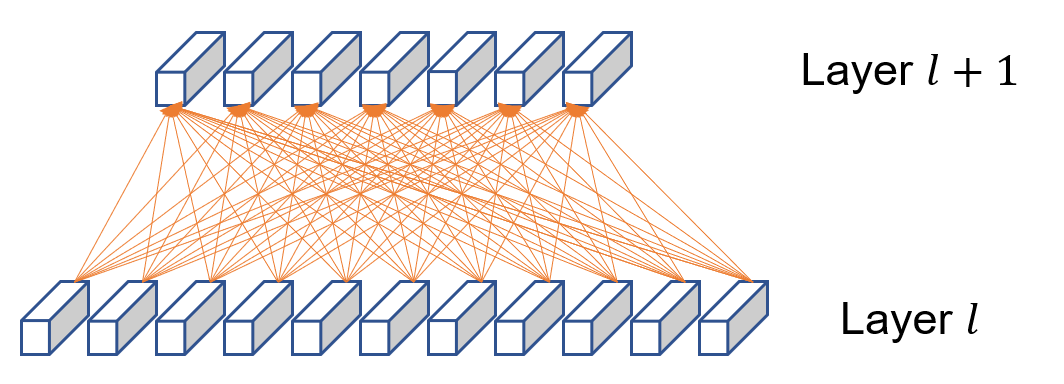
Capsule Network¶
Author: Jinjing Zhou
This tutorial explains how to use DGL library and its language to implement the capsule network proposed by Geoffrey Hinton and his team. The algorithm aims to provide a better alternative to current neural network structures. By using DGL library, users can implement the algorithm in a more intuitive way.
Model Overview¶
Introduction¶
Capsule Network is
What's a capsule?¶
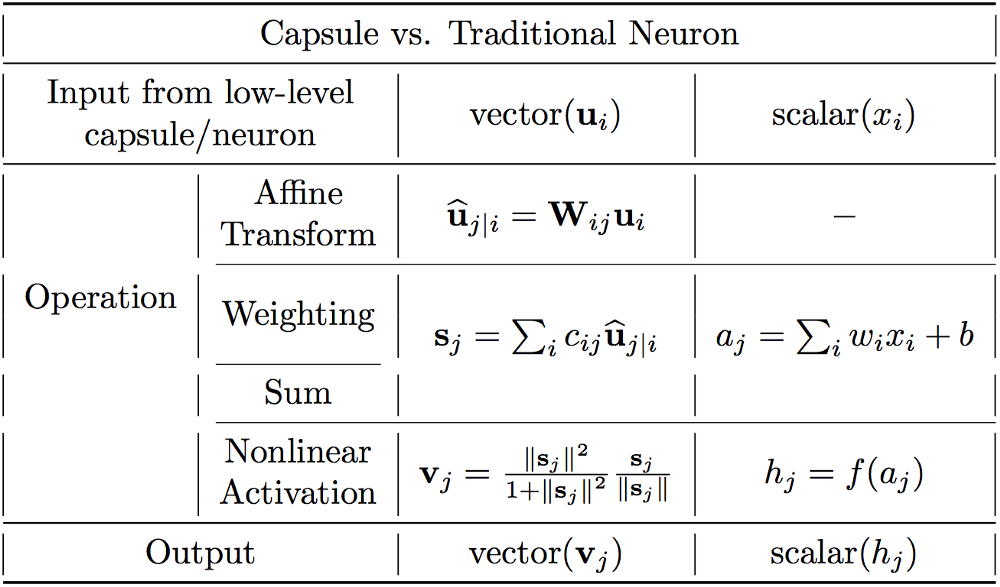
A capsule is a group of neurons whose activity vector represents the instantiation parameters of a specific type of entity such as an object or an object part.
Generally Speaking, the idea of capsule is to encode all the information about the features in a vector form, by substituting scalars in traditional neural network with vectors. And use the norm of the vector to represents the meaning of original scalars.
Dynamic Routing Algorithm¶
def construct_graph(self):
g = dgl.DGLGraph()
g.add_nodes(self.in_channel + self.num_unit)
self.in_channel_nodes = list(range(self.in_channel))
self.capsule_nodes = list(range(self.in_channel, self.in_channel + self.num_unit))
u, v = [], []
for i in self.in_channel_nodes:
for j in self.capsule_nodes:
u.append(i)
v.append(j)
g.add_edges(u, v)
return g
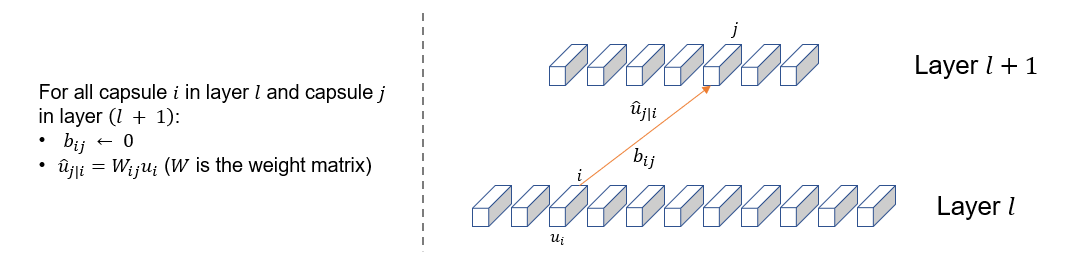
2. Pre-compute $\hat{u}_{j|i}$, initialize $b_{ij}$ and store them as edge attribute¶
x = x.transpose(1, 2)
x = torch.stack([x] * self.num_unit, dim=2).unsqueeze(4)
W = self.weight.expand(self.batch_size, *self.weight.shape)
u_hat = torch.matmul(W, x).permute(1, 2, 0, 3, 4).squeeze().contiguous()
self.g.set_e_repr({'b_ij': edge_features.view(-1)})
self.g.set_e_repr({'u_hat': u_hat.view(-1, self.batch_size, self.unit_size)})
3. Initialize node features¶
node_features = torch.zeros(self.in_channel + self.num_unit, self.batch_size, self.unit_size).to(device)
self.g.set_n_repr({'h': node_features})
4. Write message passing functions¶
@staticmethod
def capsule_msg(src, edge):
return {'b_ij': edge['b_ij'], 'h': src['h'], 'u_hat': edge['u_hat']}
@staticmethod
def capsule_reduce(node, msg):
b_ij_c, u_hat = msg['b_ij'], msg['u_hat']
# line 4
c_i = F.softmax(b_ij_c, dim=0)
# line 5
s_j = (c_i.unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(3) * u_hat).sum(dim=1)
return {'h': s_j}
def capsule_update(self, msg):
# line 6
v_j = self.squash(msg['h'])
return {'h': v_j}
def update_edge(self, u, v, edge):
# line 7
return {'b_ij': edge['b_ij'] + (v['h'] * edge['u_hat']).mean(dim=1).sum(dim=1)}
4. Executing algorithm¶
for i in range(self.num_routing):
self.g.update_all(self.capsule_msg, self.capsule_reduce, self.capsule_update)
self.g.update_edge(edge_func=self.update_edge)