性。
-2. 添加文档,提交拉取请求。
-
-### 拉取请求工作流
-
-如果你对拉取请求不了解,没关系,接下来的内容将会从零开始,一步一步地指引你如何创建一个拉取请求。如果你想深入了解拉取请求的开发模式,可以参考 github [官方文档](https://docs.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/about-pull-requests)
-
-#### 1. 复刻仓库
-
-当你第一次提交拉取请求时,先复刻 OpenMMLab 原代码库,点击 GitHub 页面右上角的 **Fork** 按钮,复刻后的代码库将会出现在你的 GitHub 个人主页下。
-
-
-
-#### 7. Resolve conflicts
-
-If your local branch conflicts with the latest master branch of "upstream", you'll need to resolove them. There are two ways to do this:
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git rebase upstream/master
```
-or
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git merge upstream/master
-```
-
-If you are very good at handling conflicts, then you can use rebase to resolve conflicts, as this will keep your commit logs tidy. If you are not familiar with `rebase`, then you can use `merge` to resolve conflicts.
-
-### Guidance
-
-#### Unit test
-
-If you cannot run the unit test of some modules for lacking of some dependencies, such as [video](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/master/mmcv/video) module, you can try to install the following dependencies:
+From the repository folder
```shell
-# Linux
-sudo apt-get update -y
-sudo apt-get install -y libturbojpeg
-sudo apt-get install -y ffmpeg
-
-# Windows
-conda install ffmpeg
+pre-commit install
```
-We should also make sure the committed code will not decrease the coverage of unit test, we could run the following command to check the coverage of unit test:
+Try the following steps to install ruby when you encounter an issue on installing markdownlint
```shell
-python -m coverage run -m pytest /path/to/test_file
-python -m coverage html
-# check file in htmlcov/index.html
-```
-
-#### Document rendering
+# install rvm
+curl -L https://get.rvm.io | bash -s -- --autolibs=read-fail
+[[ -s "$HOME/.rvm/scripts/rvm" ]] && source "$HOME/.rvm/scripts/rvm"
+rvm autolibs disable
-If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result. We could install the dependencies and run the following command to render the documents and check the results:
-
-```shell
-pip install -r requirements/docs.txt
-cd docs/zh_cn/
-# or docs/en
-make html
-# check file in ./docs/zh_cn/_build/html/index.html
+# install ruby
+rvm install 2.7.1
```
-### Code style
+Or refer to [this repo](https://github.com/innerlee/setup) and take [`zzruby.sh`](https://github.com/innerlee/setup/blob/master/zzruby.sh) according its instruction.
-#### Python
+After this on every commit check code linters and formatter will be enforced.
-We adopt [PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) as the preferred code style.
-
-We use the following tools for linting and formatting:
-
-- [flake8](https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8): A wrapper around some linter tools.
-- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): A Python utility to sort imports.
-- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): A formatter for Python files.
-- [codespell](https://github.com/codespell-project/codespell): A Python utility to fix common misspellings in text files.
-- [mdformat](https://github.com/executablebooks/mdformat): Mdformat is an opinionated Markdown formatter that can be used to enforce a consistent style in Markdown files.
-- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): A formatter to format docstring.
-
-Style configurations of yapf and isort can be found in [setup.cfg](./setup.cfg).
-
-We use [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) that checks and formats for `flake8`, `yapf`, `isort`, `trailing whitespaces`, `markdown files`,
-fixes `end-of-files`, `double-quoted-strings`, `python-encoding-pragma`, `mixed-line-ending`, sorts `requirments.txt` automatically on every commit.
-The config for a pre-commit hook is stored in [.pre-commit-config](./.pre-commit-config.yaml).
+>Before you create a PR, make sure that your code lints and is formatted by yapf.
#### C++ and CUDA
We follow the [Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html).
-
-### PR Specs
-
-1. Use [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com) hook to avoid issues of code style
-
-2. One short-time branch should be matched with only one PR
-
-3. Accomplish a detailed change in one PR. Avoid large PR
-
- - Bad: Support Faster R-CNN
- - Acceptable: Add a box head to Faster R-CNN
- - Good: Add a parameter to box head to support custom conv-layer number
-
-4. Provide clear and significant commit message
-
-5. Provide clear and meaningful PR description
-
- - Task name should be clarified in title. The general format is: \[Prefix\] Short description of the PR (Suffix)
- - Prefix: add new feature \[Feature\], fix bug \[Fix\], related to documents \[Docs\], in developing \[WIP\] (which will not be reviewed temporarily)
- - Introduce main changes, results and influences on other modules in short description
- - Associate related issues and pull requests with a milestone
diff --git a/CONTRIBUTING_zh-CN.md b/CONTRIBUTING_zh-CN.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 00622031dd567957829f38d0425d3d23741c8f2f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/CONTRIBUTING_zh-CN.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,274 +0,0 @@
-## 贡献代码
-
-欢迎加入 MMCV 社区,我们致力于打造最前沿的计算机视觉基础库,我们欢迎任何类型的贡献,包括但不限于
-
-**修复错误**
-
-修复代码实现错误的步骤如下:
-
-1. 如果提交的代码改动较大,建议先提交 issue,并正确描述 issue 的现象、原因和复现方式,讨论后确认修复方案。
-2. 修复错误并补充相应的单元测试,提交拉取请求。
-
-**新增功能或组件**
-
-1. 如果新功能或模块涉及较大的代码改动,建议先提交 issue,确认功能的必要性。
-2. 实现新增功能并添单元测试,提交拉取请求。
-
-**文档补充**
-
-修复文档可以直接提交拉取请求
-
-添加文档或将文档翻译成其他语言步骤如下
-
-1. 提交 issue,确认添加文档的必要性。
-2. 添加文档,提交拉取请求。
-
-### 拉取请求工作流
-
-如果你对拉取请求不了解,没关系,接下来的内容将会从零开始,一步一步地指引你如何创建一个拉取请求。如果你想深入了解拉取请求的开发模式,可以参考 github [官方文档](https://docs.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/about-pull-requests)
-
-#### 1. 复刻仓库
-
-当你第一次提交拉取请求时,先复刻 OpenMMLab 原代码库,点击 GitHub 页面右上角的 **Fork** 按钮,复刻后的代码库将会出现在你的 GitHub 个人主页下。
-
- -
-将代码克隆到本地
-
-```shell
-git clone git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git
-```
-
-添加原代码库为上游代码库
-
-```bash
-git remote add upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv
-```
-
-检查 remote 是否添加成功,在终端输入 `git remote -v`
-
-```bash
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (fetch)
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (push)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (fetch)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (push)
-```
-
-> 这里对 origin 和 upstream 进行一个简单的介绍,当我们使用 git clone 来克隆代码时,会默认创建一个 origin 的 remote,它指向我们克隆的代码库地址,而 upstream 则是我们自己添加的,用来指向原始代码库地址。当然如果你不喜欢他叫 upstream,也可以自己修改,比如叫 open-mmlab。我们通常向 origin 提交代码(即 fork 下来的远程仓库),然后向 upstream 提交一个 pull request。如果提交的代码和最新的代码发生冲突,再从 upstream 拉取最新的代码,和本地分支解决冲突,再提交到 origin。
-
-#### 2. 配置 pre-commit
-
-在本地开发环境中,我们使用 [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/#intro) 来检查代码风格,以确保代码风格的统一。在提交代码,需要先安装 pre-commit(需要在 MMCV 目录下执行):
-
-```shell
-pip install -U pre-commit
-pre-commit install
-```
-
-检查 pre-commit 是否配置成功,并安装 `.pre-commit-config.yaml` 中的钩子:
-
-```shell
-pre-commit run --all-files
-```
-
-
-
-将代码克隆到本地
-
-```shell
-git clone git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git
-```
-
-添加原代码库为上游代码库
-
-```bash
-git remote add upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv
-```
-
-检查 remote 是否添加成功,在终端输入 `git remote -v`
-
-```bash
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (fetch)
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (push)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (fetch)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (push)
-```
-
-> 这里对 origin 和 upstream 进行一个简单的介绍,当我们使用 git clone 来克隆代码时,会默认创建一个 origin 的 remote,它指向我们克隆的代码库地址,而 upstream 则是我们自己添加的,用来指向原始代码库地址。当然如果你不喜欢他叫 upstream,也可以自己修改,比如叫 open-mmlab。我们通常向 origin 提交代码(即 fork 下来的远程仓库),然后向 upstream 提交一个 pull request。如果提交的代码和最新的代码发生冲突,再从 upstream 拉取最新的代码,和本地分支解决冲突,再提交到 origin。
-
-#### 2. 配置 pre-commit
-
-在本地开发环境中,我们使用 [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/#intro) 来检查代码风格,以确保代码风格的统一。在提交代码,需要先安装 pre-commit(需要在 MMCV 目录下执行):
-
-```shell
-pip install -U pre-commit
-pre-commit install
-```
-
-检查 pre-commit 是否配置成功,并安装 `.pre-commit-config.yaml` 中的钩子:
-
-```shell
-pre-commit run --all-files
-```
-
- -
-
-
- -
-> 如果你是中国用户,由于网络原因,可能会出现安装失败的情况,这时可以使用国内源
-
-> pre-commit install -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-
-> pre-commit run --all-files -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-
-如果安装过程被中断,可以重复执行 `pre-commit run ...` 继续安装。
-
-如果提交的代码不符合代码风格规范,pre-commit 会发出警告,并自动修复部分错误。
-
-
-
-> 如果你是中国用户,由于网络原因,可能会出现安装失败的情况,这时可以使用国内源
-
-> pre-commit install -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-
-> pre-commit run --all-files -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-
-如果安装过程被中断,可以重复执行 `pre-commit run ...` 继续安装。
-
-如果提交的代码不符合代码风格规范,pre-commit 会发出警告,并自动修复部分错误。
-
- -
-如果我们想临时绕开 pre-commit 的检查提交一次代码,可以在 `git commit` 时加上 `--no-verify`(需要保证最后推送至远程仓库的代码能够通过 pre-commit 检查)。
-
-```shell
-git commit -m "xxx" --no-verify
-```
-
-#### 3. 创建开发分支
-
-安装完 pre-commit 之后,我们需要基于 master 创建开发分支,建议的分支命名规则为 `username/pr_name`。
-
-```shell
-git checkout -b yhc/refactor_contributing_doc
-```
-
-在后续的开发中,如果本地仓库的 master 分支落后于 upstream 的 master 分支,我们需要先拉取 upstream 的代码进行同步,再执行上面的命令
-
-```shell
-git pull upstream master
-```
-
-#### 4. 提交代码并在本地通过单元测试
-
-- MMCV 引入了 mypy 来做静态类型检查,以增加代码的鲁棒性。因此我们在提交代码时,需要补充 Type Hints。具体规则可以参考[教程](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/519335398)。
-
-- 提交的代码同样需要通过单元测试
-
- ```shell
- # 通过全量单元测试
- pytest tests
-
- # 我们需要保证提交的代码能够通过修改模块的单元测试,以 runner 为例
- pytest tests/test_runner/test_runner.py
- ```
-
- 如果你由于缺少依赖无法运行修改模块的单元测试,可以参考[指引-单元测试](#单元测试)
-
-- 如果修改/添加了文档,参考[指引](#文档渲染)确认文档渲染正常。
-
-#### 5. 推送代码到远程
-
-代码通过单元测试和 pre-commit 检查后,将代码推送到远程仓库,如果是第一次推送,可以在 `git push` 后加上 `-u` 参数以关联远程分支
-
-```shell
-git push -u origin {branch_name}
-```
-
-这样下次就可以直接使用 `git push` 命令推送代码了,而无需指定分支和远程仓库。
-
-#### 6. 提交拉取请求(PR)
-
-(1) 在 GitHub 的 Pull request 界面创建拉取请求
-
-
-如果我们想临时绕开 pre-commit 的检查提交一次代码,可以在 `git commit` 时加上 `--no-verify`(需要保证最后推送至远程仓库的代码能够通过 pre-commit 检查)。
-
-```shell
-git commit -m "xxx" --no-verify
-```
-
-#### 3. 创建开发分支
-
-安装完 pre-commit 之后,我们需要基于 master 创建开发分支,建议的分支命名规则为 `username/pr_name`。
-
-```shell
-git checkout -b yhc/refactor_contributing_doc
-```
-
-在后续的开发中,如果本地仓库的 master 分支落后于 upstream 的 master 分支,我们需要先拉取 upstream 的代码进行同步,再执行上面的命令
-
-```shell
-git pull upstream master
-```
-
-#### 4. 提交代码并在本地通过单元测试
-
-- MMCV 引入了 mypy 来做静态类型检查,以增加代码的鲁棒性。因此我们在提交代码时,需要补充 Type Hints。具体规则可以参考[教程](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/519335398)。
-
-- 提交的代码同样需要通过单元测试
-
- ```shell
- # 通过全量单元测试
- pytest tests
-
- # 我们需要保证提交的代码能够通过修改模块的单元测试,以 runner 为例
- pytest tests/test_runner/test_runner.py
- ```
-
- 如果你由于缺少依赖无法运行修改模块的单元测试,可以参考[指引-单元测试](#单元测试)
-
-- 如果修改/添加了文档,参考[指引](#文档渲染)确认文档渲染正常。
-
-#### 5. 推送代码到远程
-
-代码通过单元测试和 pre-commit 检查后,将代码推送到远程仓库,如果是第一次推送,可以在 `git push` 后加上 `-u` 参数以关联远程分支
-
-```shell
-git push -u origin {branch_name}
-```
-
-这样下次就可以直接使用 `git push` 命令推送代码了,而无需指定分支和远程仓库。
-
-#### 6. 提交拉取请求(PR)
-
-(1) 在 GitHub 的 Pull request 界面创建拉取请求
- -
-(2) 根据指引修改 PR 描述,以便于其他开发者更好地理解你的修改
-
-
-
-(2) 根据指引修改 PR 描述,以便于其他开发者更好地理解你的修改
-
- -
-描述规范详见[拉取请求规范](#拉取请求规范)
-
-
-
-**注意事项**
-
-(a) PR 描述应该包含修改理由、修改内容以及修改后带来的影响,并关联相关 Issue(具体方式见[文档](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue))
-
-(b) 如果是第一次为 OpenMMLab 做贡献,需要签署 CLA
-
-
-
-描述规范详见[拉取请求规范](#拉取请求规范)
-
-
-
-**注意事项**
-
-(a) PR 描述应该包含修改理由、修改内容以及修改后带来的影响,并关联相关 Issue(具体方式见[文档](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue))
-
-(b) 如果是第一次为 OpenMMLab 做贡献,需要签署 CLA
-
- -
-(c) 检查提交的 PR 是否通过 CI(集成测试)
-
-
-
-(c) 检查提交的 PR 是否通过 CI(集成测试)
-
- -
-MMCV 会在不同的平台(Linux、Window、Mac),基于不同版本的 Python、PyTorch、CUDA 对提交的代码进行单元测试,以保证代码的正确性,如果有任何一个没有通过,我们可点击上图中的 `Details` 来查看具体的测试信息,以便于我们修改代码。
-
-(3) 如果 PR 通过了 CI,那么就可以等待其他开发者的 review,并根据 reviewer 的意见,修改代码,并重复 [4](#4-提交代码并本地通过单元测试)-[5](#5-推送代码到远程) 步骤,直到 reviewer 同意合入 PR。
-
-
-
-MMCV 会在不同的平台(Linux、Window、Mac),基于不同版本的 Python、PyTorch、CUDA 对提交的代码进行单元测试,以保证代码的正确性,如果有任何一个没有通过,我们可点击上图中的 `Details` 来查看具体的测试信息,以便于我们修改代码。
-
-(3) 如果 PR 通过了 CI,那么就可以等待其他开发者的 review,并根据 reviewer 的意见,修改代码,并重复 [4](#4-提交代码并本地通过单元测试)-[5](#5-推送代码到远程) 步骤,直到 reviewer 同意合入 PR。
-
- -
-所有 reviewer 同意合入 PR 后,我们会尽快将 PR 合并到主分支。
-
-#### 7. 解决冲突
-
-随着时间的推移,我们的代码库会不断更新,这时候,如果你的 PR 与主分支存在冲突,你需要解决冲突,解决冲突的方式有两种:
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git rebase upstream/master
-```
-
-或者
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git merge upstream/master
-```
-
-如果你非常善于处理冲突,那么可以使用 rebase 的方式来解决冲突,因为这能够保证你的 commit log 的整洁。如果你不太熟悉 `rebase` 的使用,那么可以使用 `merge` 的方式来解决冲突。
-
-### 指引
-
-#### 单元测试
-
-如果你无法正常执行部分模块的单元测试,例如 [video](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/master/mmcv/video) 模块,可能是你的当前环境没有安装以下依赖
-
-```shell
-# Linux
-sudo apt-get update -y
-sudo apt-get install -y libturbojpeg
-sudo apt-get install -y ffmpeg
-
-# Windows
-conda install ffmpeg
-```
-
-在提交修复代码错误或新增特性的拉取请求时,我们应该尽可能的让单元测试覆盖所有提交的代码,计算单元测试覆盖率的方法如下
-
-```shell
-python -m coverage run -m pytest /path/to/test_file
-python -m coverage html
-# check file in htmlcov/index.html
-```
-
-#### 文档渲染
-
-在提交修复代码错误或新增特性的拉取请求时,可能会需要修改/新增模块的 docstring。我们需要确认渲染后的文档样式是正确的。
-本地生成渲染后的文档的方法如下
-
-```shell
-pip install -r requirements/docs.txt
-cd docs/zh_cn/
-# or docs/en
-make html
-# check file in ./docs/zh_cn/_build/html/index.html
-```
-
-### 代码风格
-
-#### Python
-
-[PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) 作为 OpenMMLab 算法库首选的代码规范,我们使用以下工具检查和格式化代码
-
-- [flake8](https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8): Python 官方发布的代码规范检查工具,是多个检查工具的封装
-- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): 自动调整模块导入顺序的工具
-- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): Google 发布的代码规范检查工具
-- [codespell](https://github.com/codespell-project/codespell): 检查单词拼写是否有误
-- [mdformat](https://github.com/executablebooks/mdformat): 检查 markdown 文件的工具
-- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): 格式化 docstring 的工具
-
-yapf 和 isort 的配置可以在 [setup.cfg](./setup.cfg) 找到
-
-通过配置 [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) ,我们可以在提交代码时自动检查和格式化 `flake8`、`yapf`、`isort`、`trailing whitespaces`、`markdown files`,
-修复 `end-of-files`、`double-quoted-strings`、`python-encoding-pragma`、`mixed-line-ending`,调整 `requirments.txt` 的包顺序。
-pre-commit 钩子的配置可以在 [.pre-commit-config](./.pre-commit-config.yaml) 找到。
-
-pre-commit 具体的安装使用方式见[拉取请求](#2-配置-pre-commit)。
-
-更具体的规范请参考 [OpenMMLab 代码规范](code_style.md)。
-
-#### C++ and CUDA
-
-C++ 和 CUDA 的代码规范遵从 [Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html)
-
-### 拉取请求规范
-
-1. 使用 [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com),尽量减少代码风格相关问题
-
-2. 一个`拉取请求`对应一个短期分支
-
-3. 粒度要细,一个`拉取请求`只做一件事情,避免超大的`拉取请求`
-
- - Bad:实现 Faster R-CNN
- - Acceptable:给 Faster R-CNN 添加一个 box head
- - Good:给 box head 增加一个参数来支持自定义的 conv 层数
-
-4. 每次 Commit 时需要提供清晰且有意义 commit 信息
-
-5. 提供清晰且有意义的`拉取请求`描述
-
- - 标题写明白任务名称,一般格式:\[Prefix\] Short description of the pull request (Suffix)
- - prefix: 新增功能 \[Feature\], 修 bug \[Fix\], 文档相关 \[Docs\], 开发中 \[WIP\] (暂时不会被review)
- - 描述里介绍`拉取请求`的主要修改内容,结果,以及对其他部分的影响, 参考`拉取请求`模板
- - 关联相关的`议题` (issue) 和其他`拉取请求`
-
-6. 如果引入了其他三方库,或借鉴了三方库的代码,请确认他们的许可证和 mmcv 兼容,并在借鉴的代码上补充 `This code is inspired from http://`
diff --git a/Dockerfile b/Dockerfile
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e163b312ca5b45dac195232979fa31024ff55ef2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Dockerfile
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+FROM python:3.7
+
+WORKDIR /mmcv
+
+COPY . /mmcv
+
+RUN pip install -e .
diff --git a/LICENSES.md b/LICENSES.md
index 3cdeddf6ff1d09ed8e2d9042f2d930e20599a0b1..9bb0c8cafa72033f503fd3f46b98d30dcfd75c29 100644
--- a/LICENSES.md
+++ b/LICENSES.md
@@ -2,10 +2,7 @@
In this file, we list the operations with other licenses instead of Apache 2.0. Users should be careful about adopting these operations in any commercial matters.
-| Operation | Files | License |
-| :--------------: | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :------------: |
-| upfirdn2d | [mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/upfirdn2d_kernel.cu](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/2.x/mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/upfirdn2d_kernel.cu) | NVIDIA License |
-| fused_leaky_relu | [mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/fused_bias_leakyrelu_cuda.cu](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/2.x/mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/fused_bias_leakyrelu_cuda.cu) | NVIDIA License |
-| bias_act | [mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/bias_act_cuda.cu](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/2.x/mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/bias_act_cuda.cu) | NVIDIA License |
-| filtered_lrelu | [mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/filtered_lrelu.cu](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/2.x/mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/filtered_lrelu.cu) | NVIDIA License |
-| conv2d_gradfix | [mmcv/ops/conv2d_gradfix.py](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/2.x/mmcv/ops/conv2d_gradfix.py) | NVIDIA License |
+| Operation | Files | License |
+| :--------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :------------: |
+| upfirdn2d | [mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/upfirdn2d_kernel.cu](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/blob/master/mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/upfirdn2d_kernel.cu) | NVIDIA License |
+| fused_leaky_relu | [mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/fused_bias_leakyrelu_cuda.cu](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/blob/master/mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/fused_bias_leakyrelu_cuda.cu) | NVIDIA License |
diff --git a/MANIFEST.in b/MANIFEST.in
index 622635caa1ec01f78d95c684b87658df87c63b38..65f232e070d43ce40d0fd425201e3b140b5af551 100644
--- a/MANIFEST.in
+++ b/MANIFEST.in
@@ -1,6 +1,5 @@
include requirements/runtime.txt
+include mmcv/model_zoo/open_mmlab.json mmcv/model_zoo/deprecated.json mmcv/model_zoo/mmcls.json
include mmcv/ops/csrc/common/cuda/*.cuh mmcv/ops/csrc/common/cuda/*.hpp mmcv/ops/csrc/common/*.hpp
include mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/*.cpp mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/*.cu mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/*.cpp mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cpu/*.cpp
include mmcv/ops/csrc/parrots/*.h mmcv/ops/csrc/parrots/*.cpp
-include mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/mps/*.mm mmcv/ops/csrc/common/mps/*.h mmcv/ops/csrc/common/mps/*.mm
-recursive-include mmcv/ops/csrc/ *.h *.hpp *.cpp *.cuh *.cu *.mm
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 098cf65f012e3cde8342e467c2391d3b303226c6..9b64100479f8f8030f1736173aa6ee3e25be8f8a 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ MMCV是计算机视觉研究的基础库,主要提供以下功能:图像处
+ Python 3.7、3.8、3.9
### 1、使用pip方式安装
-mmcv whl包下载目录:[https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/mmcv/dtk23.04](https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/mmcv/dtk23.04),选择对应的pytorch版本和python版本下载对应mmcv的whl包
+mmcv whl包下载目录:[https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/mmcv](https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/mmcv),选择对应的pytorch版本和python版本下载对应mmcv的whl包
```shell
pip install mmcv* (下载的mmcv的whl包)
```
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ pip install mmcv* (下载的mmcv的whl包)
1. 基于光源pytorch基础镜像环境:镜像下载地址:[https://sourcefind.cn/#/image/dcu/pytorch](https://sourcefind.cn/#/image/dcu/pytorch),根据pytorch、python、dtk及系统下载对应的镜像版本。
-2. 基于现有python环境:安装pytorch,pytorch whl包下载目录:[https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/pytorch/dtk23.04](https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/pytorch/dtk23.04),根据python、dtk版本,下载对应pytorch的whl包。安装命令如下:
+2. 基于现有python环境:安装pytorch,pytorch whl包下载目录:[https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/pytorch/dtk24.04.1](https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/pytorch/dtk24.04.1),根据python、dtk版本,下载对应pytorch的whl包。安装命令如下:
```shell
pip install torch* (下载的torch的whl包)
pip install setuptools==59.5.0 wheel
@@ -32,11 +32,17 @@ git clone https://developer.hpccube.com/codes/aicomponent/mmcv # 根据编译需
- 提供2种源码编译方式(进入mmcv目录):
```
1. 编译whl包并安装
-MMCV_WITH_OPS=1 ROCM_HOME=${ROCM_PATH} python3 setup.py -v bdist_wheel
+MMCV_WITH_OPS=1 python3 setup.py -v bdist_wheel
pip install dist/mmcv*
2. 源码编译安装
-MMCV_WITH_OPS=1 ROCM_HOME=${ROCM_PATH} python3 setup.py install
+MMCV_WITH_OPS=1 python3 setup.py install
+```
+3. 测试验证
+```
+cd test
+pytest -s ./test_arraymisc.py
+pytest -s ./test_ops
```
#### 注意事项
+ 若使用pip install下载安装过慢,可添加pypi清华源:-i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
@@ -52,3 +58,4 @@ MMCV_WITH_OPS=1 ROCM_HOME=${ROCM_PATH} python3 setup.py install
- [README_ORIGIN](README_ORIGIN.md)
- [README_zh-CN](README_zh-CN.md)
- [https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv)
+
diff --git a/README_ORIGIN.md b/README_ORIGIN.md
index 25d290f3dac27c8f0e87b0256ed8b0964d5bbcc9..e9e3f8efaf86059c8e7bef3fec73513b69e31442 100644
--- a/README_ORIGIN.md
+++ b/README_ORIGIN.md
@@ -1,119 +1,204 @@
-[](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/)
-[](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/get_started/installation.html)
-[](https://pypi.org/project/mmcv/)
-[](https://pytorch.org/get-started/previous-versions/)
-[](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads)
-[](https://pypi.org/project/mmcv)
-[](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/actions)
-[](https://codecov.io/gh/open-mmlab/mmcv)
-[](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/blob/master/LICENSE)
+[](https://pypi.org/project/mmcv/) [](https://pypi.org/project/mmcv) [](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/actions) [](https://codecov.io/gh/open-mmlab/mmcv) [](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/blob/master/LICENSE)
English | [简体中文](README_zh-CN.md)
## Introduction
-MMCV is a foundational library for computer vision research and it provides the following functionalities:
+MMCV is a foundational library for computer vision research and supports many
+research projects as below:
-- [Image/Video processing](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/understand_mmcv/data_process.html)
-- [Image and annotation visualization](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/understand_mmcv/visualization.html)
-- [Image transformation](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/understand_mmcv/data_transform.html)
-- [Various CNN architectures](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/understand_mmcv/cnn.html)
-- [High-quality implementation of common CPU and CUDA ops](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/understand_mmcv/ops.html)
+- [MMCV](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv): OpenMMLab foundational library for computer vision.
+- [MIM](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mim): MIM Installs OpenMMLab Packages.
+- [MMClassification](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmclassification): OpenMMLab image classification toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMDetection](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection): OpenMMLab detection toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMDetection3D](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection3d): OpenMMLab's next-generation platform for general 3D object detection.
+- [MMSegmentation](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmsegmentation): OpenMMLab semantic segmentation toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMAction2](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmaction2): OpenMMLab's next-generation action understanding toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMTracking](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmtracking): OpenMMLab video perception toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMPose](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmpose): OpenMMLab pose estimation toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMEditing](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmediting): OpenMMLab image and video editing toolbox.
+- [MMOCR](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmocr): A Comprehensive Toolbox for Text Detection, Recognition and Understanding.
+- [MMGeneration](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmgeneration): OpenMMLab image and video generative models toolbox.
+- [MMFlow](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmflow): OpenMMLab optical flow toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMFewShot](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmfewshot): OpenMMLab FewShot Learning Toolbox and Benchmark.
-It supports the following systems:
+It provides the following functionalities.
-- Linux
-- Windows
-- macOS
+- Universal IO APIs
+- Image/Video processing
+- Image and annotation visualization
+- Useful utilities (progress bar, timer, ...)
+- PyTorch runner with hooking mechanism
+- Various CNN architectures
+- High-quality implementation of common CUDA ops
-See the [documentation](http://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x) for more features and usage.
+See the [documentation](http://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/latest) for more features and usage.
-Note: MMCV requires Python 3.7+.
+Note: MMCV requires Python 3.6+.
## Installation
There are two versions of MMCV:
-- **mmcv**: comprehensive, with full features and various CUDA ops out of the box. It takes longer time to build.
-- **mmcv-lite**: lite, without CUDA ops but all other features, similar to mmcv\<1.0.0. It is useful when you do not need those CUDA ops.
+- **mmcv-full**: comprehensive, with full features and various CUDA ops out of box. It takes longer time to build.
+- **mmcv**: lite, without CUDA ops but all other features, similar to mmcv<1.0.0. It is useful when you do not need those CUDA ops.
**Note**: Do not install both versions in the same environment, otherwise you may encounter errors like `ModuleNotFound`. You need to uninstall one before installing the other. `Installing the full version is highly recommended if CUDA is available`.
-### Install mmcv
+a. Install the full version.
+
+Before installing mmcv-full, make sure that PyTorch has been successfully installed following the [official guide](https://pytorch.org/).
-Before installing mmcv, make sure that PyTorch has been successfully installed following the [PyTorch official installation guide](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch#installation). For apple silicon users, please use PyTorch 1.13+.
+We provide pre-built mmcv packages (recommended) with different PyTorch and CUDA versions to simplify the building. In addition, you can run [check_installation.py](.dev_scripts/check_installation.py) to check the installation of mmcv-full after running the installation commands.
-The command to install mmcv:
+i. Install the latest version.
-```bash
-pip install -U openmim
-mim install "mmcv>=2.0.0rc1"
+The rule for installing the latest ``mmcv-full`` is as follows:
+
+```shell
+pip install mmcv-full -f https://download.openmmlab.com/mmcv/dist/{cu_version}/{torch_version}/index.html
```
-If you need to specify the version of mmcv, you can use the following command:
+Please replace ``{cu_version}`` and ``{torch_version}`` in the url to your desired one. For example,
+to install the latest ``mmcv-full`` with ``CUDA 11.1`` and ``PyTorch 1.9.0``, use the following command:
-```bash
-mim install mmcv==2.0.0rc3
+```shell
+pip install mmcv-full -f https://download.openmmlab.com/mmcv/dist/cu111/torch1.9.0/index.html
```
-If you find that the above installation command does not use a pre-built package ending with `.whl` but a source package ending with `.tar.gz`, you may not have a pre-build package corresponding to the PyTorch or CUDA or mmcv version, in which case you can [build mmcv from source](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/get_started/build.html).
+**Note**: mmcv-full is only compiled on PyTorch 1.x.0 because the compatibility usually holds between 1.x.0 and 1.x.1. If your PyTorch version is 1.x.1, you can install mmcv-full compiled with PyTorch 1.x.0 and it usually works well. For example, if your PyTorch version is 1.8.1 and CUDA version is 11.1, you can use the following command to install mmcv-full.
-
-
-所有 reviewer 同意合入 PR 后,我们会尽快将 PR 合并到主分支。
-
-#### 7. 解决冲突
-
-随着时间的推移,我们的代码库会不断更新,这时候,如果你的 PR 与主分支存在冲突,你需要解决冲突,解决冲突的方式有两种:
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git rebase upstream/master
-```
-
-或者
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git merge upstream/master
-```
-
-如果你非常善于处理冲突,那么可以使用 rebase 的方式来解决冲突,因为这能够保证你的 commit log 的整洁。如果你不太熟悉 `rebase` 的使用,那么可以使用 `merge` 的方式来解决冲突。
-
-### 指引
-
-#### 单元测试
-
-如果你无法正常执行部分模块的单元测试,例如 [video](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/master/mmcv/video) 模块,可能是你的当前环境没有安装以下依赖
-
-```shell
-# Linux
-sudo apt-get update -y
-sudo apt-get install -y libturbojpeg
-sudo apt-get install -y ffmpeg
-
-# Windows
-conda install ffmpeg
-```
-
-在提交修复代码错误或新增特性的拉取请求时,我们应该尽可能的让单元测试覆盖所有提交的代码,计算单元测试覆盖率的方法如下
-
-```shell
-python -m coverage run -m pytest /path/to/test_file
-python -m coverage html
-# check file in htmlcov/index.html
-```
-
-#### 文档渲染
-
-在提交修复代码错误或新增特性的拉取请求时,可能会需要修改/新增模块的 docstring。我们需要确认渲染后的文档样式是正确的。
-本地生成渲染后的文档的方法如下
-
-```shell
-pip install -r requirements/docs.txt
-cd docs/zh_cn/
-# or docs/en
-make html
-# check file in ./docs/zh_cn/_build/html/index.html
-```
-
-### 代码风格
-
-#### Python
-
-[PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) 作为 OpenMMLab 算法库首选的代码规范,我们使用以下工具检查和格式化代码
-
-- [flake8](https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8): Python 官方发布的代码规范检查工具,是多个检查工具的封装
-- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): 自动调整模块导入顺序的工具
-- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): Google 发布的代码规范检查工具
-- [codespell](https://github.com/codespell-project/codespell): 检查单词拼写是否有误
-- [mdformat](https://github.com/executablebooks/mdformat): 检查 markdown 文件的工具
-- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): 格式化 docstring 的工具
-
-yapf 和 isort 的配置可以在 [setup.cfg](./setup.cfg) 找到
-
-通过配置 [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) ,我们可以在提交代码时自动检查和格式化 `flake8`、`yapf`、`isort`、`trailing whitespaces`、`markdown files`,
-修复 `end-of-files`、`double-quoted-strings`、`python-encoding-pragma`、`mixed-line-ending`,调整 `requirments.txt` 的包顺序。
-pre-commit 钩子的配置可以在 [.pre-commit-config](./.pre-commit-config.yaml) 找到。
-
-pre-commit 具体的安装使用方式见[拉取请求](#2-配置-pre-commit)。
-
-更具体的规范请参考 [OpenMMLab 代码规范](code_style.md)。
-
-#### C++ and CUDA
-
-C++ 和 CUDA 的代码规范遵从 [Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html)
-
-### 拉取请求规范
-
-1. 使用 [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com),尽量减少代码风格相关问题
-
-2. 一个`拉取请求`对应一个短期分支
-
-3. 粒度要细,一个`拉取请求`只做一件事情,避免超大的`拉取请求`
-
- - Bad:实现 Faster R-CNN
- - Acceptable:给 Faster R-CNN 添加一个 box head
- - Good:给 box head 增加一个参数来支持自定义的 conv 层数
-
-4. 每次 Commit 时需要提供清晰且有意义 commit 信息
-
-5. 提供清晰且有意义的`拉取请求`描述
-
- - 标题写明白任务名称,一般格式:\[Prefix\] Short description of the pull request (Suffix)
- - prefix: 新增功能 \[Feature\], 修 bug \[Fix\], 文档相关 \[Docs\], 开发中 \[WIP\] (暂时不会被review)
- - 描述里介绍`拉取请求`的主要修改内容,结果,以及对其他部分的影响, 参考`拉取请求`模板
- - 关联相关的`议题` (issue) 和其他`拉取请求`
-
-6. 如果引入了其他三方库,或借鉴了三方库的代码,请确认他们的许可证和 mmcv 兼容,并在借鉴的代码上补充 `This code is inspired from http://`
diff --git a/Dockerfile b/Dockerfile
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..e163b312ca5b45dac195232979fa31024ff55ef2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/Dockerfile
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+FROM python:3.7
+
+WORKDIR /mmcv
+
+COPY . /mmcv
+
+RUN pip install -e .
diff --git a/LICENSES.md b/LICENSES.md
index 3cdeddf6ff1d09ed8e2d9042f2d930e20599a0b1..9bb0c8cafa72033f503fd3f46b98d30dcfd75c29 100644
--- a/LICENSES.md
+++ b/LICENSES.md
@@ -2,10 +2,7 @@
In this file, we list the operations with other licenses instead of Apache 2.0. Users should be careful about adopting these operations in any commercial matters.
-| Operation | Files | License |
-| :--------------: | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :------------: |
-| upfirdn2d | [mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/upfirdn2d_kernel.cu](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/2.x/mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/upfirdn2d_kernel.cu) | NVIDIA License |
-| fused_leaky_relu | [mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/fused_bias_leakyrelu_cuda.cu](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/2.x/mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/fused_bias_leakyrelu_cuda.cu) | NVIDIA License |
-| bias_act | [mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/bias_act_cuda.cu](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/2.x/mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/bias_act_cuda.cu) | NVIDIA License |
-| filtered_lrelu | [mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/filtered_lrelu.cu](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/2.x/mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/filtered_lrelu.cu) | NVIDIA License |
-| conv2d_gradfix | [mmcv/ops/conv2d_gradfix.py](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/2.x/mmcv/ops/conv2d_gradfix.py) | NVIDIA License |
+| Operation | Files | License |
+| :--------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :------------: |
+| upfirdn2d | [mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/upfirdn2d_kernel.cu](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/blob/master/mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/upfirdn2d_kernel.cu) | NVIDIA License |
+| fused_leaky_relu | [mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/fused_bias_leakyrelu_cuda.cu](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/blob/master/mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/fused_bias_leakyrelu_cuda.cu) | NVIDIA License |
diff --git a/MANIFEST.in b/MANIFEST.in
index 622635caa1ec01f78d95c684b87658df87c63b38..65f232e070d43ce40d0fd425201e3b140b5af551 100644
--- a/MANIFEST.in
+++ b/MANIFEST.in
@@ -1,6 +1,5 @@
include requirements/runtime.txt
+include mmcv/model_zoo/open_mmlab.json mmcv/model_zoo/deprecated.json mmcv/model_zoo/mmcls.json
include mmcv/ops/csrc/common/cuda/*.cuh mmcv/ops/csrc/common/cuda/*.hpp mmcv/ops/csrc/common/*.hpp
include mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/*.cpp mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/*.cu mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cuda/*.cpp mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/cpu/*.cpp
include mmcv/ops/csrc/parrots/*.h mmcv/ops/csrc/parrots/*.cpp
-include mmcv/ops/csrc/pytorch/mps/*.mm mmcv/ops/csrc/common/mps/*.h mmcv/ops/csrc/common/mps/*.mm
-recursive-include mmcv/ops/csrc/ *.h *.hpp *.cpp *.cuh *.cu *.mm
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 098cf65f012e3cde8342e467c2391d3b303226c6..9b64100479f8f8030f1736173aa6ee3e25be8f8a 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ MMCV是计算机视觉研究的基础库,主要提供以下功能:图像处
+ Python 3.7、3.8、3.9
### 1、使用pip方式安装
-mmcv whl包下载目录:[https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/mmcv/dtk23.04](https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/mmcv/dtk23.04),选择对应的pytorch版本和python版本下载对应mmcv的whl包
+mmcv whl包下载目录:[https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/mmcv](https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/mmcv),选择对应的pytorch版本和python版本下载对应mmcv的whl包
```shell
pip install mmcv* (下载的mmcv的whl包)
```
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ pip install mmcv* (下载的mmcv的whl包)
1. 基于光源pytorch基础镜像环境:镜像下载地址:[https://sourcefind.cn/#/image/dcu/pytorch](https://sourcefind.cn/#/image/dcu/pytorch),根据pytorch、python、dtk及系统下载对应的镜像版本。
-2. 基于现有python环境:安装pytorch,pytorch whl包下载目录:[https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/pytorch/dtk23.04](https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/pytorch/dtk23.04),根据python、dtk版本,下载对应pytorch的whl包。安装命令如下:
+2. 基于现有python环境:安装pytorch,pytorch whl包下载目录:[https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/pytorch/dtk24.04.1](https://cancon.hpccube.com:65024/4/main/pytorch/dtk24.04.1),根据python、dtk版本,下载对应pytorch的whl包。安装命令如下:
```shell
pip install torch* (下载的torch的whl包)
pip install setuptools==59.5.0 wheel
@@ -32,11 +32,17 @@ git clone https://developer.hpccube.com/codes/aicomponent/mmcv # 根据编译需
- 提供2种源码编译方式(进入mmcv目录):
```
1. 编译whl包并安装
-MMCV_WITH_OPS=1 ROCM_HOME=${ROCM_PATH} python3 setup.py -v bdist_wheel
+MMCV_WITH_OPS=1 python3 setup.py -v bdist_wheel
pip install dist/mmcv*
2. 源码编译安装
-MMCV_WITH_OPS=1 ROCM_HOME=${ROCM_PATH} python3 setup.py install
+MMCV_WITH_OPS=1 python3 setup.py install
+```
+3. 测试验证
+```
+cd test
+pytest -s ./test_arraymisc.py
+pytest -s ./test_ops
```
#### 注意事项
+ 若使用pip install下载安装过慢,可添加pypi清华源:-i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
@@ -52,3 +58,4 @@ MMCV_WITH_OPS=1 ROCM_HOME=${ROCM_PATH} python3 setup.py install
- [README_ORIGIN](README_ORIGIN.md)
- [README_zh-CN](README_zh-CN.md)
- [https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv)
+
diff --git a/README_ORIGIN.md b/README_ORIGIN.md
index 25d290f3dac27c8f0e87b0256ed8b0964d5bbcc9..e9e3f8efaf86059c8e7bef3fec73513b69e31442 100644
--- a/README_ORIGIN.md
+++ b/README_ORIGIN.md
@@ -1,119 +1,204 @@
-[](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/)
-[](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/get_started/installation.html)
-[](https://pypi.org/project/mmcv/)
-[](https://pytorch.org/get-started/previous-versions/)
-[](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads)
-[](https://pypi.org/project/mmcv)
-[](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/actions)
-[](https://codecov.io/gh/open-mmlab/mmcv)
-[](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/blob/master/LICENSE)
+[](https://pypi.org/project/mmcv/) [](https://pypi.org/project/mmcv) [](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/actions) [](https://codecov.io/gh/open-mmlab/mmcv) [](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/blob/master/LICENSE)
English | [简体中文](README_zh-CN.md)
## Introduction
-MMCV is a foundational library for computer vision research and it provides the following functionalities:
+MMCV is a foundational library for computer vision research and supports many
+research projects as below:
-- [Image/Video processing](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/understand_mmcv/data_process.html)
-- [Image and annotation visualization](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/understand_mmcv/visualization.html)
-- [Image transformation](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/understand_mmcv/data_transform.html)
-- [Various CNN architectures](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/understand_mmcv/cnn.html)
-- [High-quality implementation of common CPU and CUDA ops](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/understand_mmcv/ops.html)
+- [MMCV](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv): OpenMMLab foundational library for computer vision.
+- [MIM](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mim): MIM Installs OpenMMLab Packages.
+- [MMClassification](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmclassification): OpenMMLab image classification toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMDetection](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection): OpenMMLab detection toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMDetection3D](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection3d): OpenMMLab's next-generation platform for general 3D object detection.
+- [MMSegmentation](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmsegmentation): OpenMMLab semantic segmentation toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMAction2](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmaction2): OpenMMLab's next-generation action understanding toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMTracking](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmtracking): OpenMMLab video perception toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMPose](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmpose): OpenMMLab pose estimation toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMEditing](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmediting): OpenMMLab image and video editing toolbox.
+- [MMOCR](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmocr): A Comprehensive Toolbox for Text Detection, Recognition and Understanding.
+- [MMGeneration](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmgeneration): OpenMMLab image and video generative models toolbox.
+- [MMFlow](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmflow): OpenMMLab optical flow toolbox and benchmark.
+- [MMFewShot](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmfewshot): OpenMMLab FewShot Learning Toolbox and Benchmark.
-It supports the following systems:
+It provides the following functionalities.
-- Linux
-- Windows
-- macOS
+- Universal IO APIs
+- Image/Video processing
+- Image and annotation visualization
+- Useful utilities (progress bar, timer, ...)
+- PyTorch runner with hooking mechanism
+- Various CNN architectures
+- High-quality implementation of common CUDA ops
-See the [documentation](http://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x) for more features and usage.
+See the [documentation](http://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/latest) for more features and usage.
-Note: MMCV requires Python 3.7+.
+Note: MMCV requires Python 3.6+.
## Installation
There are two versions of MMCV:
-- **mmcv**: comprehensive, with full features and various CUDA ops out of the box. It takes longer time to build.
-- **mmcv-lite**: lite, without CUDA ops but all other features, similar to mmcv\<1.0.0. It is useful when you do not need those CUDA ops.
+- **mmcv-full**: comprehensive, with full features and various CUDA ops out of box. It takes longer time to build.
+- **mmcv**: lite, without CUDA ops but all other features, similar to mmcv<1.0.0. It is useful when you do not need those CUDA ops.
**Note**: Do not install both versions in the same environment, otherwise you may encounter errors like `ModuleNotFound`. You need to uninstall one before installing the other. `Installing the full version is highly recommended if CUDA is available`.
-### Install mmcv
+a. Install the full version.
+
+Before installing mmcv-full, make sure that PyTorch has been successfully installed following the [official guide](https://pytorch.org/).
-Before installing mmcv, make sure that PyTorch has been successfully installed following the [PyTorch official installation guide](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch#installation). For apple silicon users, please use PyTorch 1.13+.
+We provide pre-built mmcv packages (recommended) with different PyTorch and CUDA versions to simplify the building. In addition, you can run [check_installation.py](.dev_scripts/check_installation.py) to check the installation of mmcv-full after running the installation commands.
-The command to install mmcv:
+i. Install the latest version.
-```bash
-pip install -U openmim
-mim install "mmcv>=2.0.0rc1"
+The rule for installing the latest ``mmcv-full`` is as follows:
+
+```shell
+pip install mmcv-full -f https://download.openmmlab.com/mmcv/dist/{cu_version}/{torch_version}/index.html
```
-If you need to specify the version of mmcv, you can use the following command:
+Please replace ``{cu_version}`` and ``{torch_version}`` in the url to your desired one. For example,
+to install the latest ``mmcv-full`` with ``CUDA 11.1`` and ``PyTorch 1.9.0``, use the following command:
-```bash
-mim install mmcv==2.0.0rc3
+```shell
+pip install mmcv-full -f https://download.openmmlab.com/mmcv/dist/cu111/torch1.9.0/index.html
```
-If you find that the above installation command does not use a pre-built package ending with `.whl` but a source package ending with `.tar.gz`, you may not have a pre-build package corresponding to the PyTorch or CUDA or mmcv version, in which case you can [build mmcv from source](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/get_started/build.html).
+**Note**: mmcv-full is only compiled on PyTorch 1.x.0 because the compatibility usually holds between 1.x.0 and 1.x.1. If your PyTorch version is 1.x.1, you can install mmcv-full compiled with PyTorch 1.x.0 and it usually works well. For example, if your PyTorch version is 1.8.1 and CUDA version is 11.1, you can use the following command to install mmcv-full.
-| CUDA | +torch1.10 | +torch1.9 | +torch1.8 | +torch1.7 | +torch1.6 | +torch1.5 | +
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11.3 | +install |
+ + | + | + | + | + |
| 11.1 | +install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ + | + | + |
| 11.0 | ++ | + | + | install |
+ + | + |
| 10.2 | +install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+
| 10.1 | ++ | + | install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+
| 9.2 | ++ | + | + | install |
+ install |
+ install |
+
| cpu | +install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+
| CUDA | +torch1.10 | +torch1.9 | +torch1.8 | +torch1.7 | +torch1.6 | +torch1.5 | +
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11.3 | +安装 |
+ + | + | + | + | + |
| 11.1 | +安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ + | + | + |
| 11.0 | ++ | + | + | 安装 |
+ + | + |
| 10.2 | +安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+
| 10.1 | ++ | + | 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+
| 9.2 | ++ | + | + | 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+
| cpu | +安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+


 +
+

 -
-Then, you can clone the repositories to local:
-
-```shell
-git clone git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git
-```
-
-After that, you should ddd official repository as the upstream repository
-
-```bash
-git remote add upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv
-```
-
-Check whether remote repository has been added successfully by `git remote -v`
-
-```bash
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (fetch)
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (push)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (fetch)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (push)
-```
-
-```{note}
-Here's a brief introduction to origin and upstream. When we use "git clone", we create an "origin" remote by default, which points to the repository cloned from. As for "upstream", we add it ourselves to point to the target repository. Of course, if you don't like the name "upstream", you could name it as you wish. Usually, we'll push the code to "origin". If the pushed code conflicts with the latest code in official("upstream"), we should pull the latest code from upstream to resolve the conflicts, and then push to "origin" again. The posted Pull Request will be updated automatically.
-```
-
-#### 2. Configure pre-commit
-
-You should configure [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/#intro) in the local development environment to make sure the code style matches that of OpenMMLab. **Note**: The following code should be executed under the MMCV directory.
-
-```shell
-pip install -U pre-commit
-pre-commit install
-```
-
-Check that pre-commit is configured successfully, and install the hooks defined in `.pre-commit-config.yaml`.
-
-```shell
-pre-commit run --all-files
-```
-
-
-
-Then, you can clone the repositories to local:
-
-```shell
-git clone git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git
-```
-
-After that, you should ddd official repository as the upstream repository
-
-```bash
-git remote add upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv
-```
-
-Check whether remote repository has been added successfully by `git remote -v`
-
-```bash
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (fetch)
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (push)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (fetch)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (push)
-```
-
-```{note}
-Here's a brief introduction to origin and upstream. When we use "git clone", we create an "origin" remote by default, which points to the repository cloned from. As for "upstream", we add it ourselves to point to the target repository. Of course, if you don't like the name "upstream", you could name it as you wish. Usually, we'll push the code to "origin". If the pushed code conflicts with the latest code in official("upstream"), we should pull the latest code from upstream to resolve the conflicts, and then push to "origin" again. The posted Pull Request will be updated automatically.
-```
-
-#### 2. Configure pre-commit
-
-You should configure [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/#intro) in the local development environment to make sure the code style matches that of OpenMMLab. **Note**: The following code should be executed under the MMCV directory.
-
-```shell
-pip install -U pre-commit
-pre-commit install
-```
-
-Check that pre-commit is configured successfully, and install the hooks defined in `.pre-commit-config.yaml`.
-
-```shell
-pre-commit run --all-files
-```
-
- -
-
-
- -
-```{note}
-Chinese users may fail to download the pre-commit hooks due to the network issue. In this case, you could download these hooks from gitee by setting the .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-
-pre-commit install -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-pre-commit run --all-files -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-```
-
-If the installation process is interrupted, you can repeatedly run `pre-commit run ... ` to continue the installation.
-
-If the code does not conform to the code style specification, pre-commit will raise a warning and fixes some of the errors automatically.
-
-
-
-```{note}
-Chinese users may fail to download the pre-commit hooks due to the network issue. In this case, you could download these hooks from gitee by setting the .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-
-pre-commit install -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-pre-commit run --all-files -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-```
-
-If the installation process is interrupted, you can repeatedly run `pre-commit run ... ` to continue the installation.
-
-If the code does not conform to the code style specification, pre-commit will raise a warning and fixes some of the errors automatically.
-
- -
-If we want to commit our code bypassing the pre-commit hook, we can use the `--no-verify` option(**only for temporarily commit**.
-
-```shell
-git commit -m "xxx" --no-verify
-```
-
-#### 3. Create a development branch
-
-After configuring the pre-commit, we should create a branch based on the master branch to develop the new feature or fix the bug. The proposed branch name is `username/pr_name`
-
-```shell
-git checkout -b yhc/refactor_contributing_doc
-```
-
-In subsequent development, if the master branch of the local repository is behind the master branch of "upstream", we need to pull the upstream for synchronization, and then execute the above command:
-
-```shell
-git pull upstream master
-```
-
-#### 4. Commit the code and pass the unit test
-
-- MMCV introduces mypy to do static type checking to increase the robustness of the code. Therefore, we need to add Type Hints to our code and pass the mypy check. If you are not familiar with Type Hints, you can refer to [this tutorial](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
-
-- The committed code should pass through the unit test
-
- ```shell
- # Pass all unit tests
- pytest tests
-
- # Pass the unit test of runner
- pytest tests/test_runner/test_runner.py
- ```
-
- If the unit test fails for lack of dependencies, you can install the dependencies referring to the [guidance](#unit-test)
-
-- If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result referring to [guidance](#document-rendering)
-
-#### 5. Push the code to remote
-
-We could push the local commits to remote after passing through the check of unit test and pre-commit. You can associate the local branch with remote branch by adding `-u` option.
-
-```shell
-git push -u origin {branch_name}
-```
-
-This will allow you to use the `git push` command to push code directly next time, without having to specify a branch or the remote repository.
-
-#### 6. Create a Pull Request
-
-(1) Create a pull request in GitHub's Pull request interface
-
-
-
-If we want to commit our code bypassing the pre-commit hook, we can use the `--no-verify` option(**only for temporarily commit**.
-
-```shell
-git commit -m "xxx" --no-verify
-```
-
-#### 3. Create a development branch
-
-After configuring the pre-commit, we should create a branch based on the master branch to develop the new feature or fix the bug. The proposed branch name is `username/pr_name`
-
-```shell
-git checkout -b yhc/refactor_contributing_doc
-```
-
-In subsequent development, if the master branch of the local repository is behind the master branch of "upstream", we need to pull the upstream for synchronization, and then execute the above command:
-
-```shell
-git pull upstream master
-```
-
-#### 4. Commit the code and pass the unit test
-
-- MMCV introduces mypy to do static type checking to increase the robustness of the code. Therefore, we need to add Type Hints to our code and pass the mypy check. If you are not familiar with Type Hints, you can refer to [this tutorial](https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html).
-
-- The committed code should pass through the unit test
-
- ```shell
- # Pass all unit tests
- pytest tests
-
- # Pass the unit test of runner
- pytest tests/test_runner/test_runner.py
- ```
-
- If the unit test fails for lack of dependencies, you can install the dependencies referring to the [guidance](#unit-test)
-
-- If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result referring to [guidance](#document-rendering)
-
-#### 5. Push the code to remote
-
-We could push the local commits to remote after passing through the check of unit test and pre-commit. You can associate the local branch with remote branch by adding `-u` option.
-
-```shell
-git push -u origin {branch_name}
-```
-
-This will allow you to use the `git push` command to push code directly next time, without having to specify a branch or the remote repository.
-
-#### 6. Create a Pull Request
-
-(1) Create a pull request in GitHub's Pull request interface
-
- -
-(2) Modify the PR description according to the guidelines so that other developers can better understand your changes
-
-
-
-(2) Modify the PR description according to the guidelines so that other developers can better understand your changes
-
- -
-Find more details about Pull Request description in [pull request guidelines](#pr-specs).
-
-**note**
-
-(a) The Pull Request description should contain the reason for the change, the content of the change, and the impact of the change, and be associated with the relevant Issue (see [documentation](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue)
-
-(b) If it is your first contribution, please sign the CLA
-
-
-
-Find more details about Pull Request description in [pull request guidelines](#pr-specs).
-
-**note**
-
-(a) The Pull Request description should contain the reason for the change, the content of the change, and the impact of the change, and be associated with the relevant Issue (see [documentation](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue)
-
-(b) If it is your first contribution, please sign the CLA
-
- -
-(c) Check whether the Pull Request pass through the CI
-
-
-
-(c) Check whether the Pull Request pass through the CI
-
- -
-MMCV will run unit test for the posted Pull Request on different platforms (Linux, Window, Mac), based on different versions of Python, PyTorch, CUDA to make sure the code is correct. We can see the specific test information by clicking `Details` in the above image so that we can modify the code.
-
-(3) If the Pull Request passes the CI, then you can wait for the review from other developers. You'll modify the code based on the reviewer's comments, and repeat the steps [4](#4-commit-the-code-and-pass-the-unit-test)-[5](#5-push-the-code-to-remote) until all reviewers approve it. Then, we will merge it ASAP.
-
-
-
-MMCV will run unit test for the posted Pull Request on different platforms (Linux, Window, Mac), based on different versions of Python, PyTorch, CUDA to make sure the code is correct. We can see the specific test information by clicking `Details` in the above image so that we can modify the code.
-
-(3) If the Pull Request passes the CI, then you can wait for the review from other developers. You'll modify the code based on the reviewer's comments, and repeat the steps [4](#4-commit-the-code-and-pass-the-unit-test)-[5](#5-push-the-code-to-remote) until all reviewers approve it. Then, we will merge it ASAP.
-
- -
-#### 7. Resolve conflicts
-
-If your local branch conflicts with the latest master branch of "upstream", you'll need to resolove them. There are two ways to do this:
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git rebase upstream/master
-```
-
-or
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git merge upstream/master
-```
-
-If you are very good at handling conflicts, then you can use rebase to resolve conflicts, as this will keep your commit logs tidy. If you are not familiar with `rebase`, then you can use `merge` to resolve conflicts.
-
-### Guidance
-
-#### Unit test
-
-If you cannot run the unit test of some modules for lacking of some dependencies, such as [video](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/master/mmcv/video) module, you can try to install the following dependencies:
-
-```shell
-# Linux
-sudo apt-get update -y
-sudo apt-get install -y libturbojpeg
-sudo apt-get install -y ffmpeg
-
-# Windows
-conda install ffmpeg
-```
-
-We should also make sure the committed code will not decrease the coverage of unit test, we could run the following command to check the coverage of unit test:
-
-```shell
-python -m coverage run -m pytest /path/to/test_file
-python -m coverage html
-# check file in htmlcov/index.html
-```
-
-#### Document rendering
-
-If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result. We could install the dependencies and run the following command to render the documents and check the results:
-
-```shell
-pip install -r requirements/docs.txt
-cd docs/zh_cn/
-# or docs/en
-make html
-# check file in ./docs/zh_cn/_build/html/index.html
-```
-
-### Code style
-
-#### Python
-
-We adopt [PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) as the preferred code style.
-
-We use the following tools for linting and formatting:
-
-- [flake8](https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8): A wrapper around some linter tools.
-- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): A Python utility to sort imports.
-- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): A formatter for Python files.
-- [codespell](https://github.com/codespell-project/codespell): A Python utility to fix common misspellings in text files.
-- [mdformat](https://github.com/executablebooks/mdformat): Mdformat is an opinionated Markdown formatter that can be used to enforce a consistent style in Markdown files.
-- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): A formatter to format docstring.
-
-Style configurations of yapf and isort can be found in [setup.cfg](./setup.cfg).
-
-We use [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) that checks and formats for `flake8`, `yapf`, `isort`, `trailing whitespaces`, `markdown files`,
-fixes `end-of-files`, `double-quoted-strings`, `python-encoding-pragma`, `mixed-line-ending`, sorts `requirments.txt` automatically on every commit.
-The config for a pre-commit hook is stored in [.pre-commit-config](./.pre-commit-config.yaml).
-
-#### C++ and CUDA
-
-We follow the [Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html).
-
-### PR Specs
-
-1. Use [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com) hook to avoid issues of code style
-
-2. One short-time branch should be matched with only one PR
-
-3. Accomplish a detailed change in one PR. Avoid large PR
-
- - Bad: Support Faster R-CNN
- - Acceptable: Add a box head to Faster R-CNN
- - Good: Add a parameter to box head to support custom conv-layer number
-
-4. Provide clear and significant commit message
-
-5. Provide clear and meaningful PR description
-
- - Task name should be clarified in title. The general format is: \[Prefix\] Short description of the PR (Suffix)
- - Prefix: add new feature \[Feature\], fix bug \[Fix\], related to documents \[Docs\], in developing \[WIP\] (which will not be reviewed temporarily)
- - Introduce main changes, results and influences on other modules in short description
- - Associate related issues and pull requests with a milestone
diff --git a/docs/en/community/pr.md b/docs/en/community/pr.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 1bdd90f2bc41867e5c17403690f6a35cfe2c07b7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/en/community/pr.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
-## Pull Request (PR)
-
-Content has been migrated to [contributing guidance](contributing.md).
diff --git a/docs/en/docutils.conf b/docs/en/docutils.conf
deleted file mode 100644
index 0c00c84688701117f231fd0c8ec295fb747b7d8f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/en/docutils.conf
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,2 +0,0 @@
-[html writers]
-table_style: colwidths-auto
diff --git a/docs/en/faq.md b/docs/en/faq.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 02d31c233a9ff66d5e8f3f288b5d5f64e5c5298c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/en/faq.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
-## Frequently Asked Questions
-
-We list some common troubles faced by many users and their corresponding solutions here.
-Feel free to enrich the list if you find any frequent issues and have ways to help others to solve them.
-
-### Installation
-
-- KeyError: "xxx: 'yyy is not in the zzz registry'"
-
- The registry mechanism will be triggered only when the file of the module is imported.
- So you need to import that file somewhere. More details can be found at [KeyError: "MaskRCNN: 'RefineRoIHead is not in the models registry'"](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/issues/5974).
-
-- "No module named 'mmcv.ops'"; "No module named 'mmcv.\_ext'"
-
- 1. Uninstall existing mmcv in the environment using `pip uninstall mmcv`
- 2. Install mmcv-full following the [installation instruction](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get_started/installation.html) or [Build MMCV from source](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get_started/build.html)
-
-- "invalid device function" or "no kernel image is available for execution"
-
- 1. Check the CUDA compute capability of you GPU
- 2. Run `python mmdet/utils/collect_env.py` to check whether PyTorch, torchvision, and MMCV are built for the correct GPU architecture. You may need to set `TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST` to reinstall MMCV. The compatibility issue could happen when using old GPUS, e.g., Tesla K80 (3.7) on colab.
- 3. Check whether the running environment is the same as that when mmcv/mmdet is compiled. For example, you may compile mmcv using CUDA 10.0 bug run it on CUDA9.0 environments
-
-- "undefined symbol" or "cannot open xxx.so"
-
- 1. If those symbols are CUDA/C++ symbols (e.g., libcudart.so or GLIBCXX), check
- whether the CUDA/GCC runtimes are the same as those used for compiling mmcv
- 2. If those symbols are Pytorch symbols (e.g., symbols containing caffe, aten, and TH), check whether the Pytorch version is the same as that used for compiling mmcv
- 3. Run `python mmdet/utils/collect_env.py` to check whether PyTorch, torchvision, and MMCV are built by and running on the same environment
-
-- "RuntimeError: CUDA error: invalid configuration argument"
-
- This error may be caused by the poor performance of GPU. Try to decrease the value of [THREADS_PER_BLOCK](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/blob/cac22f8cf5a904477e3b5461b1cc36856c2793da/mmcv/ops/csrc/common_cuda_helper.hpp#L10)
- and recompile mmcv.
-
-- "RuntimeError: nms is not compiled with GPU support"
-
- This error is because your CUDA environment is not installed correctly.
- You may try to re-install your CUDA environment and then delete the build/ folder before re-compile mmcv.
-
-- "Segmentation fault"
-
- 1. Check your GCC version and use GCC >= 5.4. This usually caused by the incompatibility between PyTorch and the environment (e.g., GCC \< 4.9 for PyTorch). We also recommend the users to avoid using GCC 5.5 because many feedbacks report that GCC 5.5 will cause "segmentation fault" and simply changing it to GCC 5.4 could solve the problem
- 2. Check whether PyTorch is correctly installed and could use CUDA op, e.g. type the following command in your terminal and see whether they could correctly output results
- ```shell
- python -c 'import torch; print(torch.cuda.is_available())'
- ```
- 3. If PyTorch is correctly installed, check whether MMCV is correctly installed. If MMCV is correctly installed, then there will be no issue of the command
- ```shell
- python -c 'import mmcv; import mmcv.ops'
- ```
- 4. If MMCV and PyTorch are correctly installed, you can use `ipdb` to set breakpoints or directly add `print` to debug and see which part leads the `segmentation fault`
-
-- "libtorch_cuda_cu.so: cannot open shared object file"
-
- `mmcv-full` depends on the share object but it can not be found. We can check whether the object exists in `~/miniconda3/envs/{environment-name}/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/lib` or try to re-install the PyTorch.
-
-- "fatal error C1189: #error: -- unsupported Microsoft Visual Studio version!"
-
- If you are building mmcv-full on Windows and the version of CUDA is 9.2, you will probably encounter the error `"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v9.2\include\crt/host_config.h(133): fatal error C1189: #error: -- unsupported Microsoft Visual Studio version! Only the versions 2012, 2013, 2015 and 2017 are supported!"`, in which case you can use a lower version of Microsoft Visual Studio like vs2017.
-
-- "error: member "torch::jit::detail::ModulePolicy::all_slots" may not be initialized"
-
- If your version of PyTorch is 1.5.0 and you are building mmcv-full on Windows, you will probably encounter the error `- torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h(474): error: member "torch::jit::detail::ModulePolicy::all_slots" may not be initialized`. The way to solve the error is to replace all the `static constexpr bool all_slots = false;` with `static bool all_slots = false;` at this file `https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/v1.5.0/torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h`. More details can be found at [member "torch::jit::detail::AttributePolicy::all_slots" may not be initialized](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/39394).
-
-- "error: a member with an in-class initializer must be const"
-
- If your version of PyTorch is 1.6.0 and you are building mmcv-full on Windows, you will probably encounter the error `"- torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h(483): error: a member with an in-class initializer must be const"`. The way to solve the error is to replace all the `CONSTEXPR_EXCEPT_WIN_CUDA ` with `const` at `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h`. More details can be found at [Ninja: build stopped: subcommand failed](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues/575).
-
-- "error: member "torch::jit::ProfileOptionalOp::Kind" may not be initialized"
-
- If your version of PyTorch is 1.7.0 and you are building mmcv-full on Windows, you will probably encounter the error `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/ir/ir.h(1347): error: member "torch::jit::ProfileOptionalOp::Kind" may not be initialized`. The way to solve the error needs to modify several local files of PyTorch:
-
- - delete `static constexpr Symbol Kind = ::c10::prim::profile;` and `tatic constexpr Symbol Kind = ::c10::prim::profile_optional;` at `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/ir/ir.h`
- - replace `explicit operator type&() { return *(this->value); }` with `explicit operator type&() { return *((type*)this->value); }` at `torch\include\pybind11\cast.h`
- - replace all the `CONSTEXPR_EXCEPT_WIN_CUDA` with `const` at `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h`
-
- More details can be found at [Ensure default extra_compile_args](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/45956).
-
-- Compatibility issue between MMCV and MMDetection; "ConvWS is already registered in conv layer"
-
- Please install the correct version of MMCV for the version of your MMDetection following the [installation instruction](https://mmdetection.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get_started.html#installation).
-
-### Usage
-
-- "RuntimeError: Expected to have finished reduction in the prior iteration before starting a new one"
-
- 1. This error indicates that your module has parameters that were not used in producing loss. This phenomenon may be caused by running different branches in your code in DDP mode. More datails at [Expected to have finished reduction in the prior iteration before starting a new one](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/55582).
- 2. You can set ` find_unused_parameters = True` in the config to solve the above problems or find those unused parameters manually
-
-- "RuntimeError: Trying to backward through the graph a second time"
-
- `GradientCumulativeOptimizerHook` and `OptimizerHook` are both set which causes the `loss.backward()` to be called twice so `RuntimeError` was raised. We can only use one of these. More datails at [Trying to backward through the graph a second time](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues/1379).
diff --git a/docs/en/get_started/build.md b/docs/en/get_started/build.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e3d48ec7cf486edece6ea9e622937b08602f5e6e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/en/get_started/build.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,292 +0,0 @@
-## Build MMCV from source
-
-### Build mmcv
-
-Before installing mmcv, make sure that PyTorch has been successfully installed following the [PyTorch official installation guide](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally). This can be verified using the following command
-
-```bash
-python -c 'import torch;print(torch.__version__)'
-```
-
-If version information is output, then PyTorch is installed.
-
-```{note}
-If you would like to use `opencv-python-headless` instead of `opencv-python`,
-e.g., in a minimum container environment or servers without GUI,
-you can first install it before installing MMCV to skip the installation of `opencv-python`.
-```
-
-#### Build on Linux
-
-1. Clone the repo
-
- ```bash
- git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- cd mmcv
- ```
-
-2. Install `ninja` and `psutil` to speed up the compilation
-
- ```bash
- pip install -r requirements/optional.txt
- ```
-
-3. Check the nvcc version (requires 9.2+. Skip if no GPU available.)
-
- ```bash
- nvcc --version
- ```
-
- If the above command outputs the following message, it means that the nvcc setting is OK, otherwise you need to set CUDA_HOME.
-
- ```
- nvcc: NVIDIA (R) Cuda compiler driver
- Copyright (c) 2005-2020 NVIDIA Corporation
- Built on Mon_Nov_30_19:08:53_PST_2020
- Cuda compilation tools, release 11.2, V11.2.67
- Build cuda_11.2.r11.2/compiler.29373293_0
- ```
-
- :::{note}
- If you want to support ROCm, you can refer to [AMD ROCm](https://rocmdocs.amd.com/en/latest/Installation_Guide/Installation-Guide.html) to install ROCm.
- :::
-
-4. Check the gcc version (requires 5.4+)
-
- ```bash
- gcc --version
- ```
-
-5. Start building (takes 10+ min)
-
- ```bash
- pip install -e . -v
- ```
-
-6. Validate the installation
-
- ```bash
- python .dev_scripts/check_installation.py
- ```
-
- If no error is reported by the above command, the installation is successful. If there is an error reported, please check [Frequently Asked Questions](../faq.md) to see if there is already a solution.
-
- If no solution is found, please feel free to open an [issue](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues).
-
-#### Build on macOS
-
-```{note}
-If you are using a mac with apple silicon chip, install the PyTorch 1.13+, otherwise you will encounter the problem in [issues#2218](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues/2218).
-```
-
-1. Clone the repo
-
- ```bash
- git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- cd mmcv
- ```
-
-2. Install `ninja` and `psutil` to speed up the compilation
-
- ```bash
- pip install -r requirements/optional.txt
- ```
-
-3. Start building
-
- ```bash
- MMCV_WITH_OPS=1 pip install -e .
- ```
-
-4. Validate the installation
-
- ```bash
- python .dev_scripts/check_installation.py
- ```
-
- If no error is reported by the above command, the installation is successful. If there is an error reported, please check [Frequently Asked Questions](../faq.md) to see if there is already a solution.
-
- If no solution is found, please feel free to open an [issue](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues).
-
-#### Build on Windows
-
-Building MMCV on Windows is a bit more complicated than that on Linux.
-The following instructions show how to get this accomplished.
-
-##### Prerequisite
-
-The following software is required for building MMCV on windows.
-Install them first.
-
-- [Git](https://git-scm.com/download/win)
- - During installation, tick **add git to Path**.
-- [Visual Studio Community 2019](https://visualstudio.microsoft.com)
- - A compiler for C++ and CUDA codes.
-- [Miniconda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html)
- - Official distributions of Python should work too.
-- [CUDA 10.2](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-10.2-download-archive)
- - Not required for building CPU version.
- - Customize the installation if necessary. As a recommendation, skip the driver installation if a newer version is already installed.
-
-```{note}
-You should know how to set up environment variables, especially `Path`, on Windows. The following instruction relies heavily on this skill.
-```
-
-##### Common steps
-
-1. Launch Anaconda prompt from Windows Start menu
-
- Do not use raw `cmd.exe` s instruction is based on PowerShell syntax.
-
-2. Create a new conda environment
-
- ```powershell
- (base) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda create --name mmcv python=3.7
- (base) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda activate mmcv # make sure to activate environment before any operation
- ```
-
-3. Install PyTorch. Choose a version based on your need.
-
- ```powershell
- # CUDA version
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda install pytorch torchvision cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
- # CPU version
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda install install pytorch torchvision cpuonly -c pytorch
- ```
-
-4. Clone the repo
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> cd mmcv
- ```
-
-5. Install `ninja` and `psutil` to speed up the compilation
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> pip install -r requirements/optional.txt
- ```
-
-6. Set up MSVC compiler
-
- Set Environment variable, add `C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Community\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.27.29110\bin\Hostx86\x64` to `PATH`, so that `cl.exe` will be available in prompt, as shown below.
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> cl
- Microsoft (R) C/C++ Optimizing Compiler Version 19.27.29111 for x64
- Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
-
- usage: cl [ option... ] filename... [ / link linkoption... ]
- ```
-
- For compatibility, we use the x86-hosted and x64-targeted compiler. note `Hostx86\x64` in the path.
-
- You may want to change the system language to English because pytorch will parse text output from `cl.exe` to check its version. However only utf-8 is recognized. Navigate to Control Panel -> Region -> Administrative -> Language for Non-Unicode programs and change it to English.
-
-##### Build and install MMCV
-
-mmcv can be built in two ways:
-
-1. Full version (CPU ops)
-
- Module `ops` will be compiled as a pytorch extension, but only x86 code will be compiled. The compiled ops can be executed on CPU only.
-
-2. Full version (CUDA ops)
-
- Both x86 and CUDA codes of `ops` module will be compiled. The compiled version can be run on both CPU and CUDA-enabled GPU (if implemented).
-
-###### CPU version
-
-Build and install
-
-```powershell
-(mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python setup.py build_ext
-(mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python setup.py develop
-```
-
-###### GPU version
-
-1. Make sure `CUDA_PATH` or `CUDA_HOME` is already set in `envs` via `ls env:`, desired output is shown as below:
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> ls env:
-
- Name Value
- ---- -----
- CUDA_PATH C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2
- CUDA_PATH_V10_1 C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.1
- CUDA_PATH_V10_2 C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2
- ```
-
- This should already be done by CUDA installer. If not, or you have multiple version of CUDA toolkit installed, set it with
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> $env:CUDA_HOME = "C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2"
- # OR
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> $env:CUDA_HOME = $env:CUDA_PATH_V10_2 # if CUDA_PATH_V10_2 is in envs:
- ```
-
-2. Set CUDA target arch
-
- ```shell
- # Here you need to change to the target architecture corresponding to your GPU
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> $env:TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST="7.5"
- ```
-
- :::{note}
- Check your the compute capability of your GPU from [here](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-gpus).
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> &"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2\extras\demo_suite\deviceQuery.exe"
- Device 0: "NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1660 SUPER"
- CUDA Driver Version / Runtime Version 11.7 / 11.1
- CUDA Capability Major/Minor version number: 7.5
- ```
-
- The 7.5 above indicates the target architecture. Note: You need to replace v10.2 with your CUDA version in the above command.
- :::
-
-3. Build and install
-
- ```powershell
- # build
- python setup.py build_ext # if success, cl will be launched to compile ops
- # install
- python setup.py develop
- ```
-
- ```{note}
- If you are compiling against PyTorch 1.6.0, you might meet some errors from PyTorch as described in [this issue](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/42467). Follow [this pull request](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/43380/files) to modify the source code in your local PyTorch installation.
- ```
-
-##### Validate installation
-
-```powershell
-(mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python .dev_scripts/check_installation.py
-```
-
-If no error is reported by the above command, the installation is successful. If there is an error reported, please check [Frequently Asked Questions](../faq.md) to see if there is already a solution.
-If no solution is found, please feel free to open an [issue](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues).
-
-### Build mmcv-lite
-
-If you need to use PyTorch-related modules, make sure PyTorch has been successfully installed in your environment by referring to the [PyTorch official installation guide](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch#installation).
-
-1. Clone the repo
-
- ```bash
- git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- cd mmcv
- ```
-
-2. Start building
-
- ```bash
- MMCV_WITH_OPS=0 pip install -e . -v
- ```
-
-3. Validate installation
-
- ```bash
- python -c 'import mmcv;print(mmcv.__version__)'
- ```
diff --git a/docs/en/get_started/installation.md b/docs/en/get_started/installation.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 12bad000a171c0adf5be01dc7f53a94a5933070d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/en/get_started/installation.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,348 +0,0 @@
-## Installation
-
-There are two versions of MMCV:
-
-- **mmcv**: comprehensive, with full features and various CUDA ops out of box. It takes longer time to build.
-- **mmcv-lite**: lite, without CUDA ops but all other features, similar to mmcv\<1.0.0. It is useful when you do not need those CUDA ops.
-
-```{warning}
-Do not install both versions in the same environment, otherwise you may encounter errors like `ModuleNotFound`. You need to uninstall one before installing the other. `Installing the full version is highly recommended if CUDA is avaliable`.
-```
-
-### Install mmcv
-
-Before installing mmcv, make sure that PyTorch has been successfully installed following the [PyTorch official installation guide](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally). This can be verified using the following command
-
-```bash
-python -c 'import torch;print(torch.__version__)'
-```
-
-If version information is output, then PyTorch is installed.
-
-#### Install with mim (recommended)
-
-[mim](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mim) is the package management tool for the OpenMMLab projects, which makes it easy to install mmcv
-
-```bash
-pip install -U openmim
-mim install "mmcv>=2.0.0rc1"
-```
-
-If you find that the above installation command does not use a pre-built package ending with `.whl` but a source package ending with `.tar.gz`, you may not have a pre-build package corresponding to the PyTorch or CUDA or mmcv version, in which case you can [build mmcv from source](build.md).
-
-
-
-#### 7. Resolve conflicts
-
-If your local branch conflicts with the latest master branch of "upstream", you'll need to resolove them. There are two ways to do this:
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git rebase upstream/master
-```
-
-or
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git merge upstream/master
-```
-
-If you are very good at handling conflicts, then you can use rebase to resolve conflicts, as this will keep your commit logs tidy. If you are not familiar with `rebase`, then you can use `merge` to resolve conflicts.
-
-### Guidance
-
-#### Unit test
-
-If you cannot run the unit test of some modules for lacking of some dependencies, such as [video](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/master/mmcv/video) module, you can try to install the following dependencies:
-
-```shell
-# Linux
-sudo apt-get update -y
-sudo apt-get install -y libturbojpeg
-sudo apt-get install -y ffmpeg
-
-# Windows
-conda install ffmpeg
-```
-
-We should also make sure the committed code will not decrease the coverage of unit test, we could run the following command to check the coverage of unit test:
-
-```shell
-python -m coverage run -m pytest /path/to/test_file
-python -m coverage html
-# check file in htmlcov/index.html
-```
-
-#### Document rendering
-
-If the documents are modified/added, we should check the rendering result. We could install the dependencies and run the following command to render the documents and check the results:
-
-```shell
-pip install -r requirements/docs.txt
-cd docs/zh_cn/
-# or docs/en
-make html
-# check file in ./docs/zh_cn/_build/html/index.html
-```
-
-### Code style
-
-#### Python
-
-We adopt [PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) as the preferred code style.
-
-We use the following tools for linting and formatting:
-
-- [flake8](https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8): A wrapper around some linter tools.
-- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): A Python utility to sort imports.
-- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): A formatter for Python files.
-- [codespell](https://github.com/codespell-project/codespell): A Python utility to fix common misspellings in text files.
-- [mdformat](https://github.com/executablebooks/mdformat): Mdformat is an opinionated Markdown formatter that can be used to enforce a consistent style in Markdown files.
-- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): A formatter to format docstring.
-
-Style configurations of yapf and isort can be found in [setup.cfg](./setup.cfg).
-
-We use [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) that checks and formats for `flake8`, `yapf`, `isort`, `trailing whitespaces`, `markdown files`,
-fixes `end-of-files`, `double-quoted-strings`, `python-encoding-pragma`, `mixed-line-ending`, sorts `requirments.txt` automatically on every commit.
-The config for a pre-commit hook is stored in [.pre-commit-config](./.pre-commit-config.yaml).
-
-#### C++ and CUDA
-
-We follow the [Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html).
-
-### PR Specs
-
-1. Use [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com) hook to avoid issues of code style
-
-2. One short-time branch should be matched with only one PR
-
-3. Accomplish a detailed change in one PR. Avoid large PR
-
- - Bad: Support Faster R-CNN
- - Acceptable: Add a box head to Faster R-CNN
- - Good: Add a parameter to box head to support custom conv-layer number
-
-4. Provide clear and significant commit message
-
-5. Provide clear and meaningful PR description
-
- - Task name should be clarified in title. The general format is: \[Prefix\] Short description of the PR (Suffix)
- - Prefix: add new feature \[Feature\], fix bug \[Fix\], related to documents \[Docs\], in developing \[WIP\] (which will not be reviewed temporarily)
- - Introduce main changes, results and influences on other modules in short description
- - Associate related issues and pull requests with a milestone
diff --git a/docs/en/community/pr.md b/docs/en/community/pr.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 1bdd90f2bc41867e5c17403690f6a35cfe2c07b7..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/en/community/pr.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
-## Pull Request (PR)
-
-Content has been migrated to [contributing guidance](contributing.md).
diff --git a/docs/en/docutils.conf b/docs/en/docutils.conf
deleted file mode 100644
index 0c00c84688701117f231fd0c8ec295fb747b7d8f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/en/docutils.conf
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,2 +0,0 @@
-[html writers]
-table_style: colwidths-auto
diff --git a/docs/en/faq.md b/docs/en/faq.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 02d31c233a9ff66d5e8f3f288b5d5f64e5c5298c..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/en/faq.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
-## Frequently Asked Questions
-
-We list some common troubles faced by many users and their corresponding solutions here.
-Feel free to enrich the list if you find any frequent issues and have ways to help others to solve them.
-
-### Installation
-
-- KeyError: "xxx: 'yyy is not in the zzz registry'"
-
- The registry mechanism will be triggered only when the file of the module is imported.
- So you need to import that file somewhere. More details can be found at [KeyError: "MaskRCNN: 'RefineRoIHead is not in the models registry'"](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/issues/5974).
-
-- "No module named 'mmcv.ops'"; "No module named 'mmcv.\_ext'"
-
- 1. Uninstall existing mmcv in the environment using `pip uninstall mmcv`
- 2. Install mmcv-full following the [installation instruction](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get_started/installation.html) or [Build MMCV from source](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get_started/build.html)
-
-- "invalid device function" or "no kernel image is available for execution"
-
- 1. Check the CUDA compute capability of you GPU
- 2. Run `python mmdet/utils/collect_env.py` to check whether PyTorch, torchvision, and MMCV are built for the correct GPU architecture. You may need to set `TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST` to reinstall MMCV. The compatibility issue could happen when using old GPUS, e.g., Tesla K80 (3.7) on colab.
- 3. Check whether the running environment is the same as that when mmcv/mmdet is compiled. For example, you may compile mmcv using CUDA 10.0 bug run it on CUDA9.0 environments
-
-- "undefined symbol" or "cannot open xxx.so"
-
- 1. If those symbols are CUDA/C++ symbols (e.g., libcudart.so or GLIBCXX), check
- whether the CUDA/GCC runtimes are the same as those used for compiling mmcv
- 2. If those symbols are Pytorch symbols (e.g., symbols containing caffe, aten, and TH), check whether the Pytorch version is the same as that used for compiling mmcv
- 3. Run `python mmdet/utils/collect_env.py` to check whether PyTorch, torchvision, and MMCV are built by and running on the same environment
-
-- "RuntimeError: CUDA error: invalid configuration argument"
-
- This error may be caused by the poor performance of GPU. Try to decrease the value of [THREADS_PER_BLOCK](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/blob/cac22f8cf5a904477e3b5461b1cc36856c2793da/mmcv/ops/csrc/common_cuda_helper.hpp#L10)
- and recompile mmcv.
-
-- "RuntimeError: nms is not compiled with GPU support"
-
- This error is because your CUDA environment is not installed correctly.
- You may try to re-install your CUDA environment and then delete the build/ folder before re-compile mmcv.
-
-- "Segmentation fault"
-
- 1. Check your GCC version and use GCC >= 5.4. This usually caused by the incompatibility between PyTorch and the environment (e.g., GCC \< 4.9 for PyTorch). We also recommend the users to avoid using GCC 5.5 because many feedbacks report that GCC 5.5 will cause "segmentation fault" and simply changing it to GCC 5.4 could solve the problem
- 2. Check whether PyTorch is correctly installed and could use CUDA op, e.g. type the following command in your terminal and see whether they could correctly output results
- ```shell
- python -c 'import torch; print(torch.cuda.is_available())'
- ```
- 3. If PyTorch is correctly installed, check whether MMCV is correctly installed. If MMCV is correctly installed, then there will be no issue of the command
- ```shell
- python -c 'import mmcv; import mmcv.ops'
- ```
- 4. If MMCV and PyTorch are correctly installed, you can use `ipdb` to set breakpoints or directly add `print` to debug and see which part leads the `segmentation fault`
-
-- "libtorch_cuda_cu.so: cannot open shared object file"
-
- `mmcv-full` depends on the share object but it can not be found. We can check whether the object exists in `~/miniconda3/envs/{environment-name}/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/lib` or try to re-install the PyTorch.
-
-- "fatal error C1189: #error: -- unsupported Microsoft Visual Studio version!"
-
- If you are building mmcv-full on Windows and the version of CUDA is 9.2, you will probably encounter the error `"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v9.2\include\crt/host_config.h(133): fatal error C1189: #error: -- unsupported Microsoft Visual Studio version! Only the versions 2012, 2013, 2015 and 2017 are supported!"`, in which case you can use a lower version of Microsoft Visual Studio like vs2017.
-
-- "error: member "torch::jit::detail::ModulePolicy::all_slots" may not be initialized"
-
- If your version of PyTorch is 1.5.0 and you are building mmcv-full on Windows, you will probably encounter the error `- torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h(474): error: member "torch::jit::detail::ModulePolicy::all_slots" may not be initialized`. The way to solve the error is to replace all the `static constexpr bool all_slots = false;` with `static bool all_slots = false;` at this file `https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/v1.5.0/torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h`. More details can be found at [member "torch::jit::detail::AttributePolicy::all_slots" may not be initialized](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/39394).
-
-- "error: a member with an in-class initializer must be const"
-
- If your version of PyTorch is 1.6.0 and you are building mmcv-full on Windows, you will probably encounter the error `"- torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h(483): error: a member with an in-class initializer must be const"`. The way to solve the error is to replace all the `CONSTEXPR_EXCEPT_WIN_CUDA ` with `const` at `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h`. More details can be found at [Ninja: build stopped: subcommand failed](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues/575).
-
-- "error: member "torch::jit::ProfileOptionalOp::Kind" may not be initialized"
-
- If your version of PyTorch is 1.7.0 and you are building mmcv-full on Windows, you will probably encounter the error `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/ir/ir.h(1347): error: member "torch::jit::ProfileOptionalOp::Kind" may not be initialized`. The way to solve the error needs to modify several local files of PyTorch:
-
- - delete `static constexpr Symbol Kind = ::c10::prim::profile;` and `tatic constexpr Symbol Kind = ::c10::prim::profile_optional;` at `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/ir/ir.h`
- - replace `explicit operator type&() { return *(this->value); }` with `explicit operator type&() { return *((type*)this->value); }` at `torch\include\pybind11\cast.h`
- - replace all the `CONSTEXPR_EXCEPT_WIN_CUDA` with `const` at `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h`
-
- More details can be found at [Ensure default extra_compile_args](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/45956).
-
-- Compatibility issue between MMCV and MMDetection; "ConvWS is already registered in conv layer"
-
- Please install the correct version of MMCV for the version of your MMDetection following the [installation instruction](https://mmdetection.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get_started.html#installation).
-
-### Usage
-
-- "RuntimeError: Expected to have finished reduction in the prior iteration before starting a new one"
-
- 1. This error indicates that your module has parameters that were not used in producing loss. This phenomenon may be caused by running different branches in your code in DDP mode. More datails at [Expected to have finished reduction in the prior iteration before starting a new one](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/55582).
- 2. You can set ` find_unused_parameters = True` in the config to solve the above problems or find those unused parameters manually
-
-- "RuntimeError: Trying to backward through the graph a second time"
-
- `GradientCumulativeOptimizerHook` and `OptimizerHook` are both set which causes the `loss.backward()` to be called twice so `RuntimeError` was raised. We can only use one of these. More datails at [Trying to backward through the graph a second time](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues/1379).
diff --git a/docs/en/get_started/build.md b/docs/en/get_started/build.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e3d48ec7cf486edece6ea9e622937b08602f5e6e..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/en/get_started/build.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,292 +0,0 @@
-## Build MMCV from source
-
-### Build mmcv
-
-Before installing mmcv, make sure that PyTorch has been successfully installed following the [PyTorch official installation guide](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally). This can be verified using the following command
-
-```bash
-python -c 'import torch;print(torch.__version__)'
-```
-
-If version information is output, then PyTorch is installed.
-
-```{note}
-If you would like to use `opencv-python-headless` instead of `opencv-python`,
-e.g., in a minimum container environment or servers without GUI,
-you can first install it before installing MMCV to skip the installation of `opencv-python`.
-```
-
-#### Build on Linux
-
-1. Clone the repo
-
- ```bash
- git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- cd mmcv
- ```
-
-2. Install `ninja` and `psutil` to speed up the compilation
-
- ```bash
- pip install -r requirements/optional.txt
- ```
-
-3. Check the nvcc version (requires 9.2+. Skip if no GPU available.)
-
- ```bash
- nvcc --version
- ```
-
- If the above command outputs the following message, it means that the nvcc setting is OK, otherwise you need to set CUDA_HOME.
-
- ```
- nvcc: NVIDIA (R) Cuda compiler driver
- Copyright (c) 2005-2020 NVIDIA Corporation
- Built on Mon_Nov_30_19:08:53_PST_2020
- Cuda compilation tools, release 11.2, V11.2.67
- Build cuda_11.2.r11.2/compiler.29373293_0
- ```
-
- :::{note}
- If you want to support ROCm, you can refer to [AMD ROCm](https://rocmdocs.amd.com/en/latest/Installation_Guide/Installation-Guide.html) to install ROCm.
- :::
-
-4. Check the gcc version (requires 5.4+)
-
- ```bash
- gcc --version
- ```
-
-5. Start building (takes 10+ min)
-
- ```bash
- pip install -e . -v
- ```
-
-6. Validate the installation
-
- ```bash
- python .dev_scripts/check_installation.py
- ```
-
- If no error is reported by the above command, the installation is successful. If there is an error reported, please check [Frequently Asked Questions](../faq.md) to see if there is already a solution.
-
- If no solution is found, please feel free to open an [issue](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues).
-
-#### Build on macOS
-
-```{note}
-If you are using a mac with apple silicon chip, install the PyTorch 1.13+, otherwise you will encounter the problem in [issues#2218](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues/2218).
-```
-
-1. Clone the repo
-
- ```bash
- git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- cd mmcv
- ```
-
-2. Install `ninja` and `psutil` to speed up the compilation
-
- ```bash
- pip install -r requirements/optional.txt
- ```
-
-3. Start building
-
- ```bash
- MMCV_WITH_OPS=1 pip install -e .
- ```
-
-4. Validate the installation
-
- ```bash
- python .dev_scripts/check_installation.py
- ```
-
- If no error is reported by the above command, the installation is successful. If there is an error reported, please check [Frequently Asked Questions](../faq.md) to see if there is already a solution.
-
- If no solution is found, please feel free to open an [issue](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues).
-
-#### Build on Windows
-
-Building MMCV on Windows is a bit more complicated than that on Linux.
-The following instructions show how to get this accomplished.
-
-##### Prerequisite
-
-The following software is required for building MMCV on windows.
-Install them first.
-
-- [Git](https://git-scm.com/download/win)
- - During installation, tick **add git to Path**.
-- [Visual Studio Community 2019](https://visualstudio.microsoft.com)
- - A compiler for C++ and CUDA codes.
-- [Miniconda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html)
- - Official distributions of Python should work too.
-- [CUDA 10.2](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-10.2-download-archive)
- - Not required for building CPU version.
- - Customize the installation if necessary. As a recommendation, skip the driver installation if a newer version is already installed.
-
-```{note}
-You should know how to set up environment variables, especially `Path`, on Windows. The following instruction relies heavily on this skill.
-```
-
-##### Common steps
-
-1. Launch Anaconda prompt from Windows Start menu
-
- Do not use raw `cmd.exe` s instruction is based on PowerShell syntax.
-
-2. Create a new conda environment
-
- ```powershell
- (base) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda create --name mmcv python=3.7
- (base) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda activate mmcv # make sure to activate environment before any operation
- ```
-
-3. Install PyTorch. Choose a version based on your need.
-
- ```powershell
- # CUDA version
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda install pytorch torchvision cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
- # CPU version
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda install install pytorch torchvision cpuonly -c pytorch
- ```
-
-4. Clone the repo
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> cd mmcv
- ```
-
-5. Install `ninja` and `psutil` to speed up the compilation
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> pip install -r requirements/optional.txt
- ```
-
-6. Set up MSVC compiler
-
- Set Environment variable, add `C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Community\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.27.29110\bin\Hostx86\x64` to `PATH`, so that `cl.exe` will be available in prompt, as shown below.
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> cl
- Microsoft (R) C/C++ Optimizing Compiler Version 19.27.29111 for x64
- Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
-
- usage: cl [ option... ] filename... [ / link linkoption... ]
- ```
-
- For compatibility, we use the x86-hosted and x64-targeted compiler. note `Hostx86\x64` in the path.
-
- You may want to change the system language to English because pytorch will parse text output from `cl.exe` to check its version. However only utf-8 is recognized. Navigate to Control Panel -> Region -> Administrative -> Language for Non-Unicode programs and change it to English.
-
-##### Build and install MMCV
-
-mmcv can be built in two ways:
-
-1. Full version (CPU ops)
-
- Module `ops` will be compiled as a pytorch extension, but only x86 code will be compiled. The compiled ops can be executed on CPU only.
-
-2. Full version (CUDA ops)
-
- Both x86 and CUDA codes of `ops` module will be compiled. The compiled version can be run on both CPU and CUDA-enabled GPU (if implemented).
-
-###### CPU version
-
-Build and install
-
-```powershell
-(mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python setup.py build_ext
-(mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python setup.py develop
-```
-
-###### GPU version
-
-1. Make sure `CUDA_PATH` or `CUDA_HOME` is already set in `envs` via `ls env:`, desired output is shown as below:
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> ls env:
-
- Name Value
- ---- -----
- CUDA_PATH C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2
- CUDA_PATH_V10_1 C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.1
- CUDA_PATH_V10_2 C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2
- ```
-
- This should already be done by CUDA installer. If not, or you have multiple version of CUDA toolkit installed, set it with
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> $env:CUDA_HOME = "C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2"
- # OR
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> $env:CUDA_HOME = $env:CUDA_PATH_V10_2 # if CUDA_PATH_V10_2 is in envs:
- ```
-
-2. Set CUDA target arch
-
- ```shell
- # Here you need to change to the target architecture corresponding to your GPU
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> $env:TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST="7.5"
- ```
-
- :::{note}
- Check your the compute capability of your GPU from [here](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-gpus).
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> &"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2\extras\demo_suite\deviceQuery.exe"
- Device 0: "NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1660 SUPER"
- CUDA Driver Version / Runtime Version 11.7 / 11.1
- CUDA Capability Major/Minor version number: 7.5
- ```
-
- The 7.5 above indicates the target architecture. Note: You need to replace v10.2 with your CUDA version in the above command.
- :::
-
-3. Build and install
-
- ```powershell
- # build
- python setup.py build_ext # if success, cl will be launched to compile ops
- # install
- python setup.py develop
- ```
-
- ```{note}
- If you are compiling against PyTorch 1.6.0, you might meet some errors from PyTorch as described in [this issue](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/42467). Follow [this pull request](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/43380/files) to modify the source code in your local PyTorch installation.
- ```
-
-##### Validate installation
-
-```powershell
-(mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python .dev_scripts/check_installation.py
-```
-
-If no error is reported by the above command, the installation is successful. If there is an error reported, please check [Frequently Asked Questions](../faq.md) to see if there is already a solution.
-If no solution is found, please feel free to open an [issue](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues).
-
-### Build mmcv-lite
-
-If you need to use PyTorch-related modules, make sure PyTorch has been successfully installed in your environment by referring to the [PyTorch official installation guide](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch#installation).
-
-1. Clone the repo
-
- ```bash
- git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- cd mmcv
- ```
-
-2. Start building
-
- ```bash
- MMCV_WITH_OPS=0 pip install -e . -v
- ```
-
-3. Validate installation
-
- ```bash
- python -c 'import mmcv;print(mmcv.__version__)'
- ```
diff --git a/docs/en/get_started/installation.md b/docs/en/get_started/installation.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 12bad000a171c0adf5be01dc7f53a94a5933070d..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/en/get_started/installation.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,348 +0,0 @@
-## Installation
-
-There are two versions of MMCV:
-
-- **mmcv**: comprehensive, with full features and various CUDA ops out of box. It takes longer time to build.
-- **mmcv-lite**: lite, without CUDA ops but all other features, similar to mmcv\<1.0.0. It is useful when you do not need those CUDA ops.
-
-```{warning}
-Do not install both versions in the same environment, otherwise you may encounter errors like `ModuleNotFound`. You need to uninstall one before installing the other. `Installing the full version is highly recommended if CUDA is avaliable`.
-```
-
-### Install mmcv
-
-Before installing mmcv, make sure that PyTorch has been successfully installed following the [PyTorch official installation guide](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally). This can be verified using the following command
-
-```bash
-python -c 'import torch;print(torch.__version__)'
-```
-
-If version information is output, then PyTorch is installed.
-
-#### Install with mim (recommended)
-
-[mim](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mim) is the package management tool for the OpenMMLab projects, which makes it easy to install mmcv
-
-```bash
-pip install -U openmim
-mim install "mmcv>=2.0.0rc1"
-```
-
-If you find that the above installation command does not use a pre-built package ending with `.whl` but a source package ending with `.tar.gz`, you may not have a pre-build package corresponding to the PyTorch or CUDA or mmcv version, in which case you can [build mmcv from source](build.md).
-
- -
-| CUDA | +torch 1.10 | +torch 1.9 | +torch 1.8 | +torch 1.7 | +torch 1.6 | +torch 1.5 | +
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11.3 | +install |
+ + | + | + | + | + |
| 11.1 | +install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ + | + | + |
| 11.0 | ++ | + | + | install |
+ + | + |
| 10.2 | +install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+
| 10.1 | ++ | + | install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+
| 9.2 | ++ | + | + | install |
+ install |
+ install |
+
| cpu | +install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+ install |
+
 -
-将代码克隆到本地
-
-```shell
-git clone git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git
-```
-
-添加原代码库为上游代码库
-
-```bash
-git remote add upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv
-```
-
-检查 remote 是否添加成功,在终端输入 `git remote -v`
-
-```bash
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (fetch)
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (push)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (fetch)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (push)
-```
-
-```{note}
-这里对 origin 和 upstream 进行一个简单的介绍,当我们使用 git clone 来克隆代码时,会默认创建一个 origin 的 remote,它指向我们克隆的代码库地址,而 upstream 则是我们自己添加的,用来指向原始代码库地址。当然如果你不喜欢他叫 upstream,也可以自己修改,比如叫 open-mmlab。我们通常向 origin 提交代码(即 fork 下来的远程仓库),然后向 upstream 提交一个 pull request。如果提交的代码和最新的代码发生冲突,再从 upstream 拉取最新的代码,和本地分支解决冲突,再提交到 origin。
-```
-
-#### 2. 配置 pre-commit
-
-在本地开发环境中,我们使用 [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/#intro) 来检查代码风格,以确保代码风格的统一。在提交代码,需要先安装 pre-commit(需要在 MMCV 目录下执行):
-
-```shell
-pip install -U pre-commit
-pre-commit install
-```
-
-检查 pre-commit 是否配置成功,并安装 `.pre-commit-config.yaml` 中的钩子:
-
-```shell
-pre-commit run --all-files
-```
-
-
-
-将代码克隆到本地
-
-```shell
-git clone git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git
-```
-
-添加原代码库为上游代码库
-
-```bash
-git remote add upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv
-```
-
-检查 remote 是否添加成功,在终端输入 `git remote -v`
-
-```bash
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (fetch)
-origin git@github.com:{username}/mmcv.git (push)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (fetch)
-upstream git@github.com:open-mmlab/mmcv (push)
-```
-
-```{note}
-这里对 origin 和 upstream 进行一个简单的介绍,当我们使用 git clone 来克隆代码时,会默认创建一个 origin 的 remote,它指向我们克隆的代码库地址,而 upstream 则是我们自己添加的,用来指向原始代码库地址。当然如果你不喜欢他叫 upstream,也可以自己修改,比如叫 open-mmlab。我们通常向 origin 提交代码(即 fork 下来的远程仓库),然后向 upstream 提交一个 pull request。如果提交的代码和最新的代码发生冲突,再从 upstream 拉取最新的代码,和本地分支解决冲突,再提交到 origin。
-```
-
-#### 2. 配置 pre-commit
-
-在本地开发环境中,我们使用 [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/#intro) 来检查代码风格,以确保代码风格的统一。在提交代码,需要先安装 pre-commit(需要在 MMCV 目录下执行):
-
-```shell
-pip install -U pre-commit
-pre-commit install
-```
-
-检查 pre-commit 是否配置成功,并安装 `.pre-commit-config.yaml` 中的钩子:
-
-```shell
-pre-commit run --all-files
-```
-
- -
-
-
- -
-```{note}
-如果你是中国用户,由于网络原因,可能会出现安装失败的情况,这时可以使用国内源
-
-pre-commit install -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-
-pre-commit run --all-files -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-```
-
-如果安装过程被中断,可以重复执行 `pre-commit run ...` 继续安装。
-
-如果提交的代码不符合代码风格规范,pre-commit 会发出警告,并自动修复部分错误。
-
-
-
-```{note}
-如果你是中国用户,由于网络原因,可能会出现安装失败的情况,这时可以使用国内源
-
-pre-commit install -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-
-pre-commit run --all-files -c .pre-commit-config-zh-cn.yaml
-```
-
-如果安装过程被中断,可以重复执行 `pre-commit run ...` 继续安装。
-
-如果提交的代码不符合代码风格规范,pre-commit 会发出警告,并自动修复部分错误。
-
- -
-如果我们想临时绕开 pre-commit 的检查提交一次代码,可以在 `git commit` 时加上 `--no-verify`(需要保证最后推送至远程仓库的代码能够通过 pre-commit 检查)。
-
-```shell
-git commit -m "xxx" --no-verify
-```
-
-#### 3. 创建开发分支
-
-安装完 pre-commit 之后,我们需要基于 master 创建开发分支,建议的分支命名规则为 `username/pr_name`。
-
-```shell
-git checkout -b yhc/refactor_contributing_doc
-```
-
-在后续的开发中,如果本地仓库的 master 分支落后于 upstream 的 master 分支,我们需要先拉取 upstream 的代码进行同步,再执行上面的命令
-
-```shell
-git pull upstream master
-```
-
-#### 4. 提交代码并在本地通过单元测试
-
-- MMCV 引入了 mypy 来做静态类型检查,以增加代码的鲁棒性。因此我们在提交代码时,需要补充 Type Hints。具体规则可以参考[教程](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/519335398)。
-
-- 提交的代码同样需要通过单元测试
-
- ```shell
- # 通过全量单元测试
- pytest tests
-
- # 我们需要保证提交的代码能够通过修改模块的单元测试,以 runner 为例
- pytest tests/test_runner/test_runner.py
- ```
-
- 如果你由于缺少依赖无法运行修改模块的单元测试,可以参考[指引-单元测试](#单元测试)
-
-- 如果修改/添加了文档,参考[指引](#文档渲染)确认文档渲染正常。
-
-#### 5. 推送代码到远程
-
-代码通过单元测试和 pre-commit 检查后,将代码推送到远程仓库,如果是第一次推送,可以在 `git push` 后加上 `-u` 参数以关联远程分支
-
-```shell
-git push -u origin {branch_name}
-```
-
-这样下次就可以直接使用 `git push` 命令推送代码了,而无需指定分支和远程仓库。
-
-#### 6. 提交拉取请求(PR)
-
-(1) 在 GitHub 的 Pull request 界面创建拉取请求
-
-
-如果我们想临时绕开 pre-commit 的检查提交一次代码,可以在 `git commit` 时加上 `--no-verify`(需要保证最后推送至远程仓库的代码能够通过 pre-commit 检查)。
-
-```shell
-git commit -m "xxx" --no-verify
-```
-
-#### 3. 创建开发分支
-
-安装完 pre-commit 之后,我们需要基于 master 创建开发分支,建议的分支命名规则为 `username/pr_name`。
-
-```shell
-git checkout -b yhc/refactor_contributing_doc
-```
-
-在后续的开发中,如果本地仓库的 master 分支落后于 upstream 的 master 分支,我们需要先拉取 upstream 的代码进行同步,再执行上面的命令
-
-```shell
-git pull upstream master
-```
-
-#### 4. 提交代码并在本地通过单元测试
-
-- MMCV 引入了 mypy 来做静态类型检查,以增加代码的鲁棒性。因此我们在提交代码时,需要补充 Type Hints。具体规则可以参考[教程](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/519335398)。
-
-- 提交的代码同样需要通过单元测试
-
- ```shell
- # 通过全量单元测试
- pytest tests
-
- # 我们需要保证提交的代码能够通过修改模块的单元测试,以 runner 为例
- pytest tests/test_runner/test_runner.py
- ```
-
- 如果你由于缺少依赖无法运行修改模块的单元测试,可以参考[指引-单元测试](#单元测试)
-
-- 如果修改/添加了文档,参考[指引](#文档渲染)确认文档渲染正常。
-
-#### 5. 推送代码到远程
-
-代码通过单元测试和 pre-commit 检查后,将代码推送到远程仓库,如果是第一次推送,可以在 `git push` 后加上 `-u` 参数以关联远程分支
-
-```shell
-git push -u origin {branch_name}
-```
-
-这样下次就可以直接使用 `git push` 命令推送代码了,而无需指定分支和远程仓库。
-
-#### 6. 提交拉取请求(PR)
-
-(1) 在 GitHub 的 Pull request 界面创建拉取请求
- -
-(2) 根据指引修改 PR 描述,以便于其他开发者更好地理解你的修改
-
-
-
-(2) 根据指引修改 PR 描述,以便于其他开发者更好地理解你的修改
-
- -
-描述规范详见[拉取请求规范](#拉取请求规范)
-
-
-
-**注意事项**
-
-(a) PR 描述应该包含修改理由、修改内容以及修改后带来的影响,并关联相关 Issue(具体方式见[文档](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue))
-
-(b) 如果是第一次为 OpenMMLab 做贡献,需要签署 CLA
-
-
-
-描述规范详见[拉取请求规范](#拉取请求规范)
-
-
-
-**注意事项**
-
-(a) PR 描述应该包含修改理由、修改内容以及修改后带来的影响,并关联相关 Issue(具体方式见[文档](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue))
-
-(b) 如果是第一次为 OpenMMLab 做贡献,需要签署 CLA
-
- -
-(c) 检查提交的 PR 是否通过 CI(集成测试)
-
-
-
-(c) 检查提交的 PR 是否通过 CI(集成测试)
-
- -
-MMCV 会在不同的平台(Linux、Window、Mac),基于不同版本的 Python、PyTorch、CUDA 对提交的代码进行单元测试,以保证代码的正确性,如果有任何一个没有通过,我们可点击上图中的 `Details` 来查看具体的测试信息,以便于我们修改代码。
-
-(3) 如果 PR 通过了 CI,那么就可以等待其他开发者的 review,并根据 reviewer 的意见,修改代码,并重复 [4](#4-提交代码并本地通过单元测试)-[5](#5-推送代码到远程) 步骤,直到 reviewer 同意合入 PR。
-
-
-
-MMCV 会在不同的平台(Linux、Window、Mac),基于不同版本的 Python、PyTorch、CUDA 对提交的代码进行单元测试,以保证代码的正确性,如果有任何一个没有通过,我们可点击上图中的 `Details` 来查看具体的测试信息,以便于我们修改代码。
-
-(3) 如果 PR 通过了 CI,那么就可以等待其他开发者的 review,并根据 reviewer 的意见,修改代码,并重复 [4](#4-提交代码并本地通过单元测试)-[5](#5-推送代码到远程) 步骤,直到 reviewer 同意合入 PR。
-
- -
-所有 reviewer 同意合入 PR 后,我们会尽快将 PR 合并到主分支。
-
-#### 7. 解决冲突
-
-随着时间的推移,我们的代码库会不断更新,这时候,如果你的 PR 与主分支存在冲突,你需要解决冲突,解决冲突的方式有两种:
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git rebase upstream/master
-```
-
-或者
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git merge upstream/master
-```
-
-如果你非常善于处理冲突,那么可以使用 rebase 的方式来解决冲突,因为这能够保证你的 commit log 的整洁。如果你不太熟悉 `rebase` 的使用,那么可以使用 `merge` 的方式来解决冲突。
-
-### 指引
-
-#### 单元测试
-
-如果你无法正常执行部分模块的单元测试,例如 [video](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/master/mmcv/video) 模块,可能是你的当前环境没有安装以下依赖
-
-```shell
-# Linux
-sudo apt-get update -y
-sudo apt-get install -y libturbojpeg
-sudo apt-get install -y ffmpeg
-
-# Windows
-conda install ffmpeg
-```
-
-在提交修复代码错误或新增特性的拉取请求时,我们应该尽可能的让单元测试覆盖所有提交的代码,计算单元测试覆盖率的方法如下
-
-```shell
-python -m coverage run -m pytest /path/to/test_file
-python -m coverage html
-# check file in htmlcov/index.html
-```
-
-#### 文档渲染
-
-在提交修复代码错误或新增特性的拉取请求时,可能会需要修改/新增模块的 docstring。我们需要确认渲染后的文档样式是正确的。
-本地生成渲染后的文档的方法如下
-
-```shell
-pip install -r requirements/docs.txt
-cd docs/zh_cn/
-# or docs/en
-make html
-# check file in ./docs/zh_cn/_build/html/index.html
-```
-
-### 代码风格
-
-#### Python
-
-[PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) 作为 OpenMMLab 算法库首选的代码规范,我们使用以下工具检查和格式化代码
-
-- [flake8](https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8): Python 官方发布的代码规范检查工具,是多个检查工具的封装
-- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): 自动调整模块导入顺序的工具
-- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): Google 发布的代码规范检查工具
-- [codespell](https://github.com/codespell-project/codespell): 检查单词拼写是否有误
-- [mdformat](https://github.com/executablebooks/mdformat): 检查 markdown 文件的工具
-- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): 格式化 docstring 的工具
-
-yapf 和 isort 的配置可以在 [setup.cfg](./setup.cfg) 找到
-
-通过配置 [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) ,我们可以在提交代码时自动检查和格式化 `flake8`、`yapf`、`isort`、`trailing whitespaces`、`markdown files`,
-修复 `end-of-files`、`double-quoted-strings`、`python-encoding-pragma`、`mixed-line-ending`,调整 `requirments.txt` 的包顺序。
-pre-commit 钩子的配置可以在 [.pre-commit-config](./.pre-commit-config.yaml) 找到。
-
-pre-commit 具体的安装使用方式见[拉取请求](#2-配置-pre-commit)。
-
-更具体的规范请参考 [OpenMMLab 代码规范](code_style.md)。
-
-#### C++ and CUDA
-
-C++ 和 CUDA 的代码规范遵从 [Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html)
-
-### 拉取请求规范
-
-1. 使用 [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com),尽量减少代码风格相关问题
-
-2. 一个`拉取请求`对应一个短期分支
-
-3. 粒度要细,一个`拉取请求`只做一件事情,避免超大的`拉取请求`
-
- - Bad:实现 Faster R-CNN
- - Acceptable:给 Faster R-CNN 添加一个 box head
- - Good:给 box head 增加一个参数来支持自定义的 conv 层数
-
-4. 每次 Commit 时需要提供清晰且有意义 commit 信息
-
-5. 提供清晰且有意义的`拉取请求`描述
-
- - 标题写明白任务名称,一般格式:\[Prefix\] Short description of the pull request (Suffix)
- - prefix: 新增功能 \[Feature\], 修 bug \[Fix\], 文档相关 \[Docs\], 开发中 \[WIP\] (暂时不会被review)
- - 描述里介绍`拉取请求`的主要修改内容,结果,以及对其他部分的影响, 参考`拉取请求`模板
- - 关联相关的`议题` (issue) 和其他`拉取请求`
-
-6. 如果引入了其他三方库,或借鉴了三方库的代码,请确认他们的许可证和 mmcv 兼容,并在借鉴的代码上补充 `This code is inspired from http://`
diff --git a/docs/zh_cn/community/pr.md b/docs/zh_cn/community/pr.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 427fdf9e4965e404970c761676e7edd29e7b2e56..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/zh_cn/community/pr.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
-## 拉取请求
-
-本文档的内容已迁移到[贡献指南](contributing.md)。
diff --git a/docs/zh_cn/docutils.conf b/docs/zh_cn/docutils.conf
deleted file mode 100644
index 0c00c84688701117f231fd0c8ec295fb747b7d8f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/zh_cn/docutils.conf
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,2 +0,0 @@
-[html writers]
-table_style: colwidths-auto
diff --git a/docs/zh_cn/faq.md b/docs/zh_cn/faq.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6cfb100c631b101fa0cff0650105a3cc7d735e7b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/zh_cn/faq.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,91 +0,0 @@
-## 常见问题
-
-在这里我们列出了用户经常遇到的问题以及对应的解决方法。如果您遇到了其他常见的问题,并且知道可以帮到大家的解决办法,
-欢迎随时丰富这个列表。
-
-### 安装问题
-
-- KeyError: "xxx: 'yyy is not in the zzz registry'"
-
- 只有模块所在的文件被导入时,注册机制才会被触发,所以您需要在某处导入该文件,更多详情请查看 [KeyError: "MaskRCNN: 'RefineRoIHead is not in the models registry'"](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/issues/5974)。
-
-- "No module named 'mmcv.ops'"; "No module named 'mmcv.\_ext'"
-
- 1. 使用 `pip uninstall mmcv` 卸载您环境中的 mmcv
- 2. 参考 [installation instruction](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get_started/installation.html) 或者 [Build MMCV from source](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get_started/build.html) 安装 mmcv-full
-
-- "invalid device function" 或者 "no kernel image is available for execution"
-
- 1. 检查 GPU 的 CUDA 计算能力
- 2. 运行 `python mmdet/utils/collect_env.py` 来检查 PyTorch、torchvision 和 MMCV 是否是针对正确的 GPU 架构构建的,您可能需要去设置 `TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST` 来重新安装 MMCV。兼容性问题可能会出现在使用旧版的 GPUs,如:colab 上的 Tesla K80 (3.7)
- 3. 检查运行环境是否和 mmcv/mmdet 编译时的环境相同。例如,您可能使用 CUDA 10.0 编译 mmcv,但在 CUDA 9.0 的环境中运行它
-
-- "undefined symbol" 或者 "cannot open xxx.so"
-
- 1. 如果符号和 CUDA/C++ 相关(例如:libcudart.so 或者 GLIBCXX),请检查 CUDA/GCC 运行时的版本是否和编译 mmcv 的一致
- 2. 如果符号和 PyTorch 相关(例如:符号包含 caffe、aten 和 TH),请检查 PyTorch 运行时的版本是否和编译 mmcv 的一致
- 3. 运行 `python mmdet/utils/collect_env.py` 以检查 PyTorch、torchvision 和 MMCV 构建和运行的环境是否相同
-
-- "RuntimeError: CUDA error: invalid configuration argument"
-
- 这个错误可能是由于您的 GPU 性能不佳造成的。尝试降低 [THREADS_PER_BLOCK](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/blob/cac22f8cf5a904477e3b5461b1cc36856c2793da/mmcv/ops/csrc/common_cuda_helper.hpp#L10)
- 的值并重新编译 mmcv。
-
-- "RuntimeError: nms is not compiled with GPU support"
-
- 这个错误是由于您的 CUDA 环境没有正确安装。
- 您可以尝试重新安装您的 CUDA 环境,然后删除 mmcv/build 文件夹并重新编译 mmcv。
-
-- "Segmentation fault"
-
- 1. 检查 GCC 的版本,通常是因为 PyTorch 版本与 GCC 版本不匹配 (例如 GCC \< 4.9 ),我们推荐用户使用 GCC 5.4,我们也不推荐使用 GCC 5.5, 因为有反馈 GCC 5.5 会导致 "segmentation fault" 并且切换到 GCC 5.4 就可以解决问题
- 2. 检查是否正确安装 CUDA 版本的 PyTorc。输入以下命令并检查是否返回 True
- ```shell
- python -c 'import torch; print(torch.cuda.is_available())'
- ```
- 3. 如果 `torch` 安装成功,那么检查 MMCV 是否安装成功。输入以下命令,如果没有报错说明 mmcv-full 安装成。
- ```shell
- python -c 'import mmcv; import mmcv.ops'
- ```
- 4. 如果 MMCV 与 PyTorch 都安装成功了,则可以使用 `ipdb` 设置断点或者使用 `print` 函数,分析是哪一部分的代码导致了 `segmentation fault`
-
-- "libtorch_cuda_cu.so: cannot open shared object file"
-
- `mmcv-full` 依赖 `libtorch_cuda_cu.so` 文件,但程序运行时没能找到该文件。我们可以检查该文件是否存在 `~/miniconda3/envs/{environment-name}/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/lib` 也可以尝试重装 PyTorch。
-
-- "fatal error C1189: #error: -- unsupported Microsoft Visual Studio version!"
-
- 如果您在 Windows 上编译 mmcv-full 并且 CUDA 的版本是 9.2,您很可能会遇到这个问题 `"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v9.2\include\crt/host_config.h(133): fatal error C1189: #error: -- unsupported Microsoft Visual Studio version! Only the versions 2012, 2013, 2015 and 2017 are supported!"`,您可以尝试使用低版本的 Microsoft Visual Studio,例如 vs2017。
-
-- "error: member "torch::jit::detail::ModulePolicy::all_slots" may not be initialized"
-
- 如果您在 Windows 上编译 mmcv-full 并且 PyTorch 的版本是 1.5.0,您很可能会遇到这个问题 `- torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h(474): error: member "torch::jit::detail::ModulePolicy::all_slots" may not be initialized`。解决这个问题的方法是将 `torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h` 文件中所有 `static constexpr bool all_slots = false;` 替换为 `static bool all_slots = false;`。更多细节可以查看 [member "torch::jit::detail::AttributePolicy::all_slots" may not be initialized](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/39394)。
-
-- "error: a member with an in-class initializer must be const"
-
- 如果您在 Windows 上编译 mmcv-full 并且 PyTorch 的版本是 1.6.0,您很可能会遇到这个问题 `"- torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h(483): error: a member with an in-class initializer must be const"`. 解决这个问题的方法是将 `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h` 文件中的所有 `CONSTEXPR_EXCEPT_WIN_CUDA ` 替换为 `const`。更多细节可以查看 [Ninja: build stopped: subcommand failed](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues/575)。
-
-- "error: member "torch::jit::ProfileOptionalOp::Kind" may not be initialized"
-
- 如果您在 Windows 上编译 mmcv-full 并且 PyTorch 的版本是 1.7.0,您很可能会遇到这个问题 `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/ir/ir.h(1347): error: member "torch::jit::ProfileOptionalOp::Kind" may not be initialized`. 解决这个问题的方法是修改 PyTorch 中的几个文件:
-
- - 删除 `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/ir/ir.h` 文件中的 `static constexpr Symbol Kind = ::c10::prim::profile;` 和 `tatic constexpr Symbol Kind = ::c10::prim::profile_optional;`
- - 将 `torch\include\pybind11\cast.h` 文件中的 `explicit operator type&() { return *(this->value); }` 替换为 `explicit operator type&() { return *((type*)this->value); }`
- - 将 `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h` 文件中的 所有 `CONSTEXPR_EXCEPT_WIN_CUDA` 替换为 `const`
-
- 更多细节可以查看 [Ensure default extra_compile_args](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/45956)。
-
-- MMCV 和 MMDetection 的兼容性问题;"ConvWS is already registered in conv layer"
-
- 请参考 [installation instruction](https://mmdetection.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get_started.html#installation) 为您的 MMDetection 版本安装正确版本的 MMCV。
-
-### 使用问题
-
-- "RuntimeError: Expected to have finished reduction in the prior iteration before starting a new one"
-
- 1. 这个错误是因为有些参数没有参与 loss 的计算,可能是代码中存在多个分支,导致有些分支没有参与 loss 的计算。更多细节见 [Expected to have finished reduction in the prior iteration before starting a new one](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/55582)。
- 2. 你可以设置 DDP 中的 `find_unused_parameters` 为 `True`,或者手动查找哪些参数没有用到。
-
-- "RuntimeError: Trying to backward through the graph a second time"
-
- 不能同时设置 `GradientCumulativeOptimizerHook` 和 `OptimizerHook`,这会导致 `loss.backward()` 被调用两次,于是程序抛出 `RuntimeError`。我们只需设置其中的一个。更多细节见 [Trying to backward through the graph a second time](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues/1379)。
diff --git a/docs/zh_cn/get_started/article.md b/docs/zh_cn/get_started/article.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 96768502cedb607d58ea2dc8d17b3dd8b9af20b2..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/zh_cn/get_started/article.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-## 解读文章汇总
-
-这篇文章汇总了 [OpenMMLab](https://www.zhihu.com/people/openmmlab) 解读的部分文章(更多文章和视频见 [OpenMMLabCourse](https://github.com/open-mmlab/OpenMMLabCourse)),如果您有推荐的文章(不一定是 OpenMMLab 发布的文章,可以是自己写的文章),非常欢迎提 [Pull Request](http://127.0.0.1:5501/mmcv/docs/zh_cn/_build/html/community/pr.html) 添加到这里。
-
-### MMCV 解读文章
-
-#### 框架解读
-
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(一):整体概述](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/336081587)
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(二):FileHandler](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/336097883)
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(三): FileClient](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/339190576)
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(四): Config](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/346203167)
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(五): Registry](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/355271993)
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(六): Hook](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/355272220)
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(七): Runner](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/355272459)
-- [MMCV Hook 食用指南](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/448600739)
-- [PyTorch & MMCV Dispatcher 机制解析](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/451671838)
-
-#### 工具解读
-
-- [训练可视化工具哪款是你的菜?MMCV一行代码随你挑](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/387078211)
-
-#### 安装指南
-
-- [久等了!Windows 平台 MMCV 的预编译包终于来了!](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/441653536)
-- [Windows 环境从零安装 mmcv-full](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/434491590)
-
-#### 知乎问答
-
-- [深度学习科研,如何高效进行代码和实验管理?](https://www.zhihu.com/question/269707221/answer/2480772257)
-- [深度学习方面的科研工作中的实验代码有什么规范和写作技巧?如何妥善管理实验数据?](https://www.zhihu.com/question/268193800/answer/2586000037)
-
-### 下游算法库解读文章
-
-- [MMDetection](https://mmdetection.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/article.html)
-
-### PyTorch 解读文章
-
-- [PyTorch1.11 亮点一览:TorchData、functorch、DDP 静态图](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/486222256)
-- [PyTorch1.12 亮点一览:DataPipe + TorchArrow 新的数据加载与处理范式](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/537868554)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 nn.Module:核心网络模块接口详解](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/340453841)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 torch.autograd:梯度计算详解](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/321449610)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 torch.utils.data:解析数据处理全流程](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/337850513)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 torch.optim:优化算法接口详解](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/346205754)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 DP & DDP:模型并行和分布式训练解析](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/343951042)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 BN & SyncBN:BN 与 多卡同步 BN 详解](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/337732517)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 torch.cuda.amp: 自动混合精度详解](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/348554267)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 cpp_extension:揭秘 C++/CUDA 算子实现和调用全流程](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/348555597)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之即时编译篇](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/361101354)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之分布式训练了解一下?](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/361314953)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 torch.serialization & torch.hub](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/364239544)
-
-### 其他
-
-- [困扰我 48 小时的深拷贝,今天终于...](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/470892209)
-- [拿什么拯救我的 4G 显卡](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/430123077)
-- [是谁偷偷动了我的 logger](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/481383590)
-- [三句话,让 logger 言听计从](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/487524917)
-- [Logging 不为人知的二三事](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/502610682)
-- [Type Hints 入门教程,让代码更加规范整洁](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/519335398)
-- [手把手教你如何高效地在 MMCV 中贡献算子](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/464492627)
-- [OpenMMLab 支持 IPU 训练芯片](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/517527926)
-- [基于 MMCV 走上开源大佬之路?](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/391144979)
diff --git a/docs/zh_cn/get_started/build.md b/docs/zh_cn/get_started/build.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 95f611bc2e0e616f83de448567d404c2e420981a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/zh_cn/get_started/build.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,300 +0,0 @@
-## 从源码编译 MMCV
-
-### 编译 mmcv
-
-在编译 mmcv 之前,请确保 PyTorch 已经成功安装在环境中,可以参考 [PyTorch 官方安装文档](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally)。可使用以下命令验证
-
-```bash
-python -c 'import torch;print(torch.__version__)'
-```
-
-:::{note}
-
-- 如果克隆代码仓库的速度过慢,可以使用以下命令克隆(注意:gitee 的 mmcv 不一定和 github 的保持一致,因为每天只同步一次)
-
-```bash
-git clone https://gitee.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
-```
-
-- 如果打算使用 `opencv-python-headless` 而不是 `opencv-python`,例如在一个很小的容器环境或者没有图形用户界面的服务器中,你可以先安装 `opencv-python-headless`,这样在安装 mmcv 依赖的过程中会跳过 `opencv-python`。
-
-- 如果编译过程安装依赖库的时间过长,可以[设置 pypi 源](https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/help/pypi/)
-
-```bash
-pip config set global.index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
-```
-
-:::
-
-#### 在 Linux 上编译 mmcv
-
-| TODO: 视频教程
-
-1. 克隆代码仓库
-
- ```bash
- git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- cd mmcv
- ```
-
-2. 安装 `ninja` 和 `psutil` 以加快编译速度
-
- ```bash
- pip install -r requirements/optional.txt
- ```
-
-3. 检查 nvcc 的版本(要求大于等于 9.2,如果没有 GPU,可以跳过)
-
- ```bash
- nvcc --version
- ```
-
- 上述命令如果输出以下信息,表示 nvcc 的设置没有问题,否则需要设置 CUDA_HOME
-
- ```
- nvcc: NVIDIA (R) Cuda compiler driver
- Copyright (c) 2005-2020 NVIDIA Corporation
- Built on Mon_Nov_30_19:08:53_PST_2020
- Cuda compilation tools, release 11.2, V11.2.67
- Build cuda_11.2.r11.2/compiler.29373293_0
- ```
-
- :::{note}
- 如果想要支持 ROCm,可以参考 [AMD ROCm](https://rocmdocs.amd.com/en/latest/Installation_Guide/Installation-Guide.html) 安装 ROCm。
- :::
-
-4. 检查 gcc 的版本(要求大于等于**5.4**)
-
- ```bash
- gcc --version
- ```
-
-5. 开始编译(预估耗时 10 分钟)
-
- ```bash
- pip install -e . -v
- ```
-
-6. 验证安装
-
- ```bash
- python .dev_scripts/check_installation.py
- ```
-
- 如果上述命令没有报错,说明安装成功。如有报错,请查看[问题解决页面](../faq.html)是否已经有解决方案。
-
- 如果没有找到解决方案,欢迎提 [issue](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues)。
-
-#### 在 macOS 上编译 mmcv
-
-| TODO: 视频教程
-
-```{note}
-如果你使用的是搭载 apple silicon 的 mac 设备,请安装 PyTorch 1.13+ 的版本,否则会遇到 [issues#2218](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues/2218) 中的问题。
-```
-
-1. 克隆代码仓库
-
- ```bash
- git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- cd mmcv
- ```
-
-2. 安装 `ninja` 和 `psutil` 以加快编译速度
-
- ```bash
- pip install -r requirements/optional.txt
- ```
-
-3. 开始编译
-
- ```bash
- pip install -e .
- ```
-
-4. 验证安装
-
- ```bash
- python .dev_scripts/check_installation.py
- ```
-
- 如果上述命令没有报错,说明安装成功。如有报错,请查看[问题解决页面](../faq.md)是否已经有解决方案。
-
- 如果没有找到解决方案,欢迎提 [issue](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues)。
-
-#### 在 Windows 上编译 mmcv
-
-| TODO: 视频教程
-
-在 Windows 上编译 mmcv 比 Linux 复杂,本节将一步步介绍如何在 Windows 上编译 mmcv。
-
-##### 依赖项
-
-请先安装以下的依赖项:
-
-- [Git](https://git-scm.com/download/win):安装期间,请选择 **add git to Path**
-- [Visual Studio Community 2019](https://visualstudio.microsoft.com):用于编译 C++ 和 CUDA 代码
-- [Miniconda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html):包管理工具
-- [CUDA 10.2](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-10.2-download-archive):如果只需要 CPU 版本可以不安装 CUDA,安装 CUDA 时,可根据需要进行自定义安装。如果已经安装新版本的显卡驱动,建议取消驱动程序的安装
-
-```{note}
-如果不清楚如何安装以上依赖,请参考[Windows 环境从零安装 mmcv](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/434491590)。
-另外,你需要知道如何在 Windows 上设置变量环境,尤其是 "PATH" 的设置,以下安装过程都会用到。
-```
-
-##### 通用步骤
-
-1. 从 Windows 菜单启动 Anaconda 命令行
-
- 如 Miniconda 安装程序建议,不要使用原始的 `cmd.exe` 或是 `powershell.exe`。命令行有两个版本,一个基于 PowerShell,一个基于传统的 `cmd.exe`。请注意以下说明都是使用的基于 PowerShell
-
-2. 创建一个新的 Conda 环境
-
- ```powershell
- (base) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda create --name mmcv python=3.7
- (base) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda activate mmcv # 确保做任何操作前先激活环境
- ```
-
-3. 安装 PyTorch 时,可以根据需要安装支持 CUDA 或不支持 CUDA 的版本
-
- ```powershell
- # CUDA version
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda install pytorch torchvision cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
- # CPU version
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda install install pytorch torchvision cpuonly -c pytorch
- ```
-
-4. 克隆代码仓库
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> cd mmcv
- ```
-
-5. 安装 `ninja` 和 `psutil` 以加快编译速度
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> pip install -r requirements/optional.txt
- ```
-
-6. 设置 MSVC 编译器
-
- 设置环境变量。添加 `C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Community\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.27.29110\bin\Hostx86\x64` 到 `PATH`,则 `cl.exe` 可以在命令行中运行,如下所示。
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> cl
- Microsoft (R) C/C++ Optimizing Compiler Version 19.27.29111 for x64
- Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
-
- usage: cl [ option... ] filename... [ / link linkoption... ]
- ```
-
- 为了兼容性,我们使用 x86-hosted 以及 x64-targeted 版本,即路径中的 `Hostx86\x64` 。
-
- 因为 PyTorch 将解析 `cl.exe` 的输出以检查其版本,只有 utf-8 将会被识别,你可能需要将系统语言更改为英语。控制面板 -> 地区-> 管理-> 非 Unicode 来进行语言转换。
-
-##### 编译与安装 mmcv
-
-mmcv 有两个版本:
-
-- 只包含 CPU 算子的版本
-
- 编译 CPU 算子,但只有 x86 将会被编译,并且编译版本只能在 CPU only 情况下运行
-
-- 既包含 CPU 算子,又包含 CUDA 算子的版本
-
- 同时编译 CPU 和 CUDA 算子,`ops` 模块的 x86 与 CUDA 的代码都可以被编译。同时编译的版本可以在 CUDA 上调用 GPU
-
-###### CPU 版本
-
-编译安装
-
-```powershell
-(mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python setup.py build_ext # 如果成功, cl 将被启动用于编译算子
-(mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python setup.py develop # 安装
-```
-
-###### GPU 版本
-
-1. 检查 `CUDA_PATH` 或者 `CUDA_HOME` 环境变量已经存在在 `envs` 之中
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> ls env:
-
- Name Value
- ---- -----
- CUDA_PATH C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2
- CUDA_PATH_V10_1 C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.1
- CUDA_PATH_V10_2 C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2
- ```
-
- 如果没有,你可以按照下面的步骤设置
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> $env:CUDA_HOME = "C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2"
- # 或者
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> $env:CUDA_HOME = $env:CUDA_PATH_V10_2 # CUDA_PATH_V10_2 已经在环境变量中
- ```
-
-2. 设置 CUDA 的目标架构
-
- ```powershell
- # 这里需要改成你的显卡对应的目标架构
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> $env:TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST="7.5"
- ```
-
- :::{note}
- 可以点击 [cuda-gpus](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-gpus) 查看 GPU 的计算能力,也可以通过 CUDA 目录下的 deviceQuery.exe 工具查看
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> &"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2\extras\demo_suite\deviceQuery.exe"
- Device 0: "NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1660 SUPER"
- CUDA Driver Version / Runtime Version 11.7 / 11.1
- CUDA Capability Major/Minor version number: 7.5
- ```
-
- 上面的 7.5 表示目标架构。注意:需把上面命令的 v10.2 换成你的 CUDA 版本。
- :::
-
-3. 编译安装
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python setup.py build_ext # 如果成功, cl 将被启动用于编译算子
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python setup.py develop # 安装
- ```
-
- ```{note}
- 如果你的 PyTorch 版本是 1.6.0,你可能会遇到一些 [issue](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/42467) 提到的错误,你可以参考这个 [pull request](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/43380/files) 修改本地环境的 PyTorch 源代码
- ```
-
-##### 验证安装
-
-```powershell
-(mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python .dev_scripts/check_installation.py
-```
-
-如果上述命令没有报错,说明安装成功。如有报错,请查看[问题解决页面](../faq.md)是否已经有解决方案。
-如果没有找到解决方案,欢迎提 [issue](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues)。
-
-### 编译 mmcv-lite
-
-如果你需要使用和 PyTorch 相关的模块,请确保 PyTorch 已经成功安装在环境中,可以参考 [PyTorch 官方安装文档](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally)。
-
-1. 克隆代码仓库
-
- ```bash
- git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- cd mmcv
- ```
-
-2. 开始编译
-
- ```bash
- MMCV_WITH_OPS=0 pip install -e . -v
- ```
-
-3. 验证安装
-
- ```bash
- python -c 'import mmcv;print(mmcv.__version__)'
- ```
diff --git a/docs/zh_cn/get_started/installation.md b/docs/zh_cn/get_started/installation.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 54cdbd9f3ab9c2694e78013f5b3a5841730c54a5..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/zh_cn/get_started/installation.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,369 +0,0 @@
-## 安装 MMCV
-
-MMCV 有两个版本:
-
-- **mmcv**: 完整版,包含所有的特性以及丰富的开箱即用的 CPU 和 CUDA 算子。注意,完整版本可能需要更长时间来编译。
-- **mmcv-lite**: 精简版,不包含 CPU 和 CUDA 算子但包含其余所有特性和功能,类似 MMCV 1.0 之前的版本。如果你不需要使用算子的话,精简版可以作为一个考虑选项。
-
-```{warning}
-请不要在同一个环境中安装两个版本,否则可能会遇到类似 `ModuleNotFound` 的错误。在安装一个版本之前,需要先卸载另一个。`如果 CUDA 可用,强烈推荐安装 mmcv`。
-```
-
-### 安装 mmcv
-
-在安装 mmcv 之前,请确保 PyTorch 已经成功安装在环境中,可以参考 [PyTorch 官方安装文档](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally)。可使用以下命令验证
-
-```bash
-python -c 'import torch;print(torch.__version__)'
-```
-
-如果输出版本信息,则表示 PyTorch 已安装。
-
-#### 使用 mim 安装(推荐)
-
-[mim](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mim) 是 OpenMMLab 项目的包管理工具,使用它可以很方便地安装 mmcv。
-
-```bash
-pip install -U openmim
-mim install "mmcv>=2.0.0rc1"
-```
-
-如果发现上述的安装命令没有使用预编译包(以 `.whl` 结尾)而是使用源码包(以 `.tar.gz` 结尾)安装,则有可能是我们没有提供和当前环境的 PyTorch 版本、CUDA 版本相匹配的 mmcv 预编译包,此时,你可以[源码安装 mmcv](build.md)。
-
-
-
-所有 reviewer 同意合入 PR 后,我们会尽快将 PR 合并到主分支。
-
-#### 7. 解决冲突
-
-随着时间的推移,我们的代码库会不断更新,这时候,如果你的 PR 与主分支存在冲突,你需要解决冲突,解决冲突的方式有两种:
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git rebase upstream/master
-```
-
-或者
-
-```shell
-git fetch --all --prune
-git merge upstream/master
-```
-
-如果你非常善于处理冲突,那么可以使用 rebase 的方式来解决冲突,因为这能够保证你的 commit log 的整洁。如果你不太熟悉 `rebase` 的使用,那么可以使用 `merge` 的方式来解决冲突。
-
-### 指引
-
-#### 单元测试
-
-如果你无法正常执行部分模块的单元测试,例如 [video](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/tree/master/mmcv/video) 模块,可能是你的当前环境没有安装以下依赖
-
-```shell
-# Linux
-sudo apt-get update -y
-sudo apt-get install -y libturbojpeg
-sudo apt-get install -y ffmpeg
-
-# Windows
-conda install ffmpeg
-```
-
-在提交修复代码错误或新增特性的拉取请求时,我们应该尽可能的让单元测试覆盖所有提交的代码,计算单元测试覆盖率的方法如下
-
-```shell
-python -m coverage run -m pytest /path/to/test_file
-python -m coverage html
-# check file in htmlcov/index.html
-```
-
-#### 文档渲染
-
-在提交修复代码错误或新增特性的拉取请求时,可能会需要修改/新增模块的 docstring。我们需要确认渲染后的文档样式是正确的。
-本地生成渲染后的文档的方法如下
-
-```shell
-pip install -r requirements/docs.txt
-cd docs/zh_cn/
-# or docs/en
-make html
-# check file in ./docs/zh_cn/_build/html/index.html
-```
-
-### 代码风格
-
-#### Python
-
-[PEP8](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/) 作为 OpenMMLab 算法库首选的代码规范,我们使用以下工具检查和格式化代码
-
-- [flake8](https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8): Python 官方发布的代码规范检查工具,是多个检查工具的封装
-- [isort](https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort): 自动调整模块导入顺序的工具
-- [yapf](https://github.com/google/yapf): Google 发布的代码规范检查工具
-- [codespell](https://github.com/codespell-project/codespell): 检查单词拼写是否有误
-- [mdformat](https://github.com/executablebooks/mdformat): 检查 markdown 文件的工具
-- [docformatter](https://github.com/myint/docformatter): 格式化 docstring 的工具
-
-yapf 和 isort 的配置可以在 [setup.cfg](./setup.cfg) 找到
-
-通过配置 [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com/) ,我们可以在提交代码时自动检查和格式化 `flake8`、`yapf`、`isort`、`trailing whitespaces`、`markdown files`,
-修复 `end-of-files`、`double-quoted-strings`、`python-encoding-pragma`、`mixed-line-ending`,调整 `requirments.txt` 的包顺序。
-pre-commit 钩子的配置可以在 [.pre-commit-config](./.pre-commit-config.yaml) 找到。
-
-pre-commit 具体的安装使用方式见[拉取请求](#2-配置-pre-commit)。
-
-更具体的规范请参考 [OpenMMLab 代码规范](code_style.md)。
-
-#### C++ and CUDA
-
-C++ 和 CUDA 的代码规范遵从 [Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html)
-
-### 拉取请求规范
-
-1. 使用 [pre-commit hook](https://pre-commit.com),尽量减少代码风格相关问题
-
-2. 一个`拉取请求`对应一个短期分支
-
-3. 粒度要细,一个`拉取请求`只做一件事情,避免超大的`拉取请求`
-
- - Bad:实现 Faster R-CNN
- - Acceptable:给 Faster R-CNN 添加一个 box head
- - Good:给 box head 增加一个参数来支持自定义的 conv 层数
-
-4. 每次 Commit 时需要提供清晰且有意义 commit 信息
-
-5. 提供清晰且有意义的`拉取请求`描述
-
- - 标题写明白任务名称,一般格式:\[Prefix\] Short description of the pull request (Suffix)
- - prefix: 新增功能 \[Feature\], 修 bug \[Fix\], 文档相关 \[Docs\], 开发中 \[WIP\] (暂时不会被review)
- - 描述里介绍`拉取请求`的主要修改内容,结果,以及对其他部分的影响, 参考`拉取请求`模板
- - 关联相关的`议题` (issue) 和其他`拉取请求`
-
-6. 如果引入了其他三方库,或借鉴了三方库的代码,请确认他们的许可证和 mmcv 兼容,并在借鉴的代码上补充 `This code is inspired from http://`
diff --git a/docs/zh_cn/community/pr.md b/docs/zh_cn/community/pr.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 427fdf9e4965e404970c761676e7edd29e7b2e56..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/zh_cn/community/pr.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
-## 拉取请求
-
-本文档的内容已迁移到[贡献指南](contributing.md)。
diff --git a/docs/zh_cn/docutils.conf b/docs/zh_cn/docutils.conf
deleted file mode 100644
index 0c00c84688701117f231fd0c8ec295fb747b7d8f..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/zh_cn/docutils.conf
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,2 +0,0 @@
-[html writers]
-table_style: colwidths-auto
diff --git a/docs/zh_cn/faq.md b/docs/zh_cn/faq.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6cfb100c631b101fa0cff0650105a3cc7d735e7b..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/zh_cn/faq.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,91 +0,0 @@
-## 常见问题
-
-在这里我们列出了用户经常遇到的问题以及对应的解决方法。如果您遇到了其他常见的问题,并且知道可以帮到大家的解决办法,
-欢迎随时丰富这个列表。
-
-### 安装问题
-
-- KeyError: "xxx: 'yyy is not in the zzz registry'"
-
- 只有模块所在的文件被导入时,注册机制才会被触发,所以您需要在某处导入该文件,更多详情请查看 [KeyError: "MaskRCNN: 'RefineRoIHead is not in the models registry'"](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/issues/5974)。
-
-- "No module named 'mmcv.ops'"; "No module named 'mmcv.\_ext'"
-
- 1. 使用 `pip uninstall mmcv` 卸载您环境中的 mmcv
- 2. 参考 [installation instruction](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get_started/installation.html) 或者 [Build MMCV from source](https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get_started/build.html) 安装 mmcv-full
-
-- "invalid device function" 或者 "no kernel image is available for execution"
-
- 1. 检查 GPU 的 CUDA 计算能力
- 2. 运行 `python mmdet/utils/collect_env.py` 来检查 PyTorch、torchvision 和 MMCV 是否是针对正确的 GPU 架构构建的,您可能需要去设置 `TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST` 来重新安装 MMCV。兼容性问题可能会出现在使用旧版的 GPUs,如:colab 上的 Tesla K80 (3.7)
- 3. 检查运行环境是否和 mmcv/mmdet 编译时的环境相同。例如,您可能使用 CUDA 10.0 编译 mmcv,但在 CUDA 9.0 的环境中运行它
-
-- "undefined symbol" 或者 "cannot open xxx.so"
-
- 1. 如果符号和 CUDA/C++ 相关(例如:libcudart.so 或者 GLIBCXX),请检查 CUDA/GCC 运行时的版本是否和编译 mmcv 的一致
- 2. 如果符号和 PyTorch 相关(例如:符号包含 caffe、aten 和 TH),请检查 PyTorch 运行时的版本是否和编译 mmcv 的一致
- 3. 运行 `python mmdet/utils/collect_env.py` 以检查 PyTorch、torchvision 和 MMCV 构建和运行的环境是否相同
-
-- "RuntimeError: CUDA error: invalid configuration argument"
-
- 这个错误可能是由于您的 GPU 性能不佳造成的。尝试降低 [THREADS_PER_BLOCK](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/blob/cac22f8cf5a904477e3b5461b1cc36856c2793da/mmcv/ops/csrc/common_cuda_helper.hpp#L10)
- 的值并重新编译 mmcv。
-
-- "RuntimeError: nms is not compiled with GPU support"
-
- 这个错误是由于您的 CUDA 环境没有正确安装。
- 您可以尝试重新安装您的 CUDA 环境,然后删除 mmcv/build 文件夹并重新编译 mmcv。
-
-- "Segmentation fault"
-
- 1. 检查 GCC 的版本,通常是因为 PyTorch 版本与 GCC 版本不匹配 (例如 GCC \< 4.9 ),我们推荐用户使用 GCC 5.4,我们也不推荐使用 GCC 5.5, 因为有反馈 GCC 5.5 会导致 "segmentation fault" 并且切换到 GCC 5.4 就可以解决问题
- 2. 检查是否正确安装 CUDA 版本的 PyTorc。输入以下命令并检查是否返回 True
- ```shell
- python -c 'import torch; print(torch.cuda.is_available())'
- ```
- 3. 如果 `torch` 安装成功,那么检查 MMCV 是否安装成功。输入以下命令,如果没有报错说明 mmcv-full 安装成。
- ```shell
- python -c 'import mmcv; import mmcv.ops'
- ```
- 4. 如果 MMCV 与 PyTorch 都安装成功了,则可以使用 `ipdb` 设置断点或者使用 `print` 函数,分析是哪一部分的代码导致了 `segmentation fault`
-
-- "libtorch_cuda_cu.so: cannot open shared object file"
-
- `mmcv-full` 依赖 `libtorch_cuda_cu.so` 文件,但程序运行时没能找到该文件。我们可以检查该文件是否存在 `~/miniconda3/envs/{environment-name}/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/lib` 也可以尝试重装 PyTorch。
-
-- "fatal error C1189: #error: -- unsupported Microsoft Visual Studio version!"
-
- 如果您在 Windows 上编译 mmcv-full 并且 CUDA 的版本是 9.2,您很可能会遇到这个问题 `"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v9.2\include\crt/host_config.h(133): fatal error C1189: #error: -- unsupported Microsoft Visual Studio version! Only the versions 2012, 2013, 2015 and 2017 are supported!"`,您可以尝试使用低版本的 Microsoft Visual Studio,例如 vs2017。
-
-- "error: member "torch::jit::detail::ModulePolicy::all_slots" may not be initialized"
-
- 如果您在 Windows 上编译 mmcv-full 并且 PyTorch 的版本是 1.5.0,您很可能会遇到这个问题 `- torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h(474): error: member "torch::jit::detail::ModulePolicy::all_slots" may not be initialized`。解决这个问题的方法是将 `torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h` 文件中所有 `static constexpr bool all_slots = false;` 替换为 `static bool all_slots = false;`。更多细节可以查看 [member "torch::jit::detail::AttributePolicy::all_slots" may not be initialized](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/39394)。
-
-- "error: a member with an in-class initializer must be const"
-
- 如果您在 Windows 上编译 mmcv-full 并且 PyTorch 的版本是 1.6.0,您很可能会遇到这个问题 `"- torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h(483): error: a member with an in-class initializer must be const"`. 解决这个问题的方法是将 `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h` 文件中的所有 `CONSTEXPR_EXCEPT_WIN_CUDA ` 替换为 `const`。更多细节可以查看 [Ninja: build stopped: subcommand failed](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues/575)。
-
-- "error: member "torch::jit::ProfileOptionalOp::Kind" may not be initialized"
-
- 如果您在 Windows 上编译 mmcv-full 并且 PyTorch 的版本是 1.7.0,您很可能会遇到这个问题 `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/ir/ir.h(1347): error: member "torch::jit::ProfileOptionalOp::Kind" may not be initialized`. 解决这个问题的方法是修改 PyTorch 中的几个文件:
-
- - 删除 `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/ir/ir.h` 文件中的 `static constexpr Symbol Kind = ::c10::prim::profile;` 和 `tatic constexpr Symbol Kind = ::c10::prim::profile_optional;`
- - 将 `torch\include\pybind11\cast.h` 文件中的 `explicit operator type&() { return *(this->value); }` 替换为 `explicit operator type&() { return *((type*)this->value); }`
- - 将 `torch/include\torch/csrc/jit/api/module.h` 文件中的 所有 `CONSTEXPR_EXCEPT_WIN_CUDA` 替换为 `const`
-
- 更多细节可以查看 [Ensure default extra_compile_args](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/45956)。
-
-- MMCV 和 MMDetection 的兼容性问题;"ConvWS is already registered in conv layer"
-
- 请参考 [installation instruction](https://mmdetection.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get_started.html#installation) 为您的 MMDetection 版本安装正确版本的 MMCV。
-
-### 使用问题
-
-- "RuntimeError: Expected to have finished reduction in the prior iteration before starting a new one"
-
- 1. 这个错误是因为有些参数没有参与 loss 的计算,可能是代码中存在多个分支,导致有些分支没有参与 loss 的计算。更多细节见 [Expected to have finished reduction in the prior iteration before starting a new one](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/55582)。
- 2. 你可以设置 DDP 中的 `find_unused_parameters` 为 `True`,或者手动查找哪些参数没有用到。
-
-- "RuntimeError: Trying to backward through the graph a second time"
-
- 不能同时设置 `GradientCumulativeOptimizerHook` 和 `OptimizerHook`,这会导致 `loss.backward()` 被调用两次,于是程序抛出 `RuntimeError`。我们只需设置其中的一个。更多细节见 [Trying to backward through the graph a second time](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues/1379)。
diff --git a/docs/zh_cn/get_started/article.md b/docs/zh_cn/get_started/article.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 96768502cedb607d58ea2dc8d17b3dd8b9af20b2..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/zh_cn/get_started/article.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-## 解读文章汇总
-
-这篇文章汇总了 [OpenMMLab](https://www.zhihu.com/people/openmmlab) 解读的部分文章(更多文章和视频见 [OpenMMLabCourse](https://github.com/open-mmlab/OpenMMLabCourse)),如果您有推荐的文章(不一定是 OpenMMLab 发布的文章,可以是自己写的文章),非常欢迎提 [Pull Request](http://127.0.0.1:5501/mmcv/docs/zh_cn/_build/html/community/pr.html) 添加到这里。
-
-### MMCV 解读文章
-
-#### 框架解读
-
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(一):整体概述](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/336081587)
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(二):FileHandler](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/336097883)
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(三): FileClient](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/339190576)
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(四): Config](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/346203167)
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(五): Registry](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/355271993)
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(六): Hook](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/355272220)
-- [MMCV 核心组件分析(七): Runner](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/355272459)
-- [MMCV Hook 食用指南](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/448600739)
-- [PyTorch & MMCV Dispatcher 机制解析](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/451671838)
-
-#### 工具解读
-
-- [训练可视化工具哪款是你的菜?MMCV一行代码随你挑](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/387078211)
-
-#### 安装指南
-
-- [久等了!Windows 平台 MMCV 的预编译包终于来了!](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/441653536)
-- [Windows 环境从零安装 mmcv-full](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/434491590)
-
-#### 知乎问答
-
-- [深度学习科研,如何高效进行代码和实验管理?](https://www.zhihu.com/question/269707221/answer/2480772257)
-- [深度学习方面的科研工作中的实验代码有什么规范和写作技巧?如何妥善管理实验数据?](https://www.zhihu.com/question/268193800/answer/2586000037)
-
-### 下游算法库解读文章
-
-- [MMDetection](https://mmdetection.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/article.html)
-
-### PyTorch 解读文章
-
-- [PyTorch1.11 亮点一览:TorchData、functorch、DDP 静态图](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/486222256)
-- [PyTorch1.12 亮点一览:DataPipe + TorchArrow 新的数据加载与处理范式](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/537868554)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 nn.Module:核心网络模块接口详解](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/340453841)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 torch.autograd:梯度计算详解](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/321449610)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 torch.utils.data:解析数据处理全流程](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/337850513)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 torch.optim:优化算法接口详解](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/346205754)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 DP & DDP:模型并行和分布式训练解析](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/343951042)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 BN & SyncBN:BN 与 多卡同步 BN 详解](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/337732517)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 torch.cuda.amp: 自动混合精度详解](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/348554267)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 cpp_extension:揭秘 C++/CUDA 算子实现和调用全流程](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/348555597)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之即时编译篇](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/361101354)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之分布式训练了解一下?](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/361314953)
-- [PyTorch 源码解读之 torch.serialization & torch.hub](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/364239544)
-
-### 其他
-
-- [困扰我 48 小时的深拷贝,今天终于...](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/470892209)
-- [拿什么拯救我的 4G 显卡](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/430123077)
-- [是谁偷偷动了我的 logger](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/481383590)
-- [三句话,让 logger 言听计从](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/487524917)
-- [Logging 不为人知的二三事](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/502610682)
-- [Type Hints 入门教程,让代码更加规范整洁](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/519335398)
-- [手把手教你如何高效地在 MMCV 中贡献算子](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/464492627)
-- [OpenMMLab 支持 IPU 训练芯片](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/517527926)
-- [基于 MMCV 走上开源大佬之路?](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/391144979)
diff --git a/docs/zh_cn/get_started/build.md b/docs/zh_cn/get_started/build.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 95f611bc2e0e616f83de448567d404c2e420981a..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/zh_cn/get_started/build.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,300 +0,0 @@
-## 从源码编译 MMCV
-
-### 编译 mmcv
-
-在编译 mmcv 之前,请确保 PyTorch 已经成功安装在环境中,可以参考 [PyTorch 官方安装文档](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally)。可使用以下命令验证
-
-```bash
-python -c 'import torch;print(torch.__version__)'
-```
-
-:::{note}
-
-- 如果克隆代码仓库的速度过慢,可以使用以下命令克隆(注意:gitee 的 mmcv 不一定和 github 的保持一致,因为每天只同步一次)
-
-```bash
-git clone https://gitee.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
-```
-
-- 如果打算使用 `opencv-python-headless` 而不是 `opencv-python`,例如在一个很小的容器环境或者没有图形用户界面的服务器中,你可以先安装 `opencv-python-headless`,这样在安装 mmcv 依赖的过程中会跳过 `opencv-python`。
-
-- 如果编译过程安装依赖库的时间过长,可以[设置 pypi 源](https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/help/pypi/)
-
-```bash
-pip config set global.index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
-```
-
-:::
-
-#### 在 Linux 上编译 mmcv
-
-| TODO: 视频教程
-
-1. 克隆代码仓库
-
- ```bash
- git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- cd mmcv
- ```
-
-2. 安装 `ninja` 和 `psutil` 以加快编译速度
-
- ```bash
- pip install -r requirements/optional.txt
- ```
-
-3. 检查 nvcc 的版本(要求大于等于 9.2,如果没有 GPU,可以跳过)
-
- ```bash
- nvcc --version
- ```
-
- 上述命令如果输出以下信息,表示 nvcc 的设置没有问题,否则需要设置 CUDA_HOME
-
- ```
- nvcc: NVIDIA (R) Cuda compiler driver
- Copyright (c) 2005-2020 NVIDIA Corporation
- Built on Mon_Nov_30_19:08:53_PST_2020
- Cuda compilation tools, release 11.2, V11.2.67
- Build cuda_11.2.r11.2/compiler.29373293_0
- ```
-
- :::{note}
- 如果想要支持 ROCm,可以参考 [AMD ROCm](https://rocmdocs.amd.com/en/latest/Installation_Guide/Installation-Guide.html) 安装 ROCm。
- :::
-
-4. 检查 gcc 的版本(要求大于等于**5.4**)
-
- ```bash
- gcc --version
- ```
-
-5. 开始编译(预估耗时 10 分钟)
-
- ```bash
- pip install -e . -v
- ```
-
-6. 验证安装
-
- ```bash
- python .dev_scripts/check_installation.py
- ```
-
- 如果上述命令没有报错,说明安装成功。如有报错,请查看[问题解决页面](../faq.html)是否已经有解决方案。
-
- 如果没有找到解决方案,欢迎提 [issue](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues)。
-
-#### 在 macOS 上编译 mmcv
-
-| TODO: 视频教程
-
-```{note}
-如果你使用的是搭载 apple silicon 的 mac 设备,请安装 PyTorch 1.13+ 的版本,否则会遇到 [issues#2218](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues/2218) 中的问题。
-```
-
-1. 克隆代码仓库
-
- ```bash
- git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- cd mmcv
- ```
-
-2. 安装 `ninja` 和 `psutil` 以加快编译速度
-
- ```bash
- pip install -r requirements/optional.txt
- ```
-
-3. 开始编译
-
- ```bash
- pip install -e .
- ```
-
-4. 验证安装
-
- ```bash
- python .dev_scripts/check_installation.py
- ```
-
- 如果上述命令没有报错,说明安装成功。如有报错,请查看[问题解决页面](../faq.md)是否已经有解决方案。
-
- 如果没有找到解决方案,欢迎提 [issue](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues)。
-
-#### 在 Windows 上编译 mmcv
-
-| TODO: 视频教程
-
-在 Windows 上编译 mmcv 比 Linux 复杂,本节将一步步介绍如何在 Windows 上编译 mmcv。
-
-##### 依赖项
-
-请先安装以下的依赖项:
-
-- [Git](https://git-scm.com/download/win):安装期间,请选择 **add git to Path**
-- [Visual Studio Community 2019](https://visualstudio.microsoft.com):用于编译 C++ 和 CUDA 代码
-- [Miniconda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html):包管理工具
-- [CUDA 10.2](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-10.2-download-archive):如果只需要 CPU 版本可以不安装 CUDA,安装 CUDA 时,可根据需要进行自定义安装。如果已经安装新版本的显卡驱动,建议取消驱动程序的安装
-
-```{note}
-如果不清楚如何安装以上依赖,请参考[Windows 环境从零安装 mmcv](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/434491590)。
-另外,你需要知道如何在 Windows 上设置变量环境,尤其是 "PATH" 的设置,以下安装过程都会用到。
-```
-
-##### 通用步骤
-
-1. 从 Windows 菜单启动 Anaconda 命令行
-
- 如 Miniconda 安装程序建议,不要使用原始的 `cmd.exe` 或是 `powershell.exe`。命令行有两个版本,一个基于 PowerShell,一个基于传统的 `cmd.exe`。请注意以下说明都是使用的基于 PowerShell
-
-2. 创建一个新的 Conda 环境
-
- ```powershell
- (base) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda create --name mmcv python=3.7
- (base) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda activate mmcv # 确保做任何操作前先激活环境
- ```
-
-3. 安装 PyTorch 时,可以根据需要安装支持 CUDA 或不支持 CUDA 的版本
-
- ```powershell
- # CUDA version
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda install pytorch torchvision cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
- # CPU version
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> conda install install pytorch torchvision cpuonly -c pytorch
- ```
-
-4. 克隆代码仓库
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx> cd mmcv
- ```
-
-5. 安装 `ninja` 和 `psutil` 以加快编译速度
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> pip install -r requirements/optional.txt
- ```
-
-6. 设置 MSVC 编译器
-
- 设置环境变量。添加 `C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Community\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.27.29110\bin\Hostx86\x64` 到 `PATH`,则 `cl.exe` 可以在命令行中运行,如下所示。
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> cl
- Microsoft (R) C/C++ Optimizing Compiler Version 19.27.29111 for x64
- Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
-
- usage: cl [ option... ] filename... [ / link linkoption... ]
- ```
-
- 为了兼容性,我们使用 x86-hosted 以及 x64-targeted 版本,即路径中的 `Hostx86\x64` 。
-
- 因为 PyTorch 将解析 `cl.exe` 的输出以检查其版本,只有 utf-8 将会被识别,你可能需要将系统语言更改为英语。控制面板 -> 地区-> 管理-> 非 Unicode 来进行语言转换。
-
-##### 编译与安装 mmcv
-
-mmcv 有两个版本:
-
-- 只包含 CPU 算子的版本
-
- 编译 CPU 算子,但只有 x86 将会被编译,并且编译版本只能在 CPU only 情况下运行
-
-- 既包含 CPU 算子,又包含 CUDA 算子的版本
-
- 同时编译 CPU 和 CUDA 算子,`ops` 模块的 x86 与 CUDA 的代码都可以被编译。同时编译的版本可以在 CUDA 上调用 GPU
-
-###### CPU 版本
-
-编译安装
-
-```powershell
-(mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python setup.py build_ext # 如果成功, cl 将被启动用于编译算子
-(mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python setup.py develop # 安装
-```
-
-###### GPU 版本
-
-1. 检查 `CUDA_PATH` 或者 `CUDA_HOME` 环境变量已经存在在 `envs` 之中
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> ls env:
-
- Name Value
- ---- -----
- CUDA_PATH C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2
- CUDA_PATH_V10_1 C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.1
- CUDA_PATH_V10_2 C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2
- ```
-
- 如果没有,你可以按照下面的步骤设置
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> $env:CUDA_HOME = "C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2"
- # 或者
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> $env:CUDA_HOME = $env:CUDA_PATH_V10_2 # CUDA_PATH_V10_2 已经在环境变量中
- ```
-
-2. 设置 CUDA 的目标架构
-
- ```powershell
- # 这里需要改成你的显卡对应的目标架构
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> $env:TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST="7.5"
- ```
-
- :::{note}
- 可以点击 [cuda-gpus](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-gpus) 查看 GPU 的计算能力,也可以通过 CUDA 目录下的 deviceQuery.exe 工具查看
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> &"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2\extras\demo_suite\deviceQuery.exe"
- Device 0: "NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1660 SUPER"
- CUDA Driver Version / Runtime Version 11.7 / 11.1
- CUDA Capability Major/Minor version number: 7.5
- ```
-
- 上面的 7.5 表示目标架构。注意:需把上面命令的 v10.2 换成你的 CUDA 版本。
- :::
-
-3. 编译安装
-
- ```powershell
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python setup.py build_ext # 如果成功, cl 将被启动用于编译算子
- (mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python setup.py develop # 安装
- ```
-
- ```{note}
- 如果你的 PyTorch 版本是 1.6.0,你可能会遇到一些 [issue](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/42467) 提到的错误,你可以参考这个 [pull request](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/43380/files) 修改本地环境的 PyTorch 源代码
- ```
-
-##### 验证安装
-
-```powershell
-(mmcv) PS C:\Users\xxx\mmcv> python .dev_scripts/check_installation.py
-```
-
-如果上述命令没有报错,说明安装成功。如有报错,请查看[问题解决页面](../faq.md)是否已经有解决方案。
-如果没有找到解决方案,欢迎提 [issue](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv/issues)。
-
-### 编译 mmcv-lite
-
-如果你需要使用和 PyTorch 相关的模块,请确保 PyTorch 已经成功安装在环境中,可以参考 [PyTorch 官方安装文档](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally)。
-
-1. 克隆代码仓库
-
- ```bash
- git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmcv.git
- cd mmcv
- ```
-
-2. 开始编译
-
- ```bash
- MMCV_WITH_OPS=0 pip install -e . -v
- ```
-
-3. 验证安装
-
- ```bash
- python -c 'import mmcv;print(mmcv.__version__)'
- ```
diff --git a/docs/zh_cn/get_started/installation.md b/docs/zh_cn/get_started/installation.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 54cdbd9f3ab9c2694e78013f5b3a5841730c54a5..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/docs/zh_cn/get_started/installation.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,369 +0,0 @@
-## 安装 MMCV
-
-MMCV 有两个版本:
-
-- **mmcv**: 完整版,包含所有的特性以及丰富的开箱即用的 CPU 和 CUDA 算子。注意,完整版本可能需要更长时间来编译。
-- **mmcv-lite**: 精简版,不包含 CPU 和 CUDA 算子但包含其余所有特性和功能,类似 MMCV 1.0 之前的版本。如果你不需要使用算子的话,精简版可以作为一个考虑选项。
-
-```{warning}
-请不要在同一个环境中安装两个版本,否则可能会遇到类似 `ModuleNotFound` 的错误。在安装一个版本之前,需要先卸载另一个。`如果 CUDA 可用,强烈推荐安装 mmcv`。
-```
-
-### 安装 mmcv
-
-在安装 mmcv 之前,请确保 PyTorch 已经成功安装在环境中,可以参考 [PyTorch 官方安装文档](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally)。可使用以下命令验证
-
-```bash
-python -c 'import torch;print(torch.__version__)'
-```
-
-如果输出版本信息,则表示 PyTorch 已安装。
-
-#### 使用 mim 安装(推荐)
-
-[mim](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mim) 是 OpenMMLab 项目的包管理工具,使用它可以很方便地安装 mmcv。
-
-```bash
-pip install -U openmim
-mim install "mmcv>=2.0.0rc1"
-```
-
-如果发现上述的安装命令没有使用预编译包(以 `.whl` 结尾)而是使用源码包(以 `.tar.gz` 结尾)安装,则有可能是我们没有提供和当前环境的 PyTorch 版本、CUDA 版本相匹配的 mmcv 预编译包,此时,你可以[源码安装 mmcv](build.md)。
-
- -
-| CUDA | +torch 1.10 | +torch 1.9 | +torch 1.8 | +torch 1.7 | +torch 1.6 | +torch 1.5 | +
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11.3 | +安装 |
+ + | + | + | + | + |
| 11.1 | +安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ + | + | + |
| 11.0 | ++ | + | + | 安装 |
+ + | + |
| 10.2 | +安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+
| 10.1 | ++ | + | 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+
| 9.2 | ++ | + | + | 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+
| cpu | +安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+ 安装 |
+