[](https://msdlserving.visualstudio.com/DeepScale/_build/latest?definitionId=36&branchName=master)
[](https://github.com/Microsoft/DeepSpeed/blob/master/LICENSE)
DeepSpeed is a deep learning optimization library that makes distributed training easy,
efficient, and effective.
10x Larger Models
5x Faster Training
Minimal Code Change
DeepSpeed can train DL models with over a hundred billion parameters on current generation of GPU clusters, while achieving over 5x in system performance compared to the state-of-art. Early adopters of DeepSpeed have already produced language model (LM) with over 17B parameters establishing new SOTA in the LM category.
Below we provide a brief feature list, see our detailed [feature
overview](#deepspeed-feature-overview) for descriptions and usage guide.
* [Distributed Training with Mixed Precision](#distributed-training-with-mixed-precision)
* 16-bit mixed precision
* Single-GPU/Multi-GPU/Multi-Node
* [Model Parallelism](#model-parallelism)
* Support for Custom Model Parallelism
* Integration with Megatron-LM
* [Memory and Bandwidth Optimizations](#memory-and-bandwidth-optimizations)
* The Zero Redundancy Optimizer (ZeRO)
* Constant Buffer Optimization (CBO)
* Smart Gradient Accumulation
* [Training Features](#training-features)
* Simplified training API
* Gradient Clipping
* Automatic loss scaling with mixed precision
* [Training Optimizers](#training-optimizers)
* Fused Adam optimizer and arbitrary `torch.optim.Optimizer`
* Memory bandwidth optimized FP16 Optimizer
* Large Batch Training with LAMB Optimizer
* Memory efficient Training with ZeRO Optimizer
* [Training Agnostic Checkpointing](#training-agnostic-checkpointing)
* [Advanced Parameter Search](#advanced-parameter-search)
* Learning Rate Range Test
* 1Cycle Learning Rate Schedule
* [Simplified Data Loader](#simplified-data-loader)
* [Performance Analysis and Debugging](#performance-analysis-and-debugging)
## Table of Contents
| Section | Description |
| --------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------- |
| [Why DeepSpeed?](#why-deepspeed) | DeepSpeed overview |
| [Installation](#installation) | Installation instructions |
| [Feature Overview](#feature-overview) | Preview of DeepSpeed's features |
| [Testing](#testing) | Instructions for testing DeepSpeed |
| [Contributing](#contributing) | Instructions for contributing to DeepSpeed |
## Why DeepSpeed?
Training advanced deep learning models is challenging. Beyond model design,
model scientists also need to set up the state-of-the-art training techniques
such as distributed training, mixed precision, gradient accumulation, and
checkpointing. Yet still, scientists may not achieve the desired system
performance and convergence rate. Large model sizes are even more challenging:
a large model easily runs out of memory with pure data paralelism and it is
difficult to use model parallelism. DeepSpeed addresses these challenges to
accelerate model development *and* training.
### Distributed, Effective, and Efficient Training with Ease
The DeepSpeed API is a lightweight wrapper on [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/). This
means that you can use everything you love in PyTorch and without learning a new
platform. In addition, DeepSpeed manages all of the boilerplate state-of-the-art
training techniques, such as distributed training, mixed precision, gradient
accumulation, and checkpoints so that you can focus on your model development. Most
importantly, you can leverage the distinctive efficiency and effectiveness benefit of
DeepSpeed to boost speed and scale with just a few lines of code changes to your PyTorch
models.
### Speed
DeepSpeed achieves high performance and fast convergence through a combination of
efficiency optimizations on compute/communication/memory/IO and effectiveness
optimizations on advanced hyperparameter tuning and optimizers. For example:
* DeepSpeed trains BERT-large to parity in 14 hours using 64 GPUs (4 DGX-2 boxes) and in
3.7 hours using 256 GPUs (16 DGX-2 boxes).
**BERT-large Training Times**
| Devices | Source | Training Time (hours) |
| ------------- | --------- | ---------------------:|
| 64 TPUs | Google | 96 |
| 64 V100 GPUs | DeepSpeed | **14** |
| 256 V100 GPUs | NVIDIA | 3.9 |
| 256 V100 GPUs | DeepSpeed | **3.7** |
*BERT Tutorial*: Coming Soon
* DeepSpeed trains GPT2 (1.5 billion parameters) 3.75x faster than state-of-art, NVIDIA
Megatron on Azure GPUs.
*Read more*: [GPT tutorial](../../Tutorials/Megatron_GPT2/MegatronGPT2Tutorial.md)
### Memory efficiency
DeepSpeed provides memory-efficient data parallelism and enables training models without
model parallelism. For example, DeepSpeed can train models with up to 6 billion parameters on
NVIDIA V100 GPUs with 32GB of device memory. In comparison, existing frameworks (e.g.,
PyTorch's Distributed Data Parallel) run out of memory with 1.5 billion parameter models.
DeepSpeed reduces the training memory footprint through a novel solution called Zero
Redundancy Optimizer (ZeRO). Unlike basic data parallelism where memory states are
replicated across data-parallel processes, ZeRO partitions model states to save
significant memory. The current implementation (stage 1 of ZeRO) reduces memory by up to
4x relative to the state-of-art. You can read more about ZeRO in our [technical
report](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.02054).
With this impressive memory reduction, early adopters of DeepSpeed have already produced language model (LM) with over 17B parameters called [Turing-NLG](link-to-turing-blog) establishing new SOTA in the LM category.
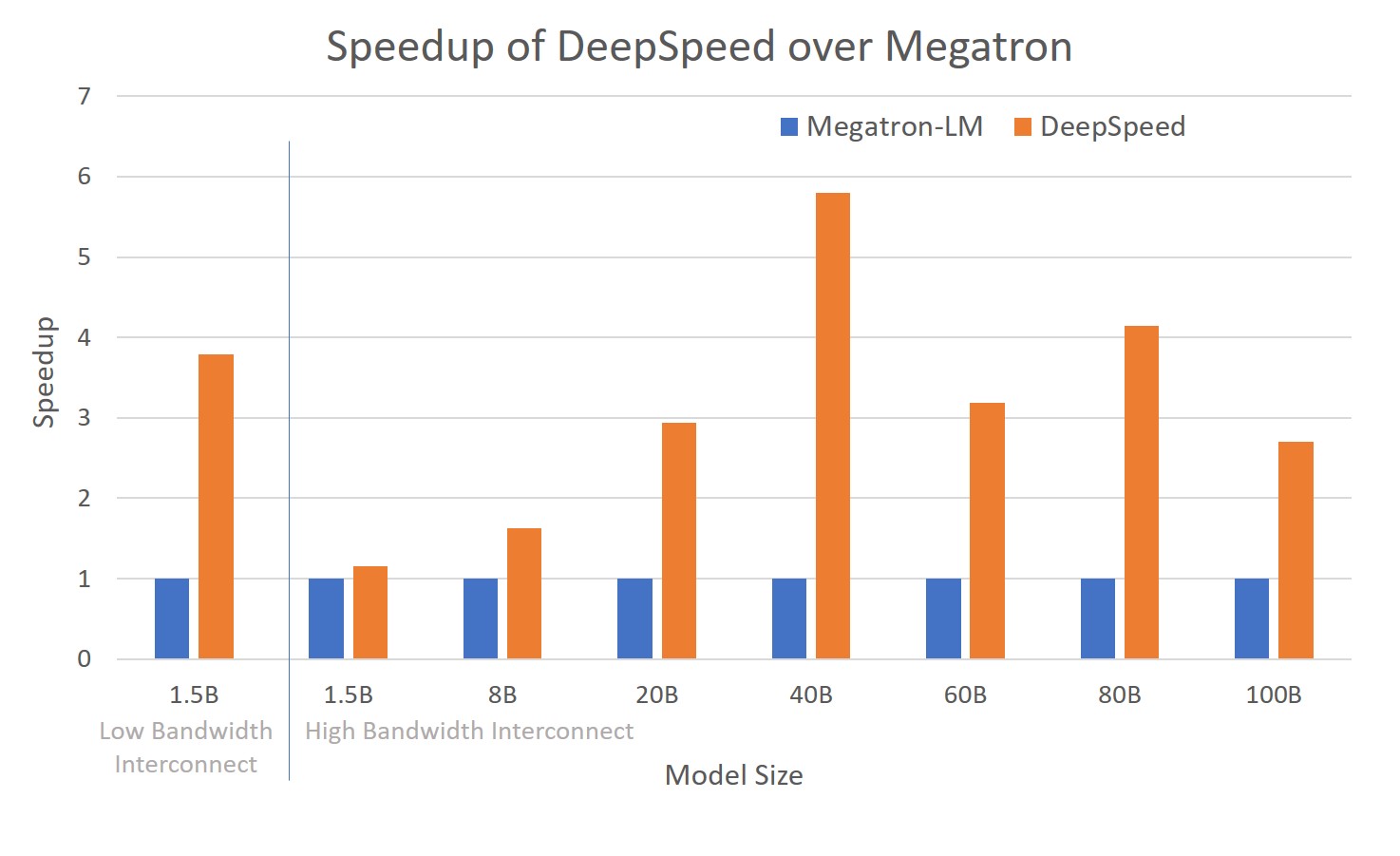
### Scalability
DeepSpeed supports efficient data parallelism, model parallelism, and their
combination. ZeRO boosts the scaling capability and efficiency further.
* DeepSpeed provides system support to run models up to 100 billion parameters,
10x larger than the state-of-art (8 billion NVIDIA GPT, 11 billion Google T5).
* DeepSpeed can run large models more efficiently, up to 6x faster for models with
various sizes spanning 1.5B to 100B.
*Read more*: [technical report](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.02054),
[GPT tutorial](../../Tutorials/Megatron_GPT2/MegatronGPT2Tutorial.md),
and [QANet tutorial](../../Tutorials/QANet/QANetTutorial.md).
### Fast convergence for effectiveness
DeepSpeed supports advanced hyperparameter tuning and large batch size
optimizers such as [LAMB](https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.00962). These improve the
effectiveness of model training and reduce the number of samples required to
convergence to desired accuracy.
*Read more*: [Tuning tutorial](../../Tutorials/1cycle/1Cycle.md), [QANet
tutorial](../../Tutorials/QANet/QANetTutorial.md) and *BERT Tutorial*: Coming Soon
## Installation
**TODO**
## Feature Overview
### Distributed Training with Mixed Precision
#### Mixed Precision Training
Enable 16-bit (FP16) training by in the `deepspeed_config` JSON.
```json
"fp16": {
"enabled": true,
"loss_scale": 0,
"loss_scale_window": 1000,
"hysteresis": 2,
"min_loss_scale": 1
}
```
#### Single-GPU, Multi-GPU, and Multi-Node Training
Easily switch between single-GPU, single-node multi-GPU, or multi-node multi-GPU
execution by specifying resources with a hostfile.
```bash
deepspeed --hostfile= \
\
--deepspeed --deepspeed_config ds_config.json
```
The script `` will execute on the resources specified in ``.
**TODO: explain hostfile formatting**
### Model Parallelism
#### Support for Custom Model Parallelism
DeepSpeed is supports all forms of model parallelism including tensor slicing based
approaches such as the [Megatron-LM](https://github.com/NVIDIA/Megatron-LM), or a
pipelined parallelism approach such as
[PipeDream](https://github.com/msr-fiddle/pipedream) or
[GPipe](https://github.com/kakaobrain/torchgpipe). It does so by only requiring the model
parallelism framework to provide a *model parallelism unit* (`mpu`) that implements a few
bookkeeping functionalities:
```python
mpu.get_model_parallel_rank()
mpu.get_model_parallel_group()
mpu.get_model_parallel_world_size()
mpu.get_data_parallel_rank/group/world_size()
mpu.get_data_parallel_group()
mpu.get_data_parallel_world_size()
```
#### Integration with Megatron-LM
**TODO: port tutorial to its own page**
DeepSpeed is fully compatible with [Megatron](https://github.com/NVIDIA/Megatron-LM).
Please see the [Megatron-LM tutorial](docs/tutorials/MegatronGPT2Tutorial.md) for details.
### Memory and Bandwidth Optimizations
#### The Zero Redundancy Optimizer (ZeRO)
[ZeRO](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.02054) is at the heart of DeepSpeed and
enables large model training at a scale that is simply not possible with model
parallelism alone. When enabled, ZeRO allows training models with
over 6 billion parameters without any model parallelism, and up to 100 billion
parameter models with model parallelism on current generation hardware.
For more details see the [ZeRO paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.02054), [GPT
tutorial](../../Tutorials/Megatron_GPT2/MegatronGPT2Tutorial.md) on integration with
DeepSpeed. Additional tutorals including *BERT Tutorial*: Coming Soon.
#### Constant Buffer Optimization (CBO)
CBO enables high network and memory throughput while restricting memory usage to a
constant size. For memory- and network-bound operations such as normalization or
allreduce collectives, the performance depends on the size of the operand. Simply fusing
all operands into a single large operand can enable great throughput at the expense of
unnecessary memory overhead. CBO in DeepSpeed fuses smaller operands into approximately a
pre-defined sized buffer large enough to achieve great performance without the
unnecessary memory overhead.
#### Smart Gradient Accumulation
Gradient accumulation allows running larger batch size with limited memory by breaking an
effective batch into several sequential micro-batches, and averaging the parameter
gradients across these micro-batches. Furthermore, instead of averaging the gradients of
each micro-batch across all GPUs, the gradients are averaged locally during each step of
the sequence, and a single `allreduce` is done at the end of the sequence to produce the
averaged gradients for the effective batch across all GPUs. This strategy significantly
reduces the communication involved over the approach of averaging globally for each
micro-batch, specially when the number of micro-batches per effective batch is large.
### Training Features
#### Simplified training API
The DeepSpeed core API consists of just a handful of methods:
* initialization: `initialize`
* training: `backward` and `step`
* argument parsing: `add_config_arguments`
* checkpointing : `load_checkpoint` and `store_checkpoint`
DeepSpeed supports all the features described in this document, via the use of these API,
along with a `deepspeed_config` JSON file for enabling and disabling the features. Please
see [core API doc](../../API/core_api/core_api.md) for more details.
#### Gradient Clipping
DeepSpeed handles gradient clipping under the hood based on the max gradient norm
specified by the user. See [core API doc](../../API/core_api/core_api.md) for more
details.
#### Automatic loss scaling with mixed precision
DeepSpeed internally handles loss scaling for mixed precision training. The parameters
for loss scaling can be specified in the `deepspeed_config` JSON file. See [core API
doc](../../API/core_api/core_api.md) for more details.
### Training Optimizers
#### Fused Adam optimizer and arbitrary torch.optim.Optimizer
With DeepSpeed, the user can choose to use a high performance implementation of ADAM from
NVIDIA, or any training optimizer that extends torch's `torch.optim.Optimizer` class.
#### Memory bandwidth optimized FP16 Optimizer
Mixed precision training is handled by the DeepSpeed FP16 Optimizer. This optimizer not
only handles FP16 training but is also highly efficient. The performance of weight update
is primarily dominated by the memory bandwidth, and the achieved memory bandwidth is
dependent on the size of the input operands. The FP16 Optimizer is designed to maximize
the achievable memory bandwidth by merging all the parameters of the model into a single
large buffer, and applying the weight updates in a single kernel, allowing it to achieve
high memory bandwidth.
#### Large Batch Training with LAMB Optimizer
**TODO: port tutorial**
DeepSpeed makes it easy to train with large batch sizes by enabling the LAMB Optimizer.
For more details on LAMB, see the [BERT
tutorial](../../Tutorials/BingBertSquad/BingBertSquadTutorial.md) and the [LAMB
paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.00962.pdf).
#### Memory-Efficient Training with ZeRO Optimizer
DeepSpeed can train models up with up to 6 billion parameters without parallelism, and
models with up to 100 billion parameters with 16-way model parallelism. This leap in
model size is possible though the memory efficiency achieved via the ZeRO Optimizer. For
more details see [ZeRO paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.02054) .
### Training Agnostic Checkpointing
**TODO: API documentation**
DeepSpeed can simplify checkpointing for you regardless of whether you are using data
parallel training, model parallel training, mixed-precision training, a mix of these
three, or using the zero optimizer to enable larger model sizes. See the [getting
started](../../Onboard/onboard/onboard.md) or [core API
doc](../../API/core_api/core_api.md) for details.
### Advanced parameter search
DeepSpeed supports multiple Learning Rate Schedules to enable faster convergence for
large batch scaling.
#### Learning Rate Range Test
Please refer to [Learning Rate Range Test](../../Tutorials/lrrt/lrrt.md).
#### 1Cycle Learning Rate Schedule
Please refer to [1Cycle Learning Rate Schedule](../../Tutorials/1cycle/1Cycle.md).
### Simplified Data Loader
DeepSpeed abstracts away data parallelism and model parallelism from the user when it
comes to data loading. Users simply provide a PyTorch dataset, and DeepSpeed data loader
can automatically handle batch creation appropriately.
### Performance Analysis and Debugging
For performance debugging, DeepSpeed can give you a detailed breakdown of the time spent
in different parts of the training with by simply enabling it in the `deepspeed_config`
file. See [core API doc](../../API/core_api/core_api.md).
```json
{
"wallclock_breakdwon": true
}
```
## Testing
DeepSpeed tracks two types of tests: unit tests and more costly model convergence tests.
The model convergence tests train
[DeepSpeedExamples](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeedExamples/) and measure
end-to-end convergence and related metrics. Unit tests are found in `tests/unit/` and
the model convergence tests are found in `tests/model/`.
### Unit Tests
[PyTest](https://docs.pytest.org/en/latest/) is used to execute tests. PyTest can be
installed from PyPI via `pip install pytest`. Simply invoke `pytest --forked` to run the
unit tests:
```bash
pytest --forked tests/unit/
```
You can also provide the `-v` flag to `pytest` to see additional information about the
tests. Note that [pytest-forked](https://github.com/pytest-dev/pytest-forked) and the
`--forked` flag are required to test CUDA functionality in distributed tests.
### Model Tests
To execute model tests, first [install DeepSpeed](#installation). The
[DeepSpeedExamples](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeedExamples/) repository is cloned
as part of this process. Next, execute the model test driver:
```bash
cd tests/model/
pytest run_sanity_check.py
```
Note that the `--forked` flag is not necessary for the model tests.
## Contributing
DeepSpeed welcomes your contributions!
### Prerequisites
DeepSpeed uses [pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/) to ensure that formatting is
consistent across DeepSpeed. First, ensure that `pre-commit` is installed from either
installing DeepSpeed or `pip install pre-commit`. Next, the pre-commit hooks must be
installed once before commits can be made:
```bash
pre-commit install
```
Afterwards, our suite of formatting tests run automatically before each `git commit`. You
can also run these manually:
```bash
pre-commit run --all-files
```
### Contributor License Agreement
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to
agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and
actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit
https://cla.opensource.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA bot will automatically determine whether you need
to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., status check, comment). Simply
follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across
all repos using our CLA.
### Code of Conduct
This project has adopted the [Microsoft Open Source Code of
Conduct](https://opensource.microsoft.com/codeofconduct/). For more information see the
[Code of Conduct FAQ](https://opensource.microsoft.com/codeofconduct/faq/) or contact
[opencode@microsoft.com](mailto:opencode@microsoft.com) with any additional questions or
comments.