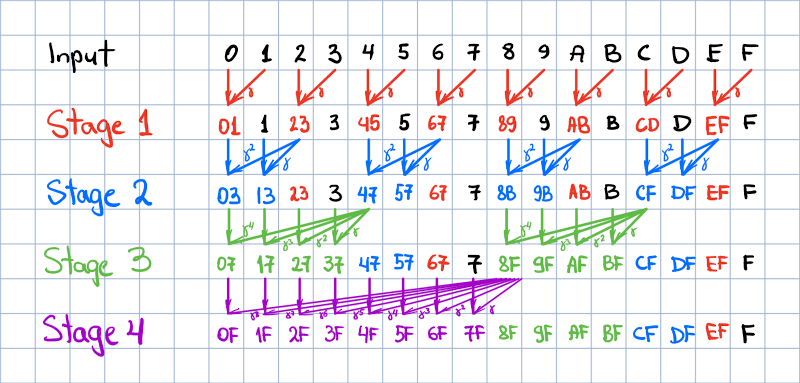
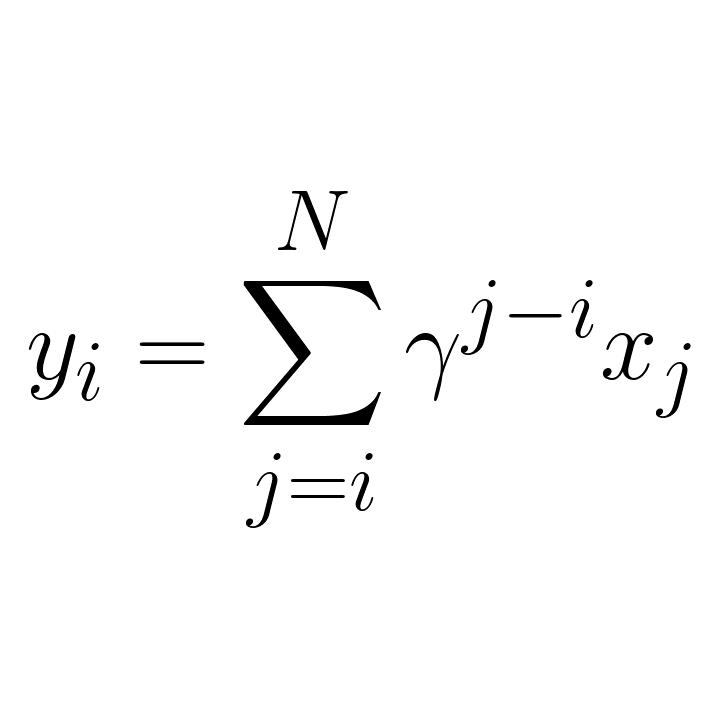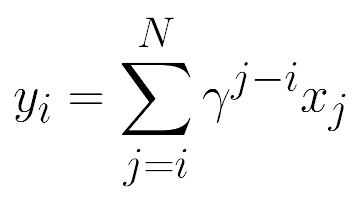Move k2 rnnt_loss here
Showing
CMakeLists.txt
0 → 100644
cmake/Modules/README.md
0 → 100644
cmake/googletest.cmake
0 → 100644
cmake/pybind11.cmake
0 → 100644
cmake/torch.cmake
0 → 100644
149 KB
doc/img/logo.png
deleted
100644 → 0
9.83 KB
6.9 KB
fast_rnnt/CMakeLists.txt
0 → 100644