megatron-lm0.3.2 based on dtk-22.10
Showing
examples/sc21/run_table_1.sh
0 → 100644
224 KB
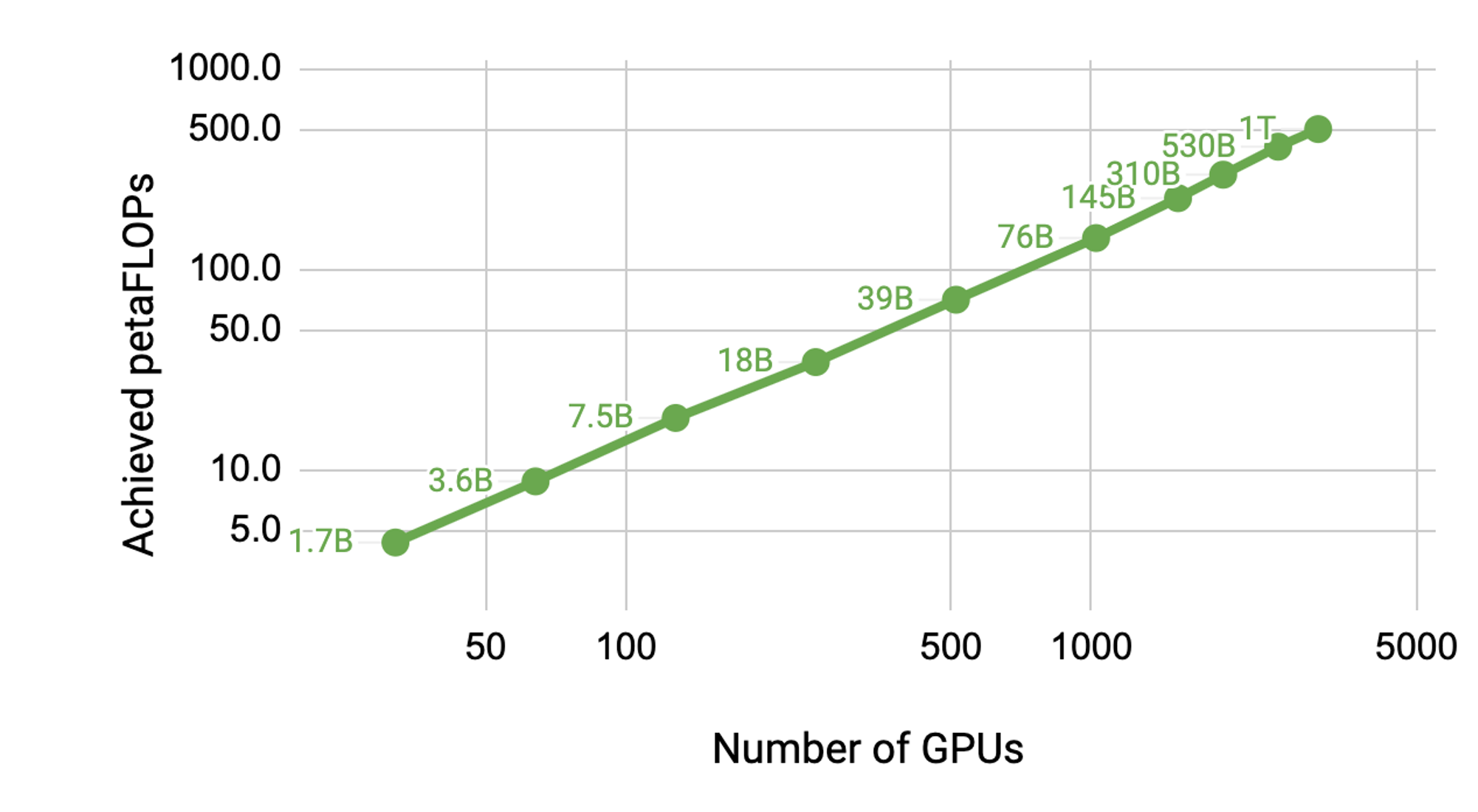
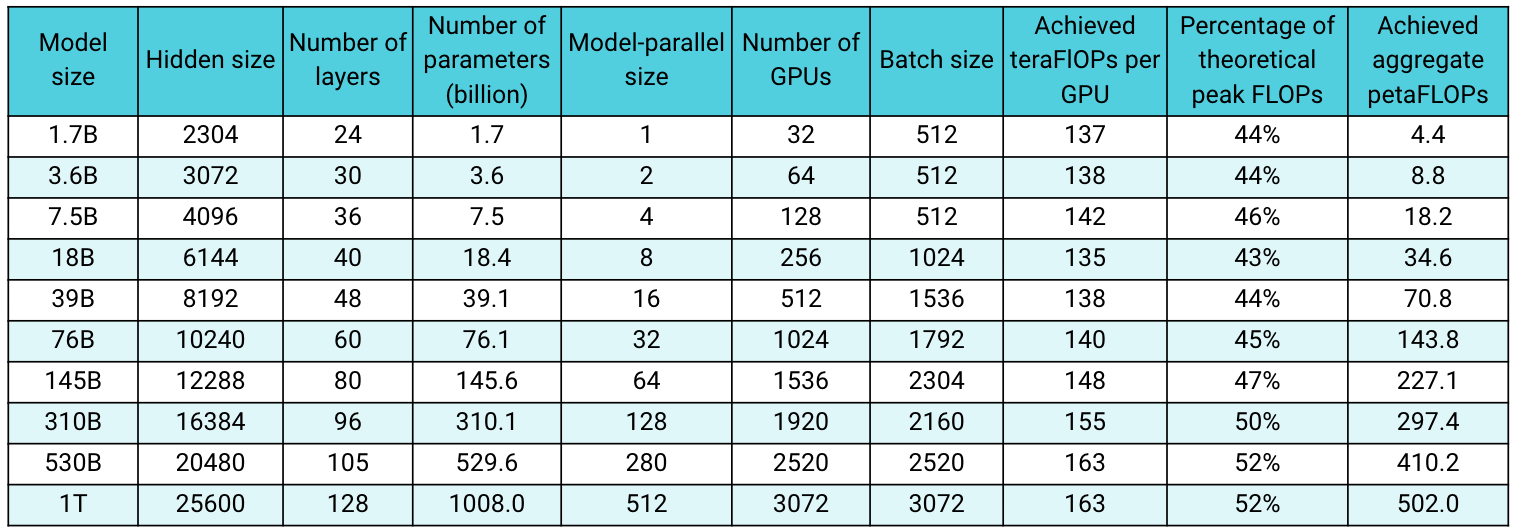
images/cases_april2021.png
0 → 100644
159 KB
megatron/__init__.py
0 → 100644
megatron/arguments.py
0 → 100644
megatron/checkpointing.py
0 → 100644
megatron/data/Makefile
0 → 100644
megatron/data/__init__.py
0 → 100644
megatron/data/autoaugment.py
0 → 100644
megatron/data/gpt_dataset.py
0 → 100644
megatron/data/helpers.cpp
0 → 100644
megatron/data/ict_dataset.py
0 → 100644